HL6165
... bidirectional AC/DC converter. In this section, based on the proposed simplified PWM strategy, a feedforward control scheme is also developed to provide better line current shaping and better output voltage regulation compared with the conventional dual loop control scheme. Based on the proposed sim ...
... bidirectional AC/DC converter. In this section, based on the proposed simplified PWM strategy, a feedforward control scheme is also developed to provide better line current shaping and better output voltage regulation compared with the conventional dual loop control scheme. Based on the proposed sim ...
SPi-OCEF - Fundamentals Ltd
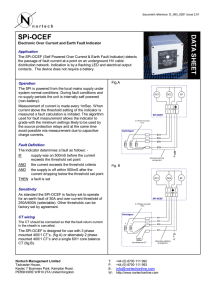
... no supply periods the unit is internally self powered (non-battery). Measurement of current is made every 1mSec. When current above the threshold setting of the indicator is measured a fault calculation is initiated. The algorithm used for fault measurement allows the indicator to grade with the min ...
... no supply periods the unit is internally self powered (non-battery). Measurement of current is made every 1mSec. When current above the threshold setting of the indicator is measured a fault calculation is initiated. The algorithm used for fault measurement allows the indicator to grade with the min ...
Module 2: Fundamentals of Electricity
... century British physicist, who is credited with developing the method of measuring capacitance. • Farad determined that a capacitor has a value of one farad of capacitance if one volt of potential difference applied across its plates moved one coulomb of electrons from one plate to the other. Michae ...
... century British physicist, who is credited with developing the method of measuring capacitance. • Farad determined that a capacitor has a value of one farad of capacitance if one volt of potential difference applied across its plates moved one coulomb of electrons from one plate to the other. Michae ...
WHY METALS CORRODE
... the pipe surface and other adjacent areas. This is analogous to the battery action just described. From the more negative areas, as before, current will flow into the soil (which acts as the electrolyte) and though it to the more positive or cathodic areas and back again though the metal of the pipe ...
... the pipe surface and other adjacent areas. This is analogous to the battery action just described. From the more negative areas, as before, current will flow into the soil (which acts as the electrolyte) and though it to the more positive or cathodic areas and back again though the metal of the pipe ...
MAX4030E/MAX4031E Low-Cost, 144MHz, Dual/Triple Op Amps with ±15kV ESD Protection General Description
... The MAX4030E/MAX4031E are low-power, voltagefeedback amplifiers featuring bandwidths up to 40MHz and 0.1dB gain flatness to 9MHz. They are designed to minimize differential-gain error and differential-phase error to 0.2% and 0.2°, respectively. They have a 40ns settling time to 0.1%, 110V/µs slew ra ...
... The MAX4030E/MAX4031E are low-power, voltagefeedback amplifiers featuring bandwidths up to 40MHz and 0.1dB gain flatness to 9MHz. They are designed to minimize differential-gain error and differential-phase error to 0.2% and 0.2°, respectively. They have a 40ns settling time to 0.1%, 110V/µs slew ra ...
OPAx348-Q1 1-MHz 45-μA CMOS Rail-to-Rail
... The OPAx348-Q1 family of devices is a low-power, rail-to-rail input and output operational amplifier. These devices operate from 1.8 V to 5.5 V, are unity-gain stable, and are suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications. The class AB output stage is capable of driving ≤ 10-kΩ loads con ...
... The OPAx348-Q1 family of devices is a low-power, rail-to-rail input and output operational amplifier. These devices operate from 1.8 V to 5.5 V, are unity-gain stable, and are suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications. The class AB output stage is capable of driving ≤ 10-kΩ loads con ...
VFC320 - Texas Instruments
... constraints. (3) Adjustable to zero. See Offset and Gain Adjustment section. (4) Linearity error at any operating frequency is defined as the deviation from a straight line drawn between the full scale frequency and 0.1% of full scale frequency. See Discussion of Specifications section. (5) When off ...
... constraints. (3) Adjustable to zero. See Offset and Gain Adjustment section. (4) Linearity error at any operating frequency is defined as the deviation from a straight line drawn between the full scale frequency and 0.1% of full scale frequency. See Discussion of Specifications section. (5) When off ...
Inductive and Capacitive Reactance
... At the beginning of the first quarter-cycle (0º to 90º) the voltage has just passed through zero and is increasing in the positive direction. Since the zero point is the steepest part of the sine wave, the voltage is changing at its greatest rate. The charge on a capacitor varies directly with the ...
... At the beginning of the first quarter-cycle (0º to 90º) the voltage has just passed through zero and is increasing in the positive direction. Since the zero point is the steepest part of the sine wave, the voltage is changing at its greatest rate. The charge on a capacitor varies directly with the ...
MAX3863 2.7Gbps Laser Driver with Modulation Compensation General Description
... ground. This shorts the feedback from the monitor diode and causes the bias current to rise to the maximum value set by the BIASMAX pin. ...
... ground. This shorts the feedback from the monitor diode and causes the bias current to rise to the maximum value set by the BIASMAX pin. ...
FDMS3602S PowerTrench Power Stage
... 1. Input ceramic bypass capacitors C1 and C2 must be placed close to the D1 and S2 pins of Power Stage to help reduce parasitic inductance and high frequency conduction loss induced by switching operation. C1 and C2 show the bypass capacitors placed close to the part between D1 and S2. Input capaci ...
... 1. Input ceramic bypass capacitors C1 and C2 must be placed close to the D1 and S2 pins of Power Stage to help reduce parasitic inductance and high frequency conduction loss induced by switching operation. C1 and C2 show the bypass capacitors placed close to the part between D1 and S2. Input capaci ...
Data Sheet - Asahi Kasei Microdevices
... Clock out Frequencies: - 12.000MHz - 13.5MHz Low Jitter Performance - Period Jitter 125 psec (max) at CLK1 205 psec (max) at CLK2 ...
... Clock out Frequencies: - 12.000MHz - 13.5MHz Low Jitter Performance - Period Jitter 125 psec (max) at CLK1 205 psec (max) at CLK2 ...
PWM Regenerative Rectifiers: State of the Art
... of a voltage supply. This is accomplished with a dc capacitor C and a feedback control loop. The basic operation principle of VSR consists on keeping the load DC-link voltage at a desired reference value, using a feedback control loop as shown in Fig. 12 [19]. This reference value Vo ref , has to be ...
... of a voltage supply. This is accomplished with a dc capacitor C and a feedback control loop. The basic operation principle of VSR consists on keeping the load DC-link voltage at a desired reference value, using a feedback control loop as shown in Fig. 12 [19]. This reference value Vo ref , has to be ...
basic electronics lab manual - Muffakham Jah College of
... accelerated and focused by one or more anodes, and strikes the front of the tube, producing a bright spot on the phosphorescent screen. The electron beam is bent, or deflected, by voltages applied to two sets of plates fixed in the tube. The horizontal deflection plates or X-plates produce side to s ...
... accelerated and focused by one or more anodes, and strikes the front of the tube, producing a bright spot on the phosphorescent screen. The electron beam is bent, or deflected, by voltages applied to two sets of plates fixed in the tube. The horizontal deflection plates or X-plates produce side to s ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.