Series Circuits
... Series circuits have the following voltage characteristic: VS V1 V2 ... Vn where VS = the source (or total supply) voltage Vn = the voltage across the highest numbered resistor in the circuit ...
... Series circuits have the following voltage characteristic: VS V1 V2 ... Vn where VS = the source (or total supply) voltage Vn = the voltage across the highest numbered resistor in the circuit ...
transistors
... Draw the symbol for an LED What happens to the resistance of a thermistor as it is heated up? What happens to the resistance of an LDR if ...
... Draw the symbol for an LED What happens to the resistance of a thermistor as it is heated up? What happens to the resistance of an LDR if ...
Lab06 - Weber State University
... Design the amplifier to achieve a small-signal gain of at least AV = -200 V/V and IC = 1 mA. Use V+=15 V, RSIG = 50 Ω, RL = 10 kΩ, RB1 =80 kΩ, and RB2 = 20 kΩ. Although there will be variations from transistor to transistor, you may assume β=100 in your calculations. Fig. 1 shows an NPN Common-Emitt ...
... Design the amplifier to achieve a small-signal gain of at least AV = -200 V/V and IC = 1 mA. Use V+=15 V, RSIG = 50 Ω, RL = 10 kΩ, RB1 =80 kΩ, and RB2 = 20 kΩ. Although there will be variations from transistor to transistor, you may assume β=100 in your calculations. Fig. 1 shows an NPN Common-Emitt ...
Worksheets
... Determine the conditions which will produce an increase in the voltage reading at V3. Is it a rise in temperature? Is it a fall in temperature? (ii) Adjust the variable resistor to 8K. If each graduation on the temperature sensor represents a 10° C shift. At what temperature will the voltage output ...
... Determine the conditions which will produce an increase in the voltage reading at V3. Is it a rise in temperature? Is it a fall in temperature? (ii) Adjust the variable resistor to 8K. If each graduation on the temperature sensor represents a 10° C shift. At what temperature will the voltage output ...
Counterpoint SA-6 tube headamp
... - Mute/Operate switch to eliminate pops and thumps during warm-up. - Bias Level control to compensate for tube aging and matching to cartridge. - Regulated filament voltage for long tube life and consistant sonic performance. The SA-6 uses the best components available for each application. The audi ...
... - Mute/Operate switch to eliminate pops and thumps during warm-up. - Bias Level control to compensate for tube aging and matching to cartridge. - Regulated filament voltage for long tube life and consistant sonic performance. The SA-6 uses the best components available for each application. The audi ...
EE302 Lesson 1: Introduction
... two points is defined as one volt if it requires one joule of energy to move one coulomb of charge from one point to another. W V Q ...
... two points is defined as one volt if it requires one joule of energy to move one coulomb of charge from one point to another. W V Q ...
an improved iupqc controller to provide additional grid
... compensated, since the harmonic voltages appear naturally across the series current source and the harmonic currents flow naturally into the shunt voltage source. In actual power converters, as the switching frequency increases, the power rate capability is reduced. ...
... compensated, since the harmonic voltages appear naturally across the series current source and the harmonic currents flow naturally into the shunt voltage source. In actual power converters, as the switching frequency increases, the power rate capability is reduced. ...
Project Renovatio
... In order to step down the voltage from the battery packs to a low voltage of 12 V for the low voltage system, a DC to DC converter is required. Only a maximum of 150 W will be pulled by the low voltage system, and the DC to DC converter is able to handle 200 W. In order to ensure that each battery d ...
... In order to step down the voltage from the battery packs to a low voltage of 12 V for the low voltage system, a DC to DC converter is required. Only a maximum of 150 W will be pulled by the low voltage system, and the DC to DC converter is able to handle 200 W. In order to ensure that each battery d ...
Experiment No. 3 Clipping and Clamping Circuits
... the Figure (l) shows a biased clipper, for the diode to turn in the input voltage must be greater +V, when Vm is greater than +V , the diode acts like a closed switch (ideally) & the voltage across the output equals +V , this output stays at +V as long as the input voltage exceeds +V. when the input ...
... the Figure (l) shows a biased clipper, for the diode to turn in the input voltage must be greater +V, when Vm is greater than +V , the diode acts like a closed switch (ideally) & the voltage across the output equals +V , this output stays at +V as long as the input voltage exceeds +V. when the input ...
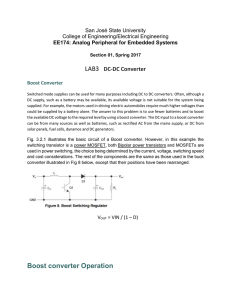
Lab3: DC-DC Boost Converter
... DC supply, such as a battery may be available, its available voltage is not suitable for the system being supplied. For example, the motors used in driving electric automobiles require much higher voltages than could be supplied by a battery alone. The answer to this problem is to use fewer batterie ...
... DC supply, such as a battery may be available, its available voltage is not suitable for the system being supplied. For example, the motors used in driving electric automobiles require much higher voltages than could be supplied by a battery alone. The answer to this problem is to use fewer batterie ...
In Electric Circuits
... exits the bottom of the battery, splits up to travel through R3 and R4, rejoins, then splits up again to travel through R1 and R2, then rejoins again to return to the top of the battery. There exists more than one path for current to travel (not series), yet there are more than two sets of electrica ...
... exits the bottom of the battery, splits up to travel through R3 and R4, rejoins, then splits up again to travel through R1 and R2, then rejoins again to return to the top of the battery. There exists more than one path for current to travel (not series), yet there are more than two sets of electrica ...
Ohm`s law - La Salle University
... Ohm’s law and combinations of resistors The voltage (or potential difference) is a push that charges experience. The potential difference is measured in volts, a unit named after Alessandro Volta. This force may result in charges moving – otherwise known as a current. The current is measured in ampe ...
... Ohm’s law and combinations of resistors The voltage (or potential difference) is a push that charges experience. The potential difference is measured in volts, a unit named after Alessandro Volta. This force may result in charges moving – otherwise known as a current. The current is measured in ampe ...
8 Channel array - K
... First we see basic working of IR pair using LM324. LM324 is used as a comparator here. We give a reference voltage to its input using a 10k pot. When the voltage across the receiver is less than this reference voltage, the comparator gives low output and when the voltage is more than the reference p ...
... First we see basic working of IR pair using LM324. LM324 is used as a comparator here. We give a reference voltage to its input using a 10k pot. When the voltage across the receiver is less than this reference voltage, the comparator gives low output and when the voltage is more than the reference p ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.