G2 Chemical Patterns – revision checklist
... describe how the induced voltage across the coil of a generator changes during each revolution of the coil and explain that the current produced in an external circuit is an alternating current (a.c.); appreciate that the current from a battery always travels in the same direction: it is a direct cu ...
... describe how the induced voltage across the coil of a generator changes during each revolution of the coil and explain that the current produced in an external circuit is an alternating current (a.c.); appreciate that the current from a battery always travels in the same direction: it is a direct cu ...
Physics 160 Lecture 6
... The base-emitter junction is forward biased, with the base about 1 diode drop (~0.6 to 0.7 V) higher than the emitter during normal operation (for currents of a few mA). The base-collector junction is normally reverse biased during operation. ...
... The base-emitter junction is forward biased, with the base about 1 diode drop (~0.6 to 0.7 V) higher than the emitter during normal operation (for currents of a few mA). The base-collector junction is normally reverse biased during operation. ...
ElectricCircuits
... Notice the letter symbols used in this equation: I = intensity of the current in amperes E = electromotive force in volts R = resistance in ohms In non-mathematical language this formula means: As voltage is increased As voltage is decreased As resistance is increased As resistance is decreased — cu ...
... Notice the letter symbols used in this equation: I = intensity of the current in amperes E = electromotive force in volts R = resistance in ohms In non-mathematical language this formula means: As voltage is increased As voltage is decreased As resistance is increased As resistance is decreased — cu ...
Download T2100 Datasheet
... The T2100 Excitation Loss Relay protects against loss of excitation in a synchronous generator. T2100 detects the high-inductive current running into a generator in case of low excitation. The faulty generator breaker is tripped, thus protecting the generator, and avoiding undervoltage on the busbar ...
... The T2100 Excitation Loss Relay protects against loss of excitation in a synchronous generator. T2100 detects the high-inductive current running into a generator in case of low excitation. The faulty generator breaker is tripped, thus protecting the generator, and avoiding undervoltage on the busbar ...
EUP3406 1.5MHz, 600mA Synchronous Step-Down Converter
... power by adjusting the inductor-peak current during the first half of each cycle. An N-channel, synchronous switch turns on during the second half of each cycle (off time). When the inductor current starts to reverse or when the PWM reaches the end of the oscillator period, the synchronous switch tu ...
... power by adjusting the inductor-peak current during the first half of each cycle. An N-channel, synchronous switch turns on during the second half of each cycle (off time). When the inductor current starts to reverse or when the PWM reaches the end of the oscillator period, the synchronous switch tu ...
• Example of Resistor Circuits • Grounding • Resistors in Series
... use Kirchhoff’s laws and rules for series and parallel resistors rebuild using current same for series and potential difference same for parallel ...
... use Kirchhoff’s laws and rules for series and parallel resistors rebuild using current same for series and potential difference same for parallel ...
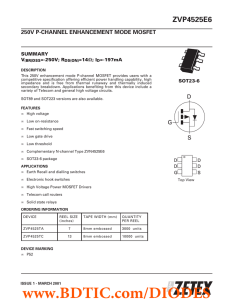
ZVP4525E6 250V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET SUMMARY
... ZVP4525E6 250V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET ...
... ZVP4525E6 250V P-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE MOSFET ...
Section 16.4
... Your nervous system uses specialized cells called neurons to transfer electrical signals from one part of your body to another. A neuron has three basic parts: the cell body; a long, thin portion called the axon; and fingerlike ...
... Your nervous system uses specialized cells called neurons to transfer electrical signals from one part of your body to another. A neuron has three basic parts: the cell body; a long, thin portion called the axon; and fingerlike ...
Using a Current Sharing Controller when the Sum Current of Both
... The output of U4A is logic low when VINA and VINB is within the threshold determined by R8 and R9. When VINA and VINB is beyond this threshold, the corresponding comparator output becomes logic low, causing the output of U4A to become a logic high. A logic high output of U4A is inverted by U4B, pr ...
... The output of U4A is logic low when VINA and VINB is within the threshold determined by R8 and R9. When VINA and VINB is beyond this threshold, the corresponding comparator output becomes logic low, causing the output of U4A to become a logic high. A logic high output of U4A is inverted by U4B, pr ...
In this new setup, the current flowing across the Pt100/polysilicon...
... before (see p.157), but forced instead using a precision ultralow offset voltage (25 µV) OP07-EP operational amplifier (Analog Devices). In essence, a very stable 10 V voltage (±25 mV) was obtained from a precision REF102 voltage reference (Burr-Brown). A 10 kΩ 0.1% precision resistor was then place ...
... before (see p.157), but forced instead using a precision ultralow offset voltage (25 µV) OP07-EP operational amplifier (Analog Devices). In essence, a very stable 10 V voltage (±25 mV) was obtained from a precision REF102 voltage reference (Burr-Brown). A 10 kΩ 0.1% precision resistor was then place ...
Appendix C Ohm`s Law, Kirchhoff`s Laws and AC Circuits
... To determine the impedance of a circuit, (i.e. its resistance including both magnitude and phase information), and also the voltages and currents, it is very convenient to introduce the use of complex algebra. That is, we represent voltages, currents and impedances by complex quantities, with the im ...
... To determine the impedance of a circuit, (i.e. its resistance including both magnitude and phase information), and also the voltages and currents, it is very convenient to introduce the use of complex algebra. That is, we represent voltages, currents and impedances by complex quantities, with the im ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... where ID is the drain current, VGS is the gate-source voltage, and IDSS is the drain current at VGS=0 V. From your plot determine the parameters IDSS and VP. ...
... where ID is the drain current, VGS is the gate-source voltage, and IDSS is the drain current at VGS=0 V. From your plot determine the parameters IDSS and VP. ...
adobe pdf
... • the higher the resistivity (ρ), the more the resistance • the longer the length of a conductor, the more the resistance • the smaller the area of a conductor, the more the resistance • the higher the temperature of a conductor, the more the resistance ...
... • the higher the resistivity (ρ), the more the resistance • the longer the length of a conductor, the more the resistance • the smaller the area of a conductor, the more the resistance • the higher the temperature of a conductor, the more the resistance ...
Zenone Frequency and Voltage Converter Datasheet
... FVC series static converters provide a symmetrical and balanced system of three-phase sinusoidal voltage with the possibility to vary output voltage and frequency. With them it’s possible to test equipments that can not be supplied by conventional mains grid; they allow to create patterns of voltage ...
... FVC series static converters provide a symmetrical and balanced system of three-phase sinusoidal voltage with the possibility to vary output voltage and frequency. With them it’s possible to test equipments that can not be supplied by conventional mains grid; they allow to create patterns of voltage ...
Lightning and Surge Protection
... in a current path being established between the two points and will often include any conductor that helps to bridge the gap such as trees, buildings or other structures. When the current path is established the resulting current flow will be extremely high, perhaps as much as 5000 amps. This curren ...
... in a current path being established between the two points and will often include any conductor that helps to bridge the gap such as trees, buildings or other structures. When the current path is established the resulting current flow will be extremely high, perhaps as much as 5000 amps. This curren ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.