SCR VI Characteristics
... Theory: An SCR is a device which can be turned on through the gate pulse and turned off using power circuit i.e., turn on is controlled but turn off is uncontrolled in an SCR. The voltage at which the SCR gets into conduction state is called forward breakover voltage(VBO). If the gate current is inc ...
... Theory: An SCR is a device which can be turned on through the gate pulse and turned off using power circuit i.e., turn on is controlled but turn off is uncontrolled in an SCR. The voltage at which the SCR gets into conduction state is called forward breakover voltage(VBO). If the gate current is inc ...
Load-commutated Current Source Inverter (CSI)
... 1. It may be observed from the equation given earlier that, as the inverter frequency ( f = 1 / T ) is increased, the turn-off time provided by the circuit decreases. But, the circuit commutation time, t off , should be more than the turn-off time of the thyristor, t q , for reliable operation. This ...
... 1. It may be observed from the equation given earlier that, as the inverter frequency ( f = 1 / T ) is increased, the turn-off time provided by the circuit decreases. But, the circuit commutation time, t off , should be more than the turn-off time of the thyristor, t q , for reliable operation. This ...
Physics 102Ohms Lawmzes word pm
... Ohm’s Law Elizabeth Silva and Maria Zavala January 30, 2006 Abstract: The purpose of this lab is to test the current intensity and potential differences when conductors of different resistance are connected in varies circuits. Equipment: ● Digital voltmeter ● Digital Ammeter ● Resistors (decade boxe ...
... Ohm’s Law Elizabeth Silva and Maria Zavala January 30, 2006 Abstract: The purpose of this lab is to test the current intensity and potential differences when conductors of different resistance are connected in varies circuits. Equipment: ● Digital voltmeter ● Digital Ammeter ● Resistors (decade boxe ...
AS Level Electricity - the basics - revision from GCSE
... acts like a closed switch when connected in forward bias and an open switch when in reverse bias. When connected in forward bias its resistance is very low (provided it has a potential difference of more than 0.6 volts across it). The diode has a very high resistance in the reverse bias therefore on ...
... acts like a closed switch when connected in forward bias and an open switch when in reverse bias. When connected in forward bias its resistance is very low (provided it has a potential difference of more than 0.6 volts across it). The diode has a very high resistance in the reverse bias therefore on ...
File
... become zero in certain intervals (those intervals in which inductor has quickly desipated its energy and firing angle hasn’t reached) ...
... become zero in certain intervals (those intervals in which inductor has quickly desipated its energy and firing angle hasn’t reached) ...
AN ELECTRONICALLY ISOLATED 12
... techniques require additional external magnetic components that are bulky and add to the cost of the system. A new electronically isolated 12-pulse autotransformer topology that does not need bulky external magnetic components is proposed in this paper. The proposed topology employs active switches ...
... techniques require additional external magnetic components that are bulky and add to the cost of the system. A new electronically isolated 12-pulse autotransformer topology that does not need bulky external magnetic components is proposed in this paper. The proposed topology employs active switches ...
Some physical problems: The driven, damped, harmonic oscillator
... experiment. It is sufficient to overplot the data with theoretical curves and to find the best parameters (C and L) by visual observation. Your discussion should include plausible estimates of your uncertainty in R, C, and L. Uncertainty in R can be quantitatively estimated from the quality of your ...
... experiment. It is sufficient to overplot the data with theoretical curves and to find the best parameters (C and L) by visual observation. Your discussion should include plausible estimates of your uncertainty in R, C, and L. Uncertainty in R can be quantitatively estimated from the quality of your ...
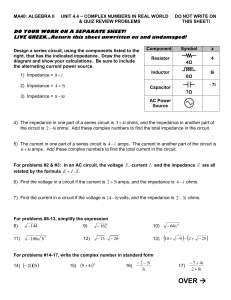
MA40: ALGEBRA II
... the circuit is 2 6i ohms. Add these complex numbers to find the total impedance in the circuit. 5) The current in one part of a series circuit is 4 i amps. The current in another part of the circuit is 6 4i amps. Add these complex numbers to find the total current in the circuit. ...
... the circuit is 2 6i ohms. Add these complex numbers to find the total impedance in the circuit. 5) The current in one part of a series circuit is 4 i amps. The current in another part of the circuit is 6 4i amps. Add these complex numbers to find the total current in the circuit. ...
Electronic_Circuits_Unit-7
... • The well known IC regulators are: 1) The 78XX series - for positive regulators (2) The 79XX series - for negative regulators (3) The LM 317 - for adjustable positive regulators (4) The LM 337 - for adjustable negative regulators ...
... • The well known IC regulators are: 1) The 78XX series - for positive regulators (2) The 79XX series - for negative regulators (3) The LM 317 - for adjustable positive regulators (4) The LM 337 - for adjustable negative regulators ...
Electricity and Measurement
... The final experiment begins by introducing the operation of two components crucial to the design of AC circuits - the Capacitor and Diode. Both of these devices are nonlinear - that is the current through them is not directly proportional to the voltage across them. Clearly Ohm’s Law will be of limi ...
... The final experiment begins by introducing the operation of two components crucial to the design of AC circuits - the Capacitor and Diode. Both of these devices are nonlinear - that is the current through them is not directly proportional to the voltage across them. Clearly Ohm’s Law will be of limi ...
Practice Electricity Questions
... You may want to color code the circuits to get a better idea of what’s going on… ...
... You may want to color code the circuits to get a better idea of what’s going on… ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.