SOLAR CELL CASCADING – Increasing Solar Energy Yield at Low
... of the area, and is hardly changed at all even by the intensity of light because a solar cell works like a current source. In order to reduce the charge time or work at even lower illumination levels with the STM modules, you may use a larger solar panel with the same open circuit voltage, or more p ...
... of the area, and is hardly changed at all even by the intensity of light because a solar cell works like a current source. In order to reduce the charge time or work at even lower illumination levels with the STM modules, you may use a larger solar panel with the same open circuit voltage, or more p ...
BU1-AC - AC-voltage relay
... supervision the lowest in each phase. Pickup of supervision circuit U> or U< is indicated by flashing of the corresponding LED. At U< - tripping LED U< extinguishes, at U> - tripping. LED U> is steady lit. At voltages < 60 % Un no trip delay takes place. Technical data rated voltage Un: 110 V, 230 V ...
... supervision the lowest in each phase. Pickup of supervision circuit U> or U< is indicated by flashing of the corresponding LED. At U< - tripping LED U< extinguishes, at U> - tripping. LED U> is steady lit. At voltages < 60 % Un no trip delay takes place. Technical data rated voltage Un: 110 V, 230 V ...
1 - Maths and Science at Al Siraat
... Turn off the power. If this is not possible, do not touch the person directly. Perhaps use an insulator such as a plastic rope or garden hose to move them away from the source of electrocution. Then give first aid. Phone 000. 16 What is the emergency phone number from: a a landline phone b a mobile ...
... Turn off the power. If this is not possible, do not touch the person directly. Perhaps use an insulator such as a plastic rope or garden hose to move them away from the source of electrocution. Then give first aid. Phone 000. 16 What is the emergency phone number from: a a landline phone b a mobile ...
Node Voltage with Thevenin Equivalent
... associated with each data point for Channel 1 and Channel 2: Look at the numbers next to CH1: and CH2: above the GND row. In this case, 1V is equivalent to 32. This means that that the value of the points in the columns CH1 and CH2 should be divided by 32 and then multiplied by 1V to finally obtain ...
... associated with each data point for Channel 1 and Channel 2: Look at the numbers next to CH1: and CH2: above the GND row. In this case, 1V is equivalent to 32. This means that that the value of the points in the columns CH1 and CH2 should be divided by 32 and then multiplied by 1V to finally obtain ...
ch 20 21 22
... Charges flow from high voltage to low voltage. Voltage difference – the push that causes charges to move. – measured in volts (V). ...
... Charges flow from high voltage to low voltage. Voltage difference – the push that causes charges to move. – measured in volts (V). ...
Current Electricity PP
... 1.There must be an energy supply capable doing work on charge to move it from a low energy location to a high energy location and thus creating an electric potential difference across the two ends of the external circuit. 2.There must be a closed conducting loop in the external circuit which stretch ...
... 1.There must be an energy supply capable doing work on charge to move it from a low energy location to a high energy location and thus creating an electric potential difference across the two ends of the external circuit. 2.There must be a closed conducting loop in the external circuit which stretch ...
Electricity Study Guide KEY
... 12. What can you predict would happen to the resistance in a device if the voltage decreases, but the current stays the same? Explain how you arrived at this answer. You can show an example if necessary. Resistance decreases 13. What can you predict would happen to the voltage in a device if the res ...
... 12. What can you predict would happen to the resistance in a device if the voltage decreases, but the current stays the same? Explain how you arrived at this answer. You can show an example if necessary. Resistance decreases 13. What can you predict would happen to the voltage in a device if the res ...
Homework #3 Solution
... 10kΩ load resistances. The input differential signal is a sinusoid of 5mV peak amplitude, which is applied to one input terminal while the other input terminal is grounded. The power supply available is 10V. To determine the required bias current I, derive an expression for the total voltage at each ...
... 10kΩ load resistances. The input differential signal is a sinusoid of 5mV peak amplitude, which is applied to one input terminal while the other input terminal is grounded. The power supply available is 10V. To determine the required bias current I, derive an expression for the total voltage at each ...
Rechargeable Battery System (REBATEM)
... Current: 0 to 80 amperes with a tolerance of ± 10 milliamps Temperature: -30 to 200 degrees Fahrenheit with a tolerance of ± 2 degrees ...
... Current: 0 to 80 amperes with a tolerance of ± 10 milliamps Temperature: -30 to 200 degrees Fahrenheit with a tolerance of ± 2 degrees ...
Series versus Parallel Circuits
... pushes charges from high to low levels! Voltage is measured in volts (V) ...
... pushes charges from high to low levels! Voltage is measured in volts (V) ...
Total Power International, Inc. AC/DC EXTERNAL WALLMOUNT
... (2) Output voltage tolerance is the variation of an output voltage due to the combined effect of output load change from minimum to maximum, input voltage change within the specified input voltage range. For example, with an output voltage tolerance of 20V +/-3%, the output voltage will be between 1 ...
... (2) Output voltage tolerance is the variation of an output voltage due to the combined effect of output load change from minimum to maximum, input voltage change within the specified input voltage range. For example, with an output voltage tolerance of 20V +/-3%, the output voltage will be between 1 ...
ECE 323L Basic Electronics Circuits Laboratory
... To use the XY horizontal mode The XY horizontal mode converts the oscilloscope from a voltsversus-time display to a volts-versus-volts display using two input channels. Channel 1 is the X-axis input, channel 2 is the Y-axis input. You can use various transducers so the display could show strain ver ...
... To use the XY horizontal mode The XY horizontal mode converts the oscilloscope from a voltsversus-time display to a volts-versus-volts display using two input channels. Channel 1 is the X-axis input, channel 2 is the Y-axis input. You can use various transducers so the display could show strain ver ...
“In parallel” means A] both resistors necessarily have the same
... It doesn’t matter. YOU choose the current! Here’s an example: I have deliberately (and obviously) drawn the current going the wrong way. Let’s solve for I1 Starting at point A and going clockwise, what are the voltage changes around the loop? First: What is the voltage change across the ideal batter ...
... It doesn’t matter. YOU choose the current! Here’s an example: I have deliberately (and obviously) drawn the current going the wrong way. Let’s solve for I1 Starting at point A and going clockwise, what are the voltage changes around the loop? First: What is the voltage change across the ideal batter ...
eet 307 power electronics 2005-2006
... The objective of current mode control is to control the ‘averaged’ inductor current. A 2-loop control system is involved OUTER voltage control loop and an INNER current control loop ...
... The objective of current mode control is to control the ‘averaged’ inductor current. A 2-loop control system is involved OUTER voltage control loop and an INNER current control loop ...
chapter 25 current, resistance and electromotive force
... Resistance is a characteristic of an object. Resistance, R, is related to Resistivity, ρ, by ...
... Resistance is a characteristic of an object. Resistance, R, is related to Resistivity, ρ, by ...
Electricity & Magnetism
... There are 2 types of currents: Current (DC) – Where electrons flow in the same direction in a wire. ...
... There are 2 types of currents: Current (DC) – Where electrons flow in the same direction in a wire. ...
Diode Analog Switches 1 M H Miller SELECTED ANALOG SWITCH
... In the preceding diode switch circuit the junction voltage drop of the ‘switch’ diode appears in the output voltage expression. This annoyance is removed (largely) with the introduction of an additional diode oriented as illustrated on the right. It would be hasty but not be unusual to question how ...
... In the preceding diode switch circuit the junction voltage drop of the ‘switch’ diode appears in the output voltage expression. This annoyance is removed (largely) with the introduction of an additional diode oriented as illustrated on the right. It would be hasty but not be unusual to question how ...
Multimeters - WFU Physics Home
... coulomb per second past a given point in the circuit. An ammeter measures the flow of charge (current) through a wire or electrical device. Two important facts about ammeters are: 1. Ammeters have very low resistance to the current so that, when placed in a circuit, the current is not impeded. 2. Am ...
... coulomb per second past a given point in the circuit. An ammeter measures the flow of charge (current) through a wire or electrical device. Two important facts about ammeters are: 1. Ammeters have very low resistance to the current so that, when placed in a circuit, the current is not impeded. 2. Am ...
manual
... Last week you looked at the behavior of a capacitor in a DC circuit. Briefly, at the end, you looked at how the voltage across the capacitor changed as a function of the frequency in an AC circuit. This week you will look at AC circuits in more detail. Consider what happens in a series circuit consi ...
... Last week you looked at the behavior of a capacitor in a DC circuit. Briefly, at the end, you looked at how the voltage across the capacitor changed as a function of the frequency in an AC circuit. This week you will look at AC circuits in more detail. Consider what happens in a series circuit consi ...
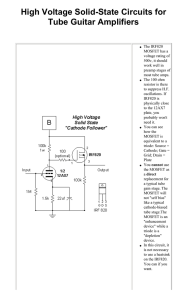
High Voltage Solid-State Circuits for Tube Guitar
... a direct replacement for a typical tube gain stage. The MOSFET will not "self bias" like a typical cathode-biased tube stage.The MOSFET is an "enhancement device" while a triode is a "depletion" device. In this circuit, it is not necessary to use a heatsink on the IRF820. You can if you want. ...
... a direct replacement for a typical tube gain stage. The MOSFET will not "self bias" like a typical cathode-biased tube stage.The MOSFET is an "enhancement device" while a triode is a "depletion" device. In this circuit, it is not necessary to use a heatsink on the IRF820. You can if you want. ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.















![“In parallel” means A] both resistors necessarily have the same](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002639832_1-e202bc5d069c0ff9b245597d40bc9b26-300x300.png)