
Time Electronics
... • Signal can also be measured as a % of span on ranges: 4 to 20mA, 0 to 20mA, square root 4 to 20mA, square root 0 to 20mA. • For all measurements a Min/Max recording function is available on demand. ...
... • Signal can also be measured as a % of span on ranges: 4 to 20mA, 0 to 20mA, square root 4 to 20mA, square root 0 to 20mA. • For all measurements a Min/Max recording function is available on demand. ...
current = potential difference resistance •1. Find the unknown
... 3. How much resistance does a light bulb create if it has a current of 25 mA through it in a 9 V circuit? ...
... 3. How much resistance does a light bulb create if it has a current of 25 mA through it in a 9 V circuit? ...
No Slide Title
... • Identify the functions of a multimeter. • Identify the advantages and disadvantages of DMM’s and VOM’s. • Describe how to use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, and resistance. • Describe how to measure current using an ammeter. • Describe how to connect an ammeter into a circuit. • List s ...
... • Identify the functions of a multimeter. • Identify the advantages and disadvantages of DMM’s and VOM’s. • Describe how to use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, and resistance. • Describe how to measure current using an ammeter. • Describe how to connect an ammeter into a circuit. • List s ...
PS 6.6 - S2TEM Centers SC
... circuits (including wire, switch, battery, and light bulb) (4-5.6), and also illustrated the path of electric current in series and parallel circuits (4-5.7). In the 6th grade students illustrate energy transformations (including the production of light, sound, heat, and mechanical motion) in electr ...
... circuits (including wire, switch, battery, and light bulb) (4-5.6), and also illustrated the path of electric current in series and parallel circuits (4-5.7). In the 6th grade students illustrate energy transformations (including the production of light, sound, heat, and mechanical motion) in electr ...
hw11
... In a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) digital logic circuit, power is consumed in steady state (when neither the input voltages nor the output voltage are changing with time) due to transistor off-state leakage current IOFF, i.e. the current which flows when |VGS| = 0V and |VDS| is gre ...
... In a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) digital logic circuit, power is consumed in steady state (when neither the input voltages nor the output voltage are changing with time) due to transistor off-state leakage current IOFF, i.e. the current which flows when |VGS| = 0V and |VDS| is gre ...
Inductors and AC
... VSUPPLY = 15V as measured with DVM From the calculations on the following page, there must be an error in these figures If VR is 10v & VL is 8V then VSUPPLY should be:VSUPPLY = 102 + 82 Tan-1 8/10 = 12.8V +38.7º (Measured as 15V +30º) ??? OR ..... If VSUPPLY = 15V and VR = 10V then VL should be: ...
... VSUPPLY = 15V as measured with DVM From the calculations on the following page, there must be an error in these figures If VR is 10v & VL is 8V then VSUPPLY should be:VSUPPLY = 102 + 82 Tan-1 8/10 = 12.8V +38.7º (Measured as 15V +30º) ??? OR ..... If VSUPPLY = 15V and VR = 10V then VL should be: ...
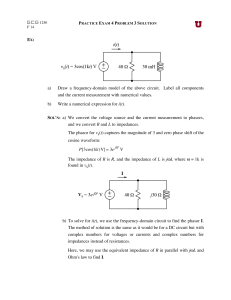
EX: a) Draw a frequency-domain model of the above circuit. Label
... The phasor for vs(t) captures the magnitude of 3 and zero phase shift of the cosine waveform: P[3cos(1kt)V] = 3e j0° V ...
... The phasor for vs(t) captures the magnitude of 3 and zero phase shift of the cosine waveform: P[3cos(1kt)V] = 3e j0° V ...
Lecture 9 – Phys 272 Currents, EMF (voltage
... Voltage drop across 2 Ohms is 4 volts Voltage drop across 4 Ohms is 8 volts Vab= Va′b′ = 8 volts ...
... Voltage drop across 2 Ohms is 4 volts Voltage drop across 4 Ohms is 8 volts Vab= Va′b′ = 8 volts ...
Electricity and Ohm`s Law Lesson Plan
... Ohm, mathematician and physicist born 1789 and died 1854 in Bavaria, defines the relationship between power, voltage, current and resistance. These are the very basic electrical units we work with. The principles apply to direct current or alternating current. Ohms Law is the foundation of electroni ...
... Ohm, mathematician and physicist born 1789 and died 1854 in Bavaria, defines the relationship between power, voltage, current and resistance. These are the very basic electrical units we work with. The principles apply to direct current or alternating current. Ohms Law is the foundation of electroni ...
Electronics Engineering Exercise 1
... The doping concentrations on the p‐side and n‐side of a silicon diode are 1 × 1016 cm‐3 and 1 × 1017 cm‐3, respectively. A forward bias of 0.3 V is applied to the diode. At T = 300 K, the intrinsic carrier concentration of silicon ni = 1.5 × 1010 cm‐3 and ...
... The doping concentrations on the p‐side and n‐side of a silicon diode are 1 × 1016 cm‐3 and 1 × 1017 cm‐3, respectively. A forward bias of 0.3 V is applied to the diode. At T = 300 K, the intrinsic carrier concentration of silicon ni = 1.5 × 1010 cm‐3 and ...
Name Chapter 14 Review parallel circuit horsepower transformer
... 5. When a new branch containing a resistor is added to a parallel circuit, the total resistance in the circuit will do what? ...
... 5. When a new branch containing a resistor is added to a parallel circuit, the total resistance in the circuit will do what? ...
L25.ppt
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
L25.ppt - University of Iowa Physics
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
... carry currents: in an electric stove this heat is used for cooking • The amount of energy converted to heat each second is called the power loss in a resistor • If the resistor has a voltage V across it and carries a current I, the electrical power converted to heat is given by ...
L 25 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Electric current (symbol I
... • the electricity that you get from the power company is not DC it is AC (alternating). • We will discuss AC in the next lecture ...
... • the electricity that you get from the power company is not DC it is AC (alternating). • We will discuss AC in the next lecture ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.






















![L 25 Electricity and Magnetism [3] Electric current (symbol I](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007903713_1-7c777a1a37e6fccaeb2ed3a9724ccb92-300x300.png)