Calculating the Efficiency of the Solar Cells
... provided, essentially limited by the movement of the electrons across the junction potential and through the doped semiconductor to the external contact. This will be the maximum current that the solar cell could provide in a particular light source, the short circuit current, Isc. Conversely, if th ...
... provided, essentially limited by the movement of the electrons across the junction potential and through the doped semiconductor to the external contact. This will be the maximum current that the solar cell could provide in a particular light source, the short circuit current, Isc. Conversely, if th ...
Structures of the Energy flow system
... Field plate (Fältplatta) A semiconductor component of which the resistance changes when a mangetic field is applied. The movement of the magnet can be measured with a bridge circuit. ...
... Field plate (Fältplatta) A semiconductor component of which the resistance changes when a mangetic field is applied. The movement of the magnet can be measured with a bridge circuit. ...
Temperature-Dependent Third Cumulant of Tunneling Noise C.W. J. Beenakker, M. Kindermann,
... limit of zero impedance, when the measurement is supposed to be noninvasive. The temperature independent result for the third cumulant of tunneling noise is recovered only if the measurement circuit has both negligible impedance and negligible temperature. The circuit is shown schematically in Fig. ...
... limit of zero impedance, when the measurement is supposed to be noninvasive. The temperature independent result for the third cumulant of tunneling noise is recovered only if the measurement circuit has both negligible impedance and negligible temperature. The circuit is shown schematically in Fig. ...
Lecture Set 6-Current and Resistance
... We will assume that the conductor is essentially an equi-potential ...
... We will assume that the conductor is essentially an equi-potential ...
High Precision 2.5 V IC Reference AD580*
... extrapolation of the temperature characteristic of any one of these devices to absolute zero (with emitter current proportional to absolute temperature) reveals that it will go to a VBE of 1.205 volts at 0K, as shown in Figure 1. Thus, if a voltage could be developed with an opposing temperature coe ...
... extrapolation of the temperature characteristic of any one of these devices to absolute zero (with emitter current proportional to absolute temperature) reveals that it will go to a VBE of 1.205 volts at 0K, as shown in Figure 1. Thus, if a voltage could be developed with an opposing temperature coe ...
RT9164B - Richtek
... tantalum or 50μF aluminum electrolytic with 30mΩ to 2Ω range capacitor is sufficient. The output capacitor does not have a theoretical upper limit and increasing its value will increase stability. COUT = 100μF or more is typical for high current regulator ...
... tantalum or 50μF aluminum electrolytic with 30mΩ to 2Ω range capacitor is sufficient. The output capacitor does not have a theoretical upper limit and increasing its value will increase stability. COUT = 100μF or more is typical for high current regulator ...
File - Electric Circuit Analysis
... We know by now that: resistance generally remains constant with change in frequency, the inductive reactance increases with increase in frequency the capacitive reactance decreases with increase in frequency ...
... We know by now that: resistance generally remains constant with change in frequency, the inductive reactance increases with increase in frequency the capacitive reactance decreases with increase in frequency ...
BDX53B
... All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale. Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and service ...
... All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale. Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and service ...
Dynamic Power Path Mgmt
... fast-charge load 1 A) instead of a peak load. If a peak system load requires an additional 0.75 A, over the average load, then the charging current is reduced by this amount during the peak load transient. The DPPM system voltage based routine would detect a current-limited adaptor or brown-out cond ...
... fast-charge load 1 A) instead of a peak load. If a peak system load requires an additional 0.75 A, over the average load, then the charging current is reduced by this amount during the peak load transient. The DPPM system voltage based routine would detect a current-limited adaptor or brown-out cond ...
Preview of Period 11: Electric Current
... Period 11 Review Questions R.1 What is electric current? How is current different from electric charge? List some sources of electric current. R.2 How is a battery similar to a capacitor? How is it different? R.3 What is necessary for an electrical device to operate? Why can't we use string instead ...
... Period 11 Review Questions R.1 What is electric current? How is current different from electric charge? List some sources of electric current. R.2 How is a battery similar to a capacitor? How is it different? R.3 What is necessary for an electrical device to operate? Why can't we use string instead ...
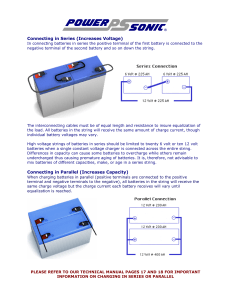
Connecting in Series (Increases Voltage) Connecting in Parallel
... Connecting in Parallel (Increases Capacity) When charging batteries in parallel (positive terminals are connected to the positive terminal and negative terminals to the negative), all batteries in the string will receive the same charge voltage but the charge current each battery receives will vary ...
... Connecting in Parallel (Increases Capacity) When charging batteries in parallel (positive terminals are connected to the positive terminal and negative terminals to the negative), all batteries in the string will receive the same charge voltage but the charge current each battery receives will vary ...
Chapter 17 Alternating Currents
... (b) If C is adjusted so that the resonant frequency of the LCR circuit equals to the frequency of the wanted station, a large current and p.d. at that frequency only will develop across C. (c) This selected and amplified p.d. is then applied to the next stage of the receiver. (d) Improvement : Use a ...
... (b) If C is adjusted so that the resonant frequency of the LCR circuit equals to the frequency of the wanted station, a large current and p.d. at that frequency only will develop across C. (c) This selected and amplified p.d. is then applied to the next stage of the receiver. (d) Improvement : Use a ...
DC Voltage and Current Sense PCB with Analog Output
... It is important that both shunt resistors carry equal current load for sensor accuracy. To ensure equal current load, the solder pads have a large via holes through which the leads must pass through then be flooded with solder. Pass the “In+” and “Out+” leads through the large via holes and solder ...
... It is important that both shunt resistors carry equal current load for sensor accuracy. To ensure equal current load, the solder pads have a large via holes through which the leads must pass through then be flooded with solder. Pass the “In+” and “Out+” leads through the large via holes and solder ...
7796 SPECIFICATION SHEET
... reduced power. • Rugged chassis for stand-alone or rack mounted operation. No additional power supplies are required. • Protection circuitry protects the AE Techron 7796 from input overloads, improper output connection (including shorted and improper loads), over-temperature, over-current, and suppl ...
... reduced power. • Rugged chassis for stand-alone or rack mounted operation. No additional power supplies are required. • Protection circuitry protects the AE Techron 7796 from input overloads, improper output connection (including shorted and improper loads), over-temperature, over-current, and suppl ...
Transistors - The Common Base Amplifier 1430 Experiment 7
... 1 330W, ½ Watt resistor (orange-orangebrown) 2 1000W, ½ Watt resistor (brown-black-red) 2 1200W, ½ Watt resistor (brown-red-red) 1 6800W, ½ Watt resistor (blue-gray-red) 2 10 kW, ½ Watt resistor (brown-black-orange) 1 MPSA-20 silicon transistor 3 10 mF electrolytic capacitor ...
... 1 330W, ½ Watt resistor (orange-orangebrown) 2 1000W, ½ Watt resistor (brown-black-red) 2 1200W, ½ Watt resistor (brown-red-red) 1 6800W, ½ Watt resistor (blue-gray-red) 2 10 kW, ½ Watt resistor (brown-black-orange) 1 MPSA-20 silicon transistor 3 10 mF electrolytic capacitor ...
Current source
A current source is an electronic circuit that delivers or absorbs an electric current which is independent of the voltage across it.A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current 'sink' is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply. Figure 1 shows the schematic symbol for an ideal current source, driving a resistor load. There are two types - an independent current source (or sink) delivers a constant current. A dependent current source delivers a current which is proportional to some other voltage or current in the circuit.