Ch13zz
... Freud in France (1885) • Through work with Jean-Martin Charcot, became interested in hysterical patients (hypnosis) • Charcot pointed to sex as the origin of Hysteria • Freud tried hypnosis, but eventually dropped it ...
... Freud in France (1885) • Through work with Jean-Martin Charcot, became interested in hysterical patients (hypnosis) • Charcot pointed to sex as the origin of Hysteria • Freud tried hypnosis, but eventually dropped it ...
therapy synopsis
... do not believe that searching for unconscious determinants or becoming more self-aware are the keys to change. Their goal is to eliminate unwanted and problematic behaviors and responses by use of counter-conditioning. Systematic Desensitization is often used to treat specific phobias. This techniqu ...
... do not believe that searching for unconscious determinants or becoming more self-aware are the keys to change. Their goal is to eliminate unwanted and problematic behaviors and responses by use of counter-conditioning. Systematic Desensitization is often used to treat specific phobias. This techniqu ...
Module 40
... MD with postgraduate training in abnormal behavior Assessment and treatment of psychological and related physical disorders Can prescribe medication ...
... MD with postgraduate training in abnormal behavior Assessment and treatment of psychological and related physical disorders Can prescribe medication ...
Darwin, Freud, Einstein
... • Sought to explore the unconscious mind • Freud specialized in treating nervous disorders and through this research established the concept of neuroses. • Often the result of childhood fears and experiences, usually sexual in nature. • Would treat these by trying to bring those experiences to light ...
... • Sought to explore the unconscious mind • Freud specialized in treating nervous disorders and through this research established the concept of neuroses. • Often the result of childhood fears and experiences, usually sexual in nature. • Would treat these by trying to bring those experiences to light ...
KHILAN KHIMASIA File
... Difficult to get CBT due to availability, and it may take a few weeks before the effects of it show Quicker than psychoanalysis, although medication may be a better solution than both Techniques can help client for future so they can cope long term ...
... Difficult to get CBT due to availability, and it may take a few weeks before the effects of it show Quicker than psychoanalysis, although medication may be a better solution than both Techniques can help client for future so they can cope long term ...
CFS 120- clickerquestions_ch02
... The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, Tenth Edition by Kathleen Stassen Berger ...
... The Developing Person Through Childhood and Adolescence, Tenth Edition by Kathleen Stassen Berger ...
Personality Theories - Mr. Hunsaker`s Classes
... that is aware of immediate surroundings and perceptions. • Preconscious mind – level of the mind in which information is available but not currently conscious. ...
... that is aware of immediate surroundings and perceptions. • Preconscious mind – level of the mind in which information is available but not currently conscious. ...
Chapter 20 Section Quiz 20-4 DIRECTIONS: Matching Match each
... statement or answers the question. (10 points each) DIRECTIONS: ...
... statement or answers the question. (10 points each) DIRECTIONS: ...
The Spectrum of Psychoanalytic Therapies
... average of five years. The evidence base for psychoanalysis is a wealth of individual case studies leading to observations that have been vigorously and contentiously discussed in scientific meetings since the early 1900s. There is a broad consensus in the field about fundamental concepts, but psych ...
... average of five years. The evidence base for psychoanalysis is a wealth of individual case studies leading to observations that have been vigorously and contentiously discussed in scientific meetings since the early 1900s. There is a broad consensus in the field about fundamental concepts, but psych ...
02Theories of development
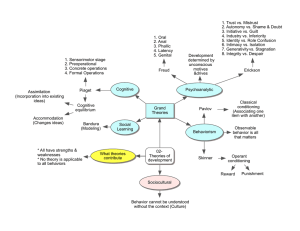
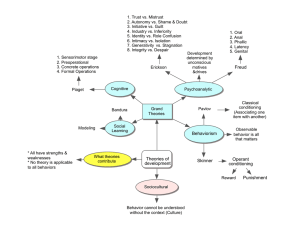
... 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair 1. Sensorimotor stage 2. Preoperational 3. Concrete operations 4. Formal Operations ...
... 1. Trust vs. Mistrust 2. Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt 3. Initiative vs. Guilt 4. Industry vs. Inferiority 5. Identity vs. Role Confusion 6. Intimacy vs. Isolation 7. Generativity vs. Stagnation 8. Integrity vs. Despair 1. Sensorimotor stage 2. Preoperational 3. Concrete operations 4. Formal Operations ...
The Biological Tradition
... Hippocrates: Greek physician (460-377 B.C.) believed psychological disorders could be treated like any other disease Galen: Roman physician (129-198 A.D.) went further with Hippocrates theories; created an influential school of thought that extended into the 19th century Hippocratic-Galenic approach ...
... Hippocrates: Greek physician (460-377 B.C.) believed psychological disorders could be treated like any other disease Galen: Roman physician (129-198 A.D.) went further with Hippocrates theories; created an influential school of thought that extended into the 19th century Hippocratic-Galenic approach ...
THE AGE OF CONFUSION
... “rules” had been smashed, experimentation became the norm… • This created an atmosphere of relativism…many sought refuge in extremism… • This process began before the war… ...
... “rules” had been smashed, experimentation became the norm… • This created an atmosphere of relativism…many sought refuge in extremism… • This process began before the war… ...
MR. GREER PRESENTS
... Psychoanalysis • Main theme of Freud’s work • Psychoanalysis- it emphasizes the recovery of unconscious conflicts, motives, and defenses through therapeutic techniques • Goal: help patient gain insight about themselves and their problems • Moving unconscious thoughts or feelings from the unconsciou ...
... Psychoanalysis • Main theme of Freud’s work • Psychoanalysis- it emphasizes the recovery of unconscious conflicts, motives, and defenses through therapeutic techniques • Goal: help patient gain insight about themselves and their problems • Moving unconscious thoughts or feelings from the unconsciou ...
The psychodynamic explanation of mental illness
... factors (i.e. a part of the brain) can have an impact on cognitive processes (e.g. memory). In terms of mental illness we can use brain imaging techniques such as MRI or PET scans to identify which areas of the brain are affected by the disorder and then this helps to understand how these might affe ...
... factors (i.e. a part of the brain) can have an impact on cognitive processes (e.g. memory). In terms of mental illness we can use brain imaging techniques such as MRI or PET scans to identify which areas of the brain are affected by the disorder and then this helps to understand how these might affe ...
Exam Revision Unit 2 2012
... Humanist theory: Rogers and his concepts of the self Psychoanalysis: Freud’s theory Psychosexual stages; levels of consciousness; id, ego and superego; ego defence mechanisms Contrasts between humanist approaches and psychoanalytic approaches Criticisms of Freudian theory and humanist theo ...
... Humanist theory: Rogers and his concepts of the self Psychoanalysis: Freud’s theory Psychosexual stages; levels of consciousness; id, ego and superego; ego defence mechanisms Contrasts between humanist approaches and psychoanalytic approaches Criticisms of Freudian theory and humanist theo ...
Sigmund Freud
... Sigmund Freud was the father of psychoanalysis. He focused on the mind’s structure and its effects on unconsciousness, repression, and infantile sexuality. Freud theorized that many neuroses (phobias, hysterical paralyses and pains, some forms of paranoia) originated from traumatic experiences which ...
... Sigmund Freud was the father of psychoanalysis. He focused on the mind’s structure and its effects on unconsciousness, repression, and infantile sexuality. Freud theorized that many neuroses (phobias, hysterical paralyses and pains, some forms of paranoia) originated from traumatic experiences which ...
According to Freud, we are born with our Id.
... psychoanalysis, had an enormous influence on art, literature, and social thinking. Psychoanalysis had replaced hypnosis with "free association." In 1900 Freud published his first major work, The Interpretation of Dreams, which established the importance of psychoanalytical movement. ...
... psychoanalysis, had an enormous influence on art, literature, and social thinking. Psychoanalysis had replaced hypnosis with "free association." In 1900 Freud published his first major work, The Interpretation of Dreams, which established the importance of psychoanalytical movement. ...
Iceberg Theory
... Freud abandoned this form of treatment as it proved ineffective for many, in favor of a treatment where the patient talked through his or her problems. This came to be known as the "talking cure", as the ultimate goal of this talking was to locate and release powerful emotional energy that had init ...
... Freud abandoned this form of treatment as it proved ineffective for many, in favor of a treatment where the patient talked through his or her problems. This came to be known as the "talking cure", as the ultimate goal of this talking was to locate and release powerful emotional energy that had init ...
Personality II
... Universal agreement – not very good. Training issues Nonetheless … used widely. ...
... Universal agreement – not very good. Training issues Nonetheless … used widely. ...