Blood Vessels
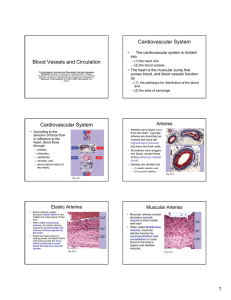
... begins and ends at the heart • Arteries: carry blood away from the heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation • Capillaries: contact tissue cells and directly serve cellular needs • Veins: carry blood toward the heart except for pulmonary circulation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... begins and ends at the heart • Arteries: carry blood away from the heart; oxygenated except for pulmonary circulation • Capillaries: contact tissue cells and directly serve cellular needs • Veins: carry blood toward the heart except for pulmonary circulation Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
GFR - ISpatula
... Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) • Filtration Fraction (FF)= Fraction of blood plasma in the afferent arterioles that becomes filtrate= 16-20%. • GFR =The volume (ml) of fluid filtered through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpus ...
... Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) • Filtration Fraction (FF)= Fraction of blood plasma in the afferent arterioles that becomes filtrate= 16-20%. • GFR =The volume (ml) of fluid filtered through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpus ...
Determinants of GFR - BHS116.3 Physiology III
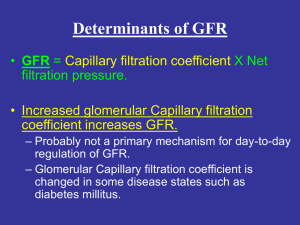
... Determinants of GFR • GFR = Capillary filtration coefficient X Net filtration pressure. • Increased hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule decreases GFR (inverse is also true). – Normally, not a primary mechanism for day-to-day regulation of GFR. – Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule can cha ...
... Determinants of GFR • GFR = Capillary filtration coefficient X Net filtration pressure. • Increased hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule decreases GFR (inverse is also true). – Normally, not a primary mechanism for day-to-day regulation of GFR. – Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule can cha ...
Problems for self
... Take into account that the left tube is a Pitot-tube, i.e. it measures total pressure. As such, p1 is the total pressure and therefore equals the sum of the static and dynamic pressure in section 1. That is why the dynamic pressure in section 1 is missing from the equation. If the left tube was a st ...
... Take into account that the left tube is a Pitot-tube, i.e. it measures total pressure. As such, p1 is the total pressure and therefore equals the sum of the static and dynamic pressure in section 1. That is why the dynamic pressure in section 1 is missing from the equation. If the left tube was a st ...
Chapter 12 Compressible Flow 12-121 12
... Solution Using EES (or other) software, the shape of a converging-diverging nozzle is to be determined for specified flow rate and stagnation conditions. The nozzle and the Mach number are to be plotted. Assumptions 1 Air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats. 2 Flow through the nozzle is ste ...
... Solution Using EES (or other) software, the shape of a converging-diverging nozzle is to be determined for specified flow rate and stagnation conditions. The nozzle and the Mach number are to be plotted. Assumptions 1 Air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats. 2 Flow through the nozzle is ste ...
Chap 19 Vessels - NSCC NetID: Personal Web Space
... but major effect is to cause veins in liver, skin and lungs to redistribute venous reserve back to arterial system (about 20% of total blood) ...
... but major effect is to cause veins in liver, skin and lungs to redistribute venous reserve back to arterial system (about 20% of total blood) ...
non-invasive blood pressure
... assessing your patient’s cardiac status because a patient’s heart rate and pulse rate may vary if there is any cardiac compromise. On the Propaq monitor you can set the HR/PR tone loudness to LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH, or OFF. This does not affect the tone of the alarm if a patient exceeds an alarm limit se ...
... assessing your patient’s cardiac status because a patient’s heart rate and pulse rate may vary if there is any cardiac compromise. On the Propaq monitor you can set the HR/PR tone loudness to LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH, or OFF. This does not affect the tone of the alarm if a patient exceeds an alarm limit se ...
BIOL242Chap19VesselsOCT2012
... but major effect is to cause veins in liver, skin and lungs to redistribute venous reserve back to arterial system (about 20% of total blood) ...
... but major effect is to cause veins in liver, skin and lungs to redistribute venous reserve back to arterial system (about 20% of total blood) ...
Regulation of Glomerular Filtration
... Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) • Filtration Fraction (FF)= Fraction of blood plasma in the afferent arterioles that becomes filtrate= 16-20%. • GFR =The volume (ml) of fluid filtered through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpus ...
... Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) • Filtration Fraction (FF)= Fraction of blood plasma in the afferent arterioles that becomes filtrate= 16-20%. • GFR =The volume (ml) of fluid filtered through all the corpuscles of both kidneys per minute. • The volume of fluid filtered daily through all the corpus ...
chapter07
... Figure 7.19 Model for deriving equation for heart-valve orifice area P1 and P2 are upstream and downstream static pressures., Velocity u is calculated for minimal flow area A at location 2. © From J. G. Webster (ed.), Medical instrumentation: application and design. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & S ...
... Figure 7.19 Model for deriving equation for heart-valve orifice area P1 and P2 are upstream and downstream static pressures., Velocity u is calculated for minimal flow area A at location 2. © From J. G. Webster (ed.), Medical instrumentation: application and design. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & S ...
Figure 1.1 Generalized instrumentation system The sensor
... Figure 7.19 Model for deriving equation for heart-valve orifice area P1 and P2 are upstream and downstream static pressures., Velocity u is calculated for minimal flow area A at location 2. © From J. G. Webster (ed.), Medical instrumentation: application and design. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & S ...
... Figure 7.19 Model for deriving equation for heart-valve orifice area P1 and P2 are upstream and downstream static pressures., Velocity u is calculated for minimal flow area A at location 2. © From J. G. Webster (ed.), Medical instrumentation: application and design. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley & S ...
FILMTEC™ NF90-4040 Mem
... shutdown, cleaning or other sequences to prevent possible membrane damage. During start-up, a gradual change from a standstill to operating state is recommended as follows: • Feed pressure should be increased gradually over a 30-60 second time frame. • Cross-flow velocity at set operating point shou ...
... shutdown, cleaning or other sequences to prevent possible membrane damage. During start-up, a gradual change from a standstill to operating state is recommended as follows: • Feed pressure should be increased gradually over a 30-60 second time frame. • Cross-flow velocity at set operating point shou ...
Logistic Regression
... For example, the odds of CHD are multiplied by the factor exp(0.0243) = 1.025 for every increase of 1 mmHg in SBP. A difference of 10 mmHg multiplies the odds of CHD by (1.025)10, or ...
... For example, the odds of CHD are multiplied by the factor exp(0.0243) = 1.025 for every increase of 1 mmHg in SBP. A difference of 10 mmHg multiplies the odds of CHD by (1.025)10, or ...
Solutions
... Show by a sketch indicating production/injection wells and their locations how we can apply superposition (or imaging) method to generate the pressure response at the actual well shown in above figure. Also sketch the log-log diagnostic plot of delta pressure and derivative vs. time that would be e ...
... Show by a sketch indicating production/injection wells and their locations how we can apply superposition (or imaging) method to generate the pressure response at the actual well shown in above figure. Also sketch the log-log diagnostic plot of delta pressure and derivative vs. time that would be e ...
Unit 4 Review - Rancho High School
... Read all of the questions carefully. All work must be shown under the appropriate problem to receive full credit. (each problem is 2 points each unless specified) The test will be 30 pts. total ...
... Read all of the questions carefully. All work must be shown under the appropriate problem to receive full credit. (each problem is 2 points each unless specified) The test will be 30 pts. total ...
PowerPoint Notes for Blood Vessels
... Heart rate is primarily controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS). ...
... Heart rate is primarily controlled by the autonomic nervous system (ANS). ...
hs-30 nitro - Hydrological Services America
... line for 5 seconds, the GCO pressure should then return to normal within 25 seconds, at which time the GCO line is switched back to the users pressure transducer for normal water level monitoring. (During this purging time, the pressure on the pressure transducer is held relatively constant through ...
... line for 5 seconds, the GCO pressure should then return to normal within 25 seconds, at which time the GCO line is switched back to the users pressure transducer for normal water level monitoring. (During this purging time, the pressure on the pressure transducer is held relatively constant through ...
8 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... osmotic pressure becomes too high? 34. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 35. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 36. What affect does aldosterone have on the ki ...
... osmotic pressure becomes too high? 34. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 35. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 36. What affect does aldosterone have on the ki ...
File - Doctorswriting
... A. resistance is inversely proportional to the square of the radius B. the wall tension necessary to balance transmural pressure is inversely proportional to the radius (PT/R) C. velocity is equal to flow for any given diameter D. flow and resistance are both related, reciprocally, to the radius to ...
... A. resistance is inversely proportional to the square of the radius B. the wall tension necessary to balance transmural pressure is inversely proportional to the radius (PT/R) C. velocity is equal to flow for any given diameter D. flow and resistance are both related, reciprocally, to the radius to ...
File - Doctorswriting
... B. Transmitters are released from synaptic knobs secondary to Na trigger C. Amount of transmitter released is proportional to Ca efflux D. Ach is present in granulated vesicles in synaptic knob E. The EPSP is caused by Na influx 9. Which of the following is an inhibitory neurotransmitter A. Gallamin ...
... B. Transmitters are released from synaptic knobs secondary to Na trigger C. Amount of transmitter released is proportional to Ca efflux D. Ach is present in granulated vesicles in synaptic knob E. The EPSP is caused by Na influx 9. Which of the following is an inhibitory neurotransmitter A. Gallamin ...
Urinary System Physiology
... • Renin released from JG cells when – blood pressure declines – osmolarity of distal convoluted tubule decreases ...
... • Renin released from JG cells when – blood pressure declines – osmolarity of distal convoluted tubule decreases ...
16 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... osmotic pressure becomes too high? 35. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the ki ...
... osmotic pressure becomes too high? 35. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the ki ...
13a Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... osmotic pressure becomes too high? 35. What affect does ADH have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, a ...
... osmotic pressure becomes too high? 35. What affect does ADH have on the kidneys, and how does this affect blood pressure? 36. When osmotic pressure is too high, what other endocrine gland secretes a hormone, and what is the name of the hormone? 37. What affect does aldosterone have on the kidneys, a ...
Pump it Up! The Effect of Tire Pressure on Bicycle Efficiency J0320
... with highest tire pressure (60 psi). The differences in speeds at the varying tire pressures were small but reproducible and statistically significant. Rolling resistance tests further validated my hypothesis. The highest tire pressures also gave lowest rolling resistance (2.583 lbs). However, the s ...
... with highest tire pressure (60 psi). The differences in speeds at the varying tire pressures were small but reproducible and statistically significant. Rolling resistance tests further validated my hypothesis. The highest tire pressures also gave lowest rolling resistance (2.583 lbs). However, the s ...
Blood pressure

Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels. When used without further specification, ""blood pressure"" usually refers to the arterial pressure in the systemic circulation. It is usually measured at a person's upper arm. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic (maximum) pressure over diastolic (minimum) pressure and is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). It is one of the vital signs along with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature. Normal resting blood pressure in an adult is approximately 120/80 mm Hg.Blood pressure varies depending on situation, activity, and disease states. It is regulated by the nervous and endocrine systems. Blood pressure that is low due to a disease state is called hypotension, and pressure that is consistently high is hypertension. Both have many causes which can range from mild to severe. Both may be of sudden onset or of long duration. Long term hypertension is a risk factor for many diseases, including kidney failure, heart disease, and stroke. Long term hypertension is more common than long term hypotension in Western countries. Long term hypertension often goes undetected because of infrequent monitoring and the absence of symptoms.