Document
... Both compounds have sharp melting points. Compound X melts at 150 °C, as shown on the left vertical axis, and Y melts at 148 °C, as shown on the right vertical axis. As compound X is added to pure Y, the melting point of the mixture decreases along curve C-B until a minimum temperature of 130 °C is ...
... Both compounds have sharp melting points. Compound X melts at 150 °C, as shown on the left vertical axis, and Y melts at 148 °C, as shown on the right vertical axis. As compound X is added to pure Y, the melting point of the mixture decreases along curve C-B until a minimum temperature of 130 °C is ...
Method
... mass transfer properties. A Rotary dryer consist of rotating cylinder that has an angle to the horizontal where input material from one end and output product from the other end. Dry air is used as a drying media. One of the important factors which will govern the size of the rotary dryer is the fee ...
... mass transfer properties. A Rotary dryer consist of rotating cylinder that has an angle to the horizontal where input material from one end and output product from the other end. Dry air is used as a drying media. One of the important factors which will govern the size of the rotary dryer is the fee ...
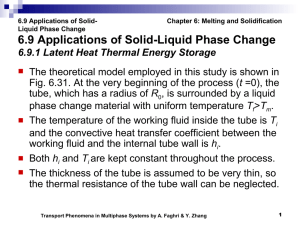
ENTHALPY CHANGE DH
... The units of entropy are: J.K-1.mol-1 Entropy decreases as temperature decreases, so that at absolute zero (0K), most substances are solids consisting of perfectly ordered particles which have ceased to vibrate. They therefore have zero entropy. This means that there is a definite starting point fo ...
... The units of entropy are: J.K-1.mol-1 Entropy decreases as temperature decreases, so that at absolute zero (0K), most substances are solids consisting of perfectly ordered particles which have ceased to vibrate. They therefore have zero entropy. This means that there is a definite starting point fo ...
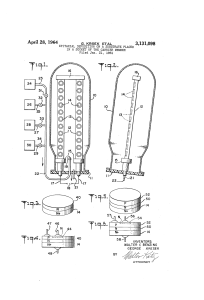
5823/ INVENTORS 48X "
... That this same problem of providing a high resistivity heating the wafers by heat from the support, contacting layer intermediate in a semiconductor body structure is the heated wafer with a decomposable vapor comprising applicable to structures other than the NPIN transistor, semiconductor atoms an ...
... That this same problem of providing a high resistivity heating the wafers by heat from the support, contacting layer intermediate in a semiconductor body structure is the heated wafer with a decomposable vapor comprising applicable to structures other than the NPIN transistor, semiconductor atoms an ...
Lecture Notes in Physical Chemistry Semester 2: Kinetics and
... (Notice that the exponent on the normalization factor is now 3/2.) If you think of the function d N v x v y v z /N as living in a three-dimensional “velocity space” whose axes are v x , v y , and v z , then the dv x dv y dv z part of Eq. (1.31) describes the volume of a small rectangular box, which ...
... (Notice that the exponent on the normalization factor is now 3/2.) If you think of the function d N v x v y v z /N as living in a three-dimensional “velocity space” whose axes are v x , v y , and v z , then the dv x dv y dv z part of Eq. (1.31) describes the volume of a small rectangular box, which ...
3Basic Polymer Chemistry
... In ancient times, people used copper, gold, iron and clay for their daily needs, which were found in their natural form in the earth. However, as time passed and technology advanced, people needed to make goods that were strong, malleable, durable, practical and cheap. Materials with these propertie ...
... In ancient times, people used copper, gold, iron and clay for their daily needs, which were found in their natural form in the earth. However, as time passed and technology advanced, people needed to make goods that were strong, malleable, durable, practical and cheap. Materials with these propertie ...
(131904) Topic: Fracture of Metal Temperature Embrittlement
... Blue Brittleness: Low-carbon steels exhibit two types of aging which causes an increase in transition temperature: quench aging & strain aging. Strain aging is the slow increase in hardness in steels finished by cold work (mainly cold rolling). Blue brittleness is attributed to strain aging caused b ...
... Blue Brittleness: Low-carbon steels exhibit two types of aging which causes an increase in transition temperature: quench aging & strain aging. Strain aging is the slow increase in hardness in steels finished by cold work (mainly cold rolling). Blue brittleness is attributed to strain aging caused b ...
Ductile fracture
... Blue Brittleness: Low-carbon steels exhibit two types of aging which causes an increase in transition temperature: quench aging & strain aging. Strain aging is the slow increase in hardness in steels finished by cold work (mainly cold rolling). Blue brittleness is attributed to strain aging caused b ...
... Blue Brittleness: Low-carbon steels exhibit two types of aging which causes an increase in transition temperature: quench aging & strain aging. Strain aging is the slow increase in hardness in steels finished by cold work (mainly cold rolling). Blue brittleness is attributed to strain aging caused b ...
A Comparative Study on the Biochemical Bases of the Maximum
... Chapman, 1964; Hagen, Kushner & Gibbons, 1964). Enzyme denaturation is usually assumed to be a major factor, and excellent agreement between the maximum temperatures for growth of several bacteria and the minimum temperatures a t which certain of their respiratory enzymes were inactivated was report ...
... Chapman, 1964; Hagen, Kushner & Gibbons, 1964). Enzyme denaturation is usually assumed to be a major factor, and excellent agreement between the maximum temperatures for growth of several bacteria and the minimum temperatures a t which certain of their respiratory enzymes were inactivated was report ...
The physics of manganites: Structure and transport
... ternal field is to increase the ratio of the former events, reducing the latter, by aligning the polarization of the magnetic layer along the direction of the external field. This effect is a few tens of percent, and has the very important advantage of not being limited to low temperatures. Spin-val ...
... ternal field is to increase the ratio of the former events, reducing the latter, by aligning the polarization of the magnetic layer along the direction of the external field. This effect is a few tens of percent, and has the very important advantage of not being limited to low temperatures. Spin-val ...
Superhard Monoclinic Polymorph of Carbon - USPEX
... graphite, diamond, hexagonal diamond (lonsdaleite), carbynes, nanotubes, fullerences, and amorphous carbon. This is because of carbon’s ability to form sp-, sp2 -, and sp3 -hybridized bonds [1]. The conversion mechanisms between various forms of carbon have long been a topic of interest since these ...
... graphite, diamond, hexagonal diamond (lonsdaleite), carbynes, nanotubes, fullerences, and amorphous carbon. This is because of carbon’s ability to form sp-, sp2 -, and sp3 -hybridized bonds [1]. The conversion mechanisms between various forms of carbon have long been a topic of interest since these ...
Enthalpy - Net Texts
... When a liquid vaporizes the liquid must absorb heat from its surroundings to replace the energy taken by the vaporizing molecules in order for the temperature to remain constant. This heat required to vaporize the liquid is called enthalpy, or often, heat of vaporization. For the vaporization of one ...
... When a liquid vaporizes the liquid must absorb heat from its surroundings to replace the energy taken by the vaporizing molecules in order for the temperature to remain constant. This heat required to vaporize the liquid is called enthalpy, or often, heat of vaporization. For the vaporization of one ...
Electric conductivity of Cu (NO ) 2∙3 Н2 О solutions in
... Electric conductivity of Cu(NO3)2.3Н2О solutions in DMSO quickly increases at temperature 288 K with growth of the salt content in a solution till 0.4 M. The further increase of copper nitrate trihydrate solution concentration in DMSO leads to gradual decrease of electric conductivity till some li ...
... Electric conductivity of Cu(NO3)2.3Н2О solutions in DMSO quickly increases at temperature 288 K with growth of the salt content in a solution till 0.4 M. The further increase of copper nitrate trihydrate solution concentration in DMSO leads to gradual decrease of electric conductivity till some li ...
Slide 1
... velocity in a straight line from the source to the substrate – They condense on the low temperature substrate – The condensed atoms of Si or dopant will diffuse on the surface until they reach a low energy site that they fit well the atomic structure of the surface – The “adatom” then bonds in that ...
... velocity in a straight line from the source to the substrate – They condense on the low temperature substrate – The condensed atoms of Si or dopant will diffuse on the surface until they reach a low energy site that they fit well the atomic structure of the surface – The “adatom” then bonds in that ...
Mohammad.Nazari-Dissertation-
... characterized as either a narrow gap insulator or semiconductor, to high-temperature tetragonal rutile (R) phase, in which the material is metallic. Phase transition in vanadium dioxide was reported for the first time by Morin in 1959 with TMIT at ~ 68 °C.4 ...
... characterized as either a narrow gap insulator or semiconductor, to high-temperature tetragonal rutile (R) phase, in which the material is metallic. Phase transition in vanadium dioxide was reported for the first time by Morin in 1959 with TMIT at ~ 68 °C.4 ...
Herbert Ipser, Olga P. Semenova, Regina
... The new ternary compound In5.25Pd13Sb3.75 was found. It's crystal structure was determined using a CCD-diffractometer at room temperature. Evaluations and refinements finally yielded a C-centered monoclinic structure (space group: C 2/c; Pearson symbol: mC88, Z = 4) with a = 15.189(2) Å, b = 8.799(1 ...
... The new ternary compound In5.25Pd13Sb3.75 was found. It's crystal structure was determined using a CCD-diffractometer at room temperature. Evaluations and refinements finally yielded a C-centered monoclinic structure (space group: C 2/c; Pearson symbol: mC88, Z = 4) with a = 15.189(2) Å, b = 8.799(1 ...
Glass transition
The glass–liquid transition or glass transition for short is the reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle state into a molten or rubber-like state. An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. Supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state is called vitrification, from the Latin vitreum, ""glass"" via French vitrifier.Despite the massive change in the physical properties of a material through its glass transition, the transition is not itself a phase transition of any kind; rather it is a laboratory phenomenon extending over a range of temperature and defined by one of several conventions. Such conventions include a constant cooling rate (20 K/min) and a viscosity threshold of 1012 Pa·s, among others. Upon cooling or heating through this glass-transition range, the material also exhibits a smooth step in the thermal-expansion coefficient and in the specific heat, with the location of these effects again being dependent on the history of the material. However, the question of whether some phase transition underlies the glass transition is a matter of continuing research.The glass-transition temperature Tg is always lower than the melting temperature, Tm, of the crystalline state of the material, if one exists.