Section 4.8: Acid-Base Reactions
... Two compounds react to form two new compounds. All double replacement reactions must have a "driving force" that removes a pair of ions from solution. Ions in a precipitation reaction will keep their same charges as reactants and products. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble su ...
... Two compounds react to form two new compounds. All double replacement reactions must have a "driving force" that removes a pair of ions from solution. Ions in a precipitation reaction will keep their same charges as reactants and products. Formation of a precipitate: A precipitate is an insoluble su ...
Worksheet to accompany demos on exchange reactions
... atom must get short-shrifted! That is, the electrons ―assigned‖ to O were effectively ―taken away‖ from C. Since the two O atoms each get 2 extra electrons, the C atom must be deficient by 4 electrons, and so it would have 4 fewer electrons than a neutral C atom and so it would have a ―fictitious‖ c ...
... atom must get short-shrifted! That is, the electrons ―assigned‖ to O were effectively ―taken away‖ from C. Since the two O atoms each get 2 extra electrons, the C atom must be deficient by 4 electrons, and so it would have 4 fewer electrons than a neutral C atom and so it would have a ―fictitious‖ c ...
homework_#1_10
... of atoms on each side and the same total mass on each side. You DO NOT have the same number of MOLES on each side (7 on the left, 6 on the right) or VOLUME (7 x 22.4 Liters on the left, 6 x 22.4 on the right) or MOLECULES (7 on the left, 6 on the right) ...
... of atoms on each side and the same total mass on each side. You DO NOT have the same number of MOLES on each side (7 on the left, 6 on the right) or VOLUME (7 x 22.4 Liters on the left, 6 x 22.4 on the right) or MOLECULES (7 on the left, 6 on the right) ...
Beverley John C. Beverley IE 500/PHI 598: Ontological Engineering
... arbitrary regions of space. Systems have accompanying properties, and it is from consideration of properties in a system, some held constant while others vary, that the famous Thermodynamic Laws are derived.2 Indeed, when certain properties are assumed constant then various thermodynamic equilibria ...
... arbitrary regions of space. Systems have accompanying properties, and it is from consideration of properties in a system, some held constant while others vary, that the famous Thermodynamic Laws are derived.2 Indeed, when certain properties are assumed constant then various thermodynamic equilibria ...
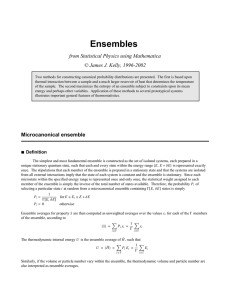
Ensembles - UMD Physics
... The classic example of negative temperature is provided by nuclear spin systems which interact so weakly with the surrounding crystal lattice that macrostates with nuclear magnetization opposed to the external magnetic field can be maintained in constrained or partial equilibrium for a long time. Th ...
... The classic example of negative temperature is provided by nuclear spin systems which interact so weakly with the surrounding crystal lattice that macrostates with nuclear magnetization opposed to the external magnetic field can be maintained in constrained or partial equilibrium for a long time. Th ...
lect 7
... O2 > NO3- > Mn(VI) > Fe(III) > AsO43- >SO42A lack of oxygen leads to an anaerobic condition and results in the build up of reduced species: Mn(II), N2, Fe(II), As(III), and S2-. When reduced species are build up in the system, it is termed "REDUCED". When O2 is present with reduced species such as S ...
... O2 > NO3- > Mn(VI) > Fe(III) > AsO43- >SO42A lack of oxygen leads to an anaerobic condition and results in the build up of reduced species: Mn(II), N2, Fe(II), As(III), and S2-. When reduced species are build up in the system, it is termed "REDUCED". When O2 is present with reduced species such as S ...
Slide 1 / 55 Slide 2 / 55 Slide 3 / 55
... 45 A reaction that is not spontaneous at low temperature can become spontaneous at high temperature if ΔH is ____ and ΔS is ____. A ...
... 45 A reaction that is not spontaneous at low temperature can become spontaneous at high temperature if ΔH is ____ and ΔS is ____. A ...
BASIC CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS
... the properties such as pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, much be known to determine the 'thermodynamic state’ of the working medium. Thus, if the thermodynamic state is fixed, all these properties are fixed with it. 1.5 Process and Cycle A change of state occurs when ...
... the properties such as pressure, volume, temperature, internal energy, enthalpy, entropy, much be known to determine the 'thermodynamic state’ of the working medium. Thus, if the thermodynamic state is fixed, all these properties are fixed with it. 1.5 Process and Cycle A change of state occurs when ...
0.08206 L atm/K mol - Arizona State University
... Water molecules undergo a chemical change in which hydrogen and oxygen molecules form. Water molecules undergo a physical change in which hydrogen and oxygen molecules form. Water molecules undergo a chemical change in which gaseous water vapor molecules form. Water molecules undergo a physical chan ...
... Water molecules undergo a chemical change in which hydrogen and oxygen molecules form. Water molecules undergo a physical change in which hydrogen and oxygen molecules form. Water molecules undergo a chemical change in which gaseous water vapor molecules form. Water molecules undergo a physical chan ...
Chemistry Lab 2010
... • Bonds between atoms of the reactants (N2 and O2) are broken, and new bonds (NO) form. • Energy needed to start the reaction (break reactant bonds) is called the Activation Energy (Ea) ...
... • Bonds between atoms of the reactants (N2 and O2) are broken, and new bonds (NO) form. • Energy needed to start the reaction (break reactant bonds) is called the Activation Energy (Ea) ...
Cluster Coagulation and Growth Limited by Surface Interactions with
... y/x e 4 (according to the coordination chemistry of metal carbonyl complexes30), and m ) j + k in eq 1. In the main reaction, the clusters are formed from smaller reactions. The Co-PS* complexes formed during this process are the products of the secondary reaction described in eq 2, which competes w ...
... y/x e 4 (according to the coordination chemistry of metal carbonyl complexes30), and m ) j + k in eq 1. In the main reaction, the clusters are formed from smaller reactions. The Co-PS* complexes formed during this process are the products of the secondary reaction described in eq 2, which competes w ...
Chapter 6 PowerPoint
... Equations A and B have to be manipulated by reversal and/or multiplication by factors in order to sum to the first, or target, equation. ...
... Equations A and B have to be manipulated by reversal and/or multiplication by factors in order to sum to the first, or target, equation. ...
Ch1small - Rutgers University
... Physical properties: color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, hardness. Chemical properties: reactivity; change in chemical composition. Intensive properties: independent of amount of material present (melting point, density). Extensive properties: depend on amount of material present (ma ...
... Physical properties: color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, hardness. Chemical properties: reactivity; change in chemical composition. Intensive properties: independent of amount of material present (melting point, density). Extensive properties: depend on amount of material present (ma ...
Lecture Notes 1 - Rutgers University
... Physical properties: color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, hardness. Chemical properties: reactivity; change in chemical composition. Intensive properties: independent of amount of material present (melting point, density). Extensive properties: depend on amount of material present (ma ...
... Physical properties: color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, hardness. Chemical properties: reactivity; change in chemical composition. Intensive properties: independent of amount of material present (melting point, density). Extensive properties: depend on amount of material present (ma ...
Document
... If you drop a small ball into a bowl, the ball will bounce around and then come to rest in the center of the bowl. The ball has reached static equilibrium. Static equilibrium is a state in which nothing changes. Chemical equilibrium is different from static equilibrium because it is dynamic. In a dy ...
... If you drop a small ball into a bowl, the ball will bounce around and then come to rest in the center of the bowl. The ball has reached static equilibrium. Static equilibrium is a state in which nothing changes. Chemical equilibrium is different from static equilibrium because it is dynamic. In a dy ...
Chapter 7: Recent advances in enzyme technology
... of hydrolysis will not be affected as the reaction proceeds. By greatly reducing the water activity in these systems they can be used to transfer to other acceptors. Examples of this can be found in the transesterification reactions of esterases and lipases, described more fully later, and the (unde ...
... of hydrolysis will not be affected as the reaction proceeds. By greatly reducing the water activity in these systems they can be used to transfer to other acceptors. Examples of this can be found in the transesterification reactions of esterases and lipases, described more fully later, and the (unde ...
Chemical thermodynamics

Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the spontaneity of processes.The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the ""fundamental equations of Gibbs"" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics.