Thermodynamics - WordPress.com
... 1. The reaction of cyanamide, NH2CN(s) with oxygen was affected in a bomb calorimeter and ∆U was found to be -742.7 kJ mol-1 of cyanamide at 298K. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction at 298 K. NH2CN(s) + 3/2 O2 (g) → N2(g) + CO2(g) +H2O( l ) 2. Calculate the number of kJ necessary to rais ...
... 1. The reaction of cyanamide, NH2CN(s) with oxygen was affected in a bomb calorimeter and ∆U was found to be -742.7 kJ mol-1 of cyanamide at 298K. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction at 298 K. NH2CN(s) + 3/2 O2 (g) → N2(g) + CO2(g) +H2O( l ) 2. Calculate the number of kJ necessary to rais ...
CHAPTER I
... Copper, in Group IB, will also have one electron assigned to the 4s orbital, plus 28 other electrons assigned to other orbitals. The configuration of Be 1s2 2s2.All elements of Group 2A have electron configurations [electrons of preceding rare gas + ns2], where n is the period in which the element ...
... Copper, in Group IB, will also have one electron assigned to the 4s orbital, plus 28 other electrons assigned to other orbitals. The configuration of Be 1s2 2s2.All elements of Group 2A have electron configurations [electrons of preceding rare gas + ns2], where n is the period in which the element ...
Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... The amount of carbon dioxide emitted by fossil fuel combustion is related to the amount of fossil fuel that is burned—the balanced chemical equations for the combustion reactions give the exact relationships between these amounts. In this discussion, we use octane (a component of gasoline) as a repr ...
... The amount of carbon dioxide emitted by fossil fuel combustion is related to the amount of fossil fuel that is burned—the balanced chemical equations for the combustion reactions give the exact relationships between these amounts. In this discussion, we use octane (a component of gasoline) as a repr ...
Document
... Skipped these in 2011-2012 Questions – 1. Nitrogen gas is also present in the atmosphere and it reacted with the Mg to magnesium nitride. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2. When you added water to the crucible. The water reacts with the magnesium nitride (as heat is applied) t ...
... Skipped these in 2011-2012 Questions – 1. Nitrogen gas is also present in the atmosphere and it reacted with the Mg to magnesium nitride. Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. 2. When you added water to the crucible. The water reacts with the magnesium nitride (as heat is applied) t ...
Document
... Convert the mass of the Mg into moles. Convert the mass of the oxygen into moles. Are there more moles of Mg or oxygen? By how many times? Round to the nearest whole number. 7. What is the chemical formula for magnesium oxide? Explain how you know. ...
... Convert the mass of the Mg into moles. Convert the mass of the oxygen into moles. Are there more moles of Mg or oxygen? By how many times? Round to the nearest whole number. 7. What is the chemical formula for magnesium oxide? Explain how you know. ...
chem - CBSE Guess
... 2Fe+3/2O2 +xH2O----------> Fe2O3.xH2O(Hydrated ferric oxide rust) Rancidity: The oily and fatty food oxidizes and give bad smell and test is called rancidity.Preventatioin:By adding antioxidant which slow down the process of oxidation.2. Vaccum packing,3Flusing N2 gas in chips packets.3.Refrigeratio ...
... 2Fe+3/2O2 +xH2O----------> Fe2O3.xH2O(Hydrated ferric oxide rust) Rancidity: The oily and fatty food oxidizes and give bad smell and test is called rancidity.Preventatioin:By adding antioxidant which slow down the process of oxidation.2. Vaccum packing,3Flusing N2 gas in chips packets.3.Refrigeratio ...
Tittikpina et al., Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. (2016) 13(1):85
... redundancy when it comes to finding the (most) active plant material for a particular disease. Secondly, some plants, such as C. aralioides, S. longipedunculata, P. thonningii and N. laevis are also used against two or more diseases. Hence there is a similar redundancy when it comes to potential use ...
... redundancy when it comes to finding the (most) active plant material for a particular disease. Secondly, some plants, such as C. aralioides, S. longipedunculata, P. thonningii and N. laevis are also used against two or more diseases. Hence there is a similar redundancy when it comes to potential use ...
Document
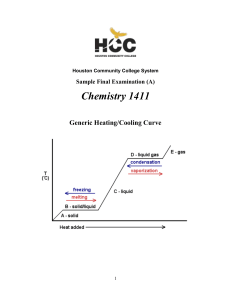
... An endothermic reaction is endothermic at all temperatures. You should think of heat as ________________for endothermic reactions and as ________________ for exothermic reactions. B. Le Châtelier's principle - add heat to an equilibrium mixture, net reaction occurs in the direction that reli ...
... An endothermic reaction is endothermic at all temperatures. You should think of heat as ________________for endothermic reactions and as ________________ for exothermic reactions. B. Le Châtelier's principle - add heat to an equilibrium mixture, net reaction occurs in the direction that reli ...
C:\Documents and Settings\mrh70950\My Documents
... Silicon, which is isoelectronic with carbon, can be found immediately below carbon in the periodic table. Not surprisingly, silicon is very similar to carbon: it is tetravalent, and readily makes tetrahedral analogs of alkanes. Thus, tetramethylsilane, Si(CH3)4 (bp 27EC), like 2,2dimethylpropane C(C ...
... Silicon, which is isoelectronic with carbon, can be found immediately below carbon in the periodic table. Not surprisingly, silicon is very similar to carbon: it is tetravalent, and readily makes tetrahedral analogs of alkanes. Thus, tetramethylsilane, Si(CH3)4 (bp 27EC), like 2,2dimethylpropane C(C ...
1411FINALSAMPLEs and Key
... overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizatio ...
... overall geometry is tetrahedral and the molecular geometry is trigonal pyramidal. The hybridization of the sulfur atom in the first structure is therefore sp3. However, the sulfur is not simply sp3 hybridized in the second structure, which has an “expanded octet” around the sulfur atom. Hybridizatio ...
Laboratory 3
... In this equation, the (+) symbol indicates that nitrogen reacts with oxygen and the arrow indicates that nitric oxide is formed. The chemical formulas on the left side of the equation are collectively known as the reactants and those on the right side as the products. In this case we have one kind o ...
... In this equation, the (+) symbol indicates that nitrogen reacts with oxygen and the arrow indicates that nitric oxide is formed. The chemical formulas on the left side of the equation are collectively known as the reactants and those on the right side as the products. In this case we have one kind o ...
SrF 2(s)
... Lesson #R7: Review of Chemical Reactions A. For each of the following reactions, identify the reaction type and balance the reaction. ________________1. _____Al(s) + _____O2(g) ...
... Lesson #R7: Review of Chemical Reactions A. For each of the following reactions, identify the reaction type and balance the reaction. ________________1. _____Al(s) + _____O2(g) ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... A. It is oxidized as it gains electrons. B. It is oxidized as it loses electrons. C. It is reduced as it gains electrons D. It is reduced as it loses electrons 2. The cell potential. E°, for an oxidation-reduction reaction was found to equal +1.10V. What can be said about this reaction? A. at equili ...
... A. It is oxidized as it gains electrons. B. It is oxidized as it loses electrons. C. It is reduced as it gains electrons D. It is reduced as it loses electrons 2. The cell potential. E°, for an oxidation-reduction reaction was found to equal +1.10V. What can be said about this reaction? A. at equili ...
Organic Chemistry
... they rotate polarized light. Isomerisation is the process by which one molecule is transformed into another molecule which has exactly the same atoms, but the atoms are rearranged. In some molecules and under some conditions, isomerisation occurs spontaneously. Many isomers are equal or roughly equa ...
... they rotate polarized light. Isomerisation is the process by which one molecule is transformed into another molecule which has exactly the same atoms, but the atoms are rearranged. In some molecules and under some conditions, isomerisation occurs spontaneously. Many isomers are equal or roughly equa ...
Stoichiometry - HCC Learning Web
... Since the moles of FeCl3 based on moles of Cl2 is the smaller answer, Cl2 is the limiting reactant. Iron metal is therefore in excess amount, so there will be some Fe left over unreacted. Note that we might have reasonably assumed that iron metal was the limiting reactant since it was present in les ...
... Since the moles of FeCl3 based on moles of Cl2 is the smaller answer, Cl2 is the limiting reactant. Iron metal is therefore in excess amount, so there will be some Fe left over unreacted. Note that we might have reasonably assumed that iron metal was the limiting reactant since it was present in les ...
Chapter 2 - Chemistry
... - class of molecular substances that contain carbon combined with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen hydrocarbon - simplest organic compounds - those compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon - extensively used as sources of energy - starting materials for plastics functional ...
... - class of molecular substances that contain carbon combined with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen hydrocarbon - simplest organic compounds - those compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon - extensively used as sources of energy - starting materials for plastics functional ...
IChO 2012
... One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia-borane adduct. Pyrolysis of this compound leads to the generation of H2 gas and polyborazylene. H3N–BH3(s) 2.5 H2(g) + (polyborazylene, BNH) (If an efficient and low-cost method can be found to regenerate H 3N–BH3 from BNH, the s ...
... One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia-borane adduct. Pyrolysis of this compound leads to the generation of H2 gas and polyborazylene. H3N–BH3(s) 2.5 H2(g) + (polyborazylene, BNH) (If an efficient and low-cost method can be found to regenerate H 3N–BH3 from BNH, the s ...
AH 2015 incl MG
... A classic chemistry demonstration involves vanadium changing oxidation states. Some zinc metal is added to a flask containing an acidified solution of the dioxovanadium(V) ion, VO2+(aq). The flask is stoppered with some cotton wool and gently swirled. The colour of the solution turns from yellow to ...
... A classic chemistry demonstration involves vanadium changing oxidation states. Some zinc metal is added to a flask containing an acidified solution of the dioxovanadium(V) ion, VO2+(aq). The flask is stoppered with some cotton wool and gently swirled. The colour of the solution turns from yellow to ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Review
... The density of liquid ethanol (C2H5OH) is 0.790 g/mL. Calculate the number of molecules in a 35.0 mL sample of liquid ethanol. (NOTE: You CAN’T use 22.4 L/mol since this is NOT a gas at STP!) ...
... The density of liquid ethanol (C2H5OH) is 0.790 g/mL. Calculate the number of molecules in a 35.0 mL sample of liquid ethanol. (NOTE: You CAN’T use 22.4 L/mol since this is NOT a gas at STP!) ...
2011-2012 ACAD REVIEW SHEET Chapter 16
... are not included in the equilibrium expression. (ANS: Keq = [K]) Write the equilibrium expression for 2 NO(g) + 2 H 2(g) N2(g) + 2 H2O(l). (ANS: Keq = [N2]/([NO]2[H2]2)) At 340C, Keq = 0.064 for the reaction Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g) 2Fe(s) + 3H2O(g). Given the [H2] = 0.45 M and [H2O] = 0.37 M, find Q ...
... are not included in the equilibrium expression. (ANS: Keq = [K]) Write the equilibrium expression for 2 NO(g) + 2 H 2(g) N2(g) + 2 H2O(l). (ANS: Keq = [N2]/([NO]2[H2]2)) At 340C, Keq = 0.064 for the reaction Fe2O3(s) + 3H2(g) 2Fe(s) + 3H2O(g). Given the [H2] = 0.45 M and [H2O] = 0.37 M, find Q ...
Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. • Count the total number of each type of atom on the reactant (ingredient) side. • Count the total number of each type of atom in the product (what you make) side • If the number of each type of atom matches, the equation is ...
... 3. Balancing Equations: Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. • Count the total number of each type of atom on the reactant (ingredient) side. • Count the total number of each type of atom in the product (what you make) side • If the number of each type of atom matches, the equation is ...
SODIUM HYDROGEN CARBONATE
... The CO2 can be recycled to produce more NaHCO3 by the Solvay process. In recent years, only about 15% of Na2CO3 was produced by the Solvay process. The remainder was mined from large deposits of trona, Na2CO3∙NaHCO3∙H2O, which were discovered in 1938 near the Green River in Wyoming. It is cheaper to ...
... The CO2 can be recycled to produce more NaHCO3 by the Solvay process. In recent years, only about 15% of Na2CO3 was produced by the Solvay process. The remainder was mined from large deposits of trona, Na2CO3∙NaHCO3∙H2O, which were discovered in 1938 near the Green River in Wyoming. It is cheaper to ...
Topic 20 Organic Chemistry
... Identify the feature which both molecules possess that accounts for this property. When 2-hydroxypropanoic acid is formed from 2-chloropropanoic acid, the product shows no optical activity. Deduce the type of nucleophilic substitution that takes place and explain your answer. ...
... Identify the feature which both molecules possess that accounts for this property. When 2-hydroxypropanoic acid is formed from 2-chloropropanoic acid, the product shows no optical activity. Deduce the type of nucleophilic substitution that takes place and explain your answer. ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... 57 Describe, in terms of valence electrons, how the chemical bonds form in the substance represented in diagram 1. [1] 58 Determine the total number of electrons in the bonds between the nitrogen atom and the three hydrogen atoms represented in diagram 2. [1] 59 Explain, in terms of distribution of ...
... 57 Describe, in terms of valence electrons, how the chemical bonds form in the substance represented in diagram 1. [1] 58 Determine the total number of electrons in the bonds between the nitrogen atom and the three hydrogen atoms represented in diagram 2. [1] 59 Explain, in terms of distribution of ...
Ground state reactants Ground state products Ground state
... Paradigm for electronic energy transfer from a triplet sensitizer to molecular oxygen • It cannot occur if the sensitizer energy is significantly below 22 kcal/mol. • It can only populate the 1∆g level of molecular oxygen if the sensitizer energy is between 22 and 37 kcal/mol, since population of t ...
... Paradigm for electronic energy transfer from a triplet sensitizer to molecular oxygen • It cannot occur if the sensitizer energy is significantly below 22 kcal/mol. • It can only populate the 1∆g level of molecular oxygen if the sensitizer energy is between 22 and 37 kcal/mol, since population of t ...
Redox

Redox reactions include all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed; in general, redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between species. The term ""redox"" comes from two concepts involved with electron transfer: reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms: Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion. Reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in oxidation state by a molecule, atom, or ion.Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides from oxygen molecules, these are only specific examples of a more general concept of reactions involving electron transfer.Redox reactions, or oxidation-reduction reactions, have a number of similarities to acid–base reactions. Like acid–base reactions, redox reactions are a matched set, that is, there cannot be an oxidation reaction without a reduction reaction happening simultaneously. The oxidation alone and the reduction alone are each called a half-reaction, because two half-reactions always occur together to form a whole reaction. When writing half-reactions, the gained or lost electrons are typically included explicitly in order that the half-reaction be balanced with respect to electric charge.Though sufficient for many purposes, these descriptions are not precisely correct. Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation state — the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. The oxidation state of an atom is the fictitious charge that an atom would have if all bonds between atoms of different elements were 100% ionic. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation state, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation state. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation state, but there are many reactions that are classed as ""redox"" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).There are simple redox processes, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide (CO2) or the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), and more complex processes such as the oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in the human body through a series of complex electron transfer processes.