Disadvantages of futures
... All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & So ...
... All rights reserved. Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted in section 117 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without express permission of the copyright owner is unlawful. Request for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & So ...
solutions
... waiting to exercise, but there is a “volatility benefit” from waiting. To show this more rigorously, consider the following portfolio: lend $X and short one share of stock. The cost to establish the portfolio is (X – S 0). The payoff at time T (with zero interest earnings on the loan) is (X – S T). ...
... waiting to exercise, but there is a “volatility benefit” from waiting. To show this more rigorously, consider the following portfolio: lend $X and short one share of stock. The cost to establish the portfolio is (X – S 0). The payoff at time T (with zero interest earnings on the loan) is (X – S T). ...
Problem Set 5
... 2. Jared values an hour fishing at $100. His opportunity cost of fishing for an hour is $40. Jared's consumer surplus from one hour fishing is (A) $100. (B) $60. (C) $40. (Answer: (B)) (D) Impossible to determine, since Jared didn't actually purchase the hour of fishing time. 3. At any quantity, the ...
... 2. Jared values an hour fishing at $100. His opportunity cost of fishing for an hour is $40. Jared's consumer surplus from one hour fishing is (A) $100. (B) $60. (C) $40. (Answer: (B)) (D) Impossible to determine, since Jared didn't actually purchase the hour of fishing time. 3. At any quantity, the ...
notes - University of Essex
... 1. Option payoff (gross of premium): $4000 = 1000 × (94 − 90) 2. One futures contract is received from option writer – In frictionless market: futures contract could be sold without loss – In a frictionless market: payoff from selling option ≥ exercise Why? For American call options, C ≥ f − X, wher ...
... 1. Option payoff (gross of premium): $4000 = 1000 × (94 − 90) 2. One futures contract is received from option writer – In frictionless market: futures contract could be sold without loss – In a frictionless market: payoff from selling option ≥ exercise Why? For American call options, C ≥ f − X, wher ...
Recovering Risk-Neutral Densities from Exchange Rate Options: Evidence in Turkey
... prices. Options contracts give the right to buy or sell an asset in the future at a price (strike) set now. Options have a value since there is a chance that the options can be exercised, that is, the underlying asset price will be more/less than a particular strike price. Hence, when we look at opt ...
... prices. Options contracts give the right to buy or sell an asset in the future at a price (strike) set now. Options have a value since there is a chance that the options can be exercised, that is, the underlying asset price will be more/less than a particular strike price. Hence, when we look at opt ...
A EXTENDED WITH ROBUST OPTION REPLICATION FOR BLACK-
... effects and B h is fBm with Hurst index h E It is known that B h for h E 1[ is a process of unbounded variation and square variation zero. See [8, 10]. From this it follows that B h is not a semi-martingale and the use of fractional Brownian motion B h or a more general process Z with zero quadratic ...
... effects and B h is fBm with Hurst index h E It is known that B h for h E 1[ is a process of unbounded variation and square variation zero. See [8, 10]. From this it follows that B h is not a semi-martingale and the use of fractional Brownian motion B h or a more general process Z with zero quadratic ...
option
... Period over which a contract trades Derivatives contracts have one, two and three months expiry cycles Contracts expire on last Thursday New contracts are fired on Friday ...
... Period over which a contract trades Derivatives contracts have one, two and three months expiry cycles Contracts expire on last Thursday New contracts are fired on Friday ...
FIN 377L – Portfolio Analysis and Management
... However, her revised view is that they also will not increase in value much, if at all. ...
... However, her revised view is that they also will not increase in value much, if at all. ...
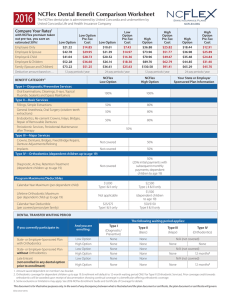
NCFlex Dental Benefit Comparison Worksheet
... 2. Orthodontic coverage for dependent children up to age 19. Enrollment will default to 12-month waiting period ONLY for Type IV (Orthodontic Services). Prior coverage credit towards orthodontics will be awarded upon receipt of documentation showing continual coverage in a benefit plan offering ort ...
... 2. Orthodontic coverage for dependent children up to age 19. Enrollment will default to 12-month waiting period ONLY for Type IV (Orthodontic Services). Prior coverage credit towards orthodontics will be awarded upon receipt of documentation showing continual coverage in a benefit plan offering ort ...
Notes
... premium of $.02, and a 180-day expiration date. Patton Co. has developed the following probability distribution for the spot rate in 180 days: Possible Spot Rate in 180 Days ...
... premium of $.02, and a 180-day expiration date. Patton Co. has developed the following probability distribution for the spot rate in 180 days: Possible Spot Rate in 180 Days ...
Chapter 5
... Put options gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a given quantity of some asset at some time in the future, at prices agreed upon today. ...
... Put options gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell a given quantity of some asset at some time in the future, at prices agreed upon today. ...
Question 1
... not directly reflect any market expectations on the development of the currency rate. Only if there is no risk premium on currency risk, the forward rate equals the expected currency rate (see section 3.15 of Hull) Question 2. [15 points] Give an intuitive explanation of why early exercise of an Ame ...
... not directly reflect any market expectations on the development of the currency rate. Only if there is no risk premium on currency risk, the forward rate equals the expected currency rate (see section 3.15 of Hull) Question 2. [15 points] Give an intuitive explanation of why early exercise of an Ame ...
C14_Reilly1ce
... • CBOE, AMEX, PHLX, PSE • Typical contract for 100 shares • Require secondary transaction if exercised • Time premium affects pricing • Stock Index Options • First traded on the CBOE in 1983 • Index options can only be settled in cash • Index puts are particularly useful in portfolio insurance appli ...
... • CBOE, AMEX, PHLX, PSE • Typical contract for 100 shares • Require secondary transaction if exercised • Time premium affects pricing • Stock Index Options • First traded on the CBOE in 1983 • Index options can only be settled in cash • Index puts are particularly useful in portfolio insurance appli ...
Introduction To Options - Michigan State University
... a put option can convert an option position into a short futures position, established at the strike price, by exercising the put option. Similarly, the buyer of a call option can convert an option position into a long futures position, established at the strike price, by exercising the call option. ...
... a put option can convert an option position into a short futures position, established at the strike price, by exercising the put option. Similarly, the buyer of a call option can convert an option position into a long futures position, established at the strike price, by exercising the call option. ...
Black-Scholes Formula
... The expected return μ of the asset, a parameter in the underlying asset model , does not appear in the Black-Scholes equation . Instead, the risk-free interest rate r appears it. As we have seen in the discrete model, by the Δ---hedging technique, the Black-Scholes equation puts the investors in a r ...
... The expected return μ of the asset, a parameter in the underlying asset model , does not appear in the Black-Scholes equation . Instead, the risk-free interest rate r appears it. As we have seen in the discrete model, by the Δ---hedging technique, the Black-Scholes equation puts the investors in a r ...
Derivatives Market in inDia: a success story
... delivery. Second, futures contracts are standardised, while forwards are customised to meet the special needs of the two parties involved (counterparties). Third, unlike futures contracts, which are settled through an established clearing house, forwards are settled between the counterparties. Fourt ...
... delivery. Second, futures contracts are standardised, while forwards are customised to meet the special needs of the two parties involved (counterparties). Third, unlike futures contracts, which are settled through an established clearing house, forwards are settled between the counterparties. Fourt ...
Why We Have Never Used the Black-Scholes
... The formal financial economics canon does not include historical sources from outside economics, a mechanism discussed in Taleb (2007a). The put-call parity was according to the formal option literature first fully described by Stoll (1969), but neither he not others in the field even mention Nelson ...
... The formal financial economics canon does not include historical sources from outside economics, a mechanism discussed in Taleb (2007a). The put-call parity was according to the formal option literature first fully described by Stoll (1969), but neither he not others in the field even mention Nelson ...