APUSH TKarnes Summary: Chapter 3,The British Empire in America
... The Northern Maritime Economy Because sugar production brought such high returns, planters in the West Indies preferred to buy their produce, livestock, and supplies from others than to produce them at home. This provided a ready market for grain, livestock, and supplies produced by farmers or craft ...
... The Northern Maritime Economy Because sugar production brought such high returns, planters in the West Indies preferred to buy their produce, livestock, and supplies from others than to produce them at home. This provided a ready market for grain, livestock, and supplies produced by farmers or craft ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... a) House of Commons: elected representatives b) House of Lords: non-elected nobles, judges, and clergy 2. Colonies formed their own elected assemblies, or smaller versions of the House of Commons 3. House of Burgesses in Virginia (1st colonial assembly) English Rights Threatened A. Kings Limit Self- ...
... a) House of Commons: elected representatives b) House of Lords: non-elected nobles, judges, and clergy 2. Colonies formed their own elected assemblies, or smaller versions of the House of Commons 3. House of Burgesses in Virginia (1st colonial assembly) English Rights Threatened A. Kings Limit Self- ...
Chapter 3
... • Religious and political turmoil in England shaped settlement in New England and the middle colonies • The Protestant Reformation provided the major impetus and leadership for the settlement of New England. The New England colonies developed a fairly homogeneous social order based on religion and s ...
... • Religious and political turmoil in England shaped settlement in New England and the middle colonies • The Protestant Reformation provided the major impetus and leadership for the settlement of New England. The New England colonies developed a fairly homogeneous social order based on religion and s ...
Colonial Regions Notes Mid-Atlantic (Middle) Colonies Southern
... Religion – Most people in the Southern Colonies were Anglican (Baptist or Presbyterian), though most of the original settlers from the Maryland colony were Catholic, as Lord Baltimore founded it as a refuge for English Catholics. Religion did not have the same impact on communities as in the New Eng ...
... Religion – Most people in the Southern Colonies were Anglican (Baptist or Presbyterian), though most of the original settlers from the Maryland colony were Catholic, as Lord Baltimore founded it as a refuge for English Catholics. Religion did not have the same impact on communities as in the New Eng ...
Unit 1: Beginnings to 1861
... a. Thomas Hooker – Connecticut b. Roger Williams – Rhode Island – religious tolerance to all settlers D. War With the Indians a. King Philip’s War (Metacom) – attempt to drive out the English VI. ...
... a. Thomas Hooker – Connecticut b. Roger Williams – Rhode Island – religious tolerance to all settlers D. War With the Indians a. King Philip’s War (Metacom) – attempt to drive out the English VI. ...
General Characteristics of Southern Colonies
... – Needed fresh land to replace depleted soil due to tobacco farming ...
... – Needed fresh land to replace depleted soil due to tobacco farming ...
From Comfort to Discontent
... political freedom attract settlers to America. – Southern colonies = financial profit. – New England colonies = religious freedoms – Middle Colonies= some religious, some financial – Idealism (the perfect society!!) Examples: ...
... political freedom attract settlers to America. – Southern colonies = financial profit. – New England colonies = religious freedoms – Middle Colonies= some religious, some financial – Idealism (the perfect society!!) Examples: ...
Colonization of the Americas
... people in a distant region that is governed by their home country). ...
... people in a distant region that is governed by their home country). ...
Colonization of the Americas
... people in a distant region that is governed by their home country). ...
... people in a distant region that is governed by their home country). ...
Colonization of the Americas
... people in a distant region that is governed by their home country). ...
... people in a distant region that is governed by their home country). ...
Unit 1 power point
... 1774, to punish Massachusetts colonist for the Boston Tea party. • These laws took away colonists right to trial by ...
... 1774, to punish Massachusetts colonist for the Boston Tea party. • These laws took away colonists right to trial by ...
Ch1 summary - Mr Clotzman
... indentured servants. These people agreed to work for a few years on land owned by the tobacco farmers. In return, the farmers paid for their trip from Europe to Virginia. Other settlers were members of a Protestant group that hoped to make the English church more pure. For this reason they were call ...
... indentured servants. These people agreed to work for a few years on land owned by the tobacco farmers. In return, the farmers paid for their trip from Europe to Virginia. Other settlers were members of a Protestant group that hoped to make the English church more pure. For this reason they were call ...
8-1.3 England`s 13 Colonies PPT Notes English and European
... The New England colonies were founded as a ____________ (safe place) for religious groups persecuted (mistreated) in England. The Separatists, also known as the ________________, sailed across the Atlantic Ocean and landed at Plymouth, Massachusetts. The pilgrims signed the Mayflower _______________ ...
... The New England colonies were founded as a ____________ (safe place) for religious groups persecuted (mistreated) in England. The Separatists, also known as the ________________, sailed across the Atlantic Ocean and landed at Plymouth, Massachusetts. The pilgrims signed the Mayflower _______________ ...
Murrin-CH02 - Arbortown Properties
... • William Penn, gentleman and a Quaker • Granted a charter for a proprietary colony: Pennsylvania • Led a group of Quaker colonists to America • Pennsylvania: – economic success – Policy of of religious freedom ...
... • William Penn, gentleman and a Quaker • Granted a charter for a proprietary colony: Pennsylvania • Led a group of Quaker colonists to America • Pennsylvania: – economic success – Policy of of religious freedom ...
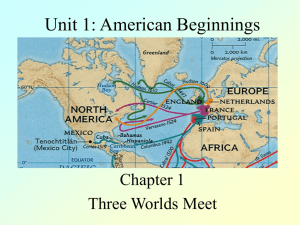
Unit 1: American Beginnings
... 4. Delaware—originally owned by Penn…manufactued oil form whales 5. North Carolina 6. South Carolina ...
... 4. Delaware—originally owned by Penn…manufactued oil form whales 5. North Carolina 6. South Carolina ...
Maryland*s Acts of Toleration
... What was the trend for Native Americans when it came to land conflict with the English Colonists? Native Americans lost land because • They were ravaged by disease • Did not have modern weapons • They were eventually outnumbered on the East Coast ...
... What was the trend for Native Americans when it came to land conflict with the English Colonists? Native Americans lost land because • They were ravaged by disease • Did not have modern weapons • They were eventually outnumbered on the East Coast ...
A. The Jamestown colony
... e. Time of Reckoning: diseases, Powhattan attacks, indentured servants, & few women f. ...
... e. Time of Reckoning: diseases, Powhattan attacks, indentured servants, & few women f. ...
Unit I terms and questions and charts
... economic problems, for merchants North America could provide excellent markets for wool and clothes through trade with naked Indians while supplying economic resources for timber, furs. Overpopulated England and excess workers could be transformed to America to become productive within the colonies. ...
... economic problems, for merchants North America could provide excellent markets for wool and clothes through trade with naked Indians while supplying economic resources for timber, furs. Overpopulated England and excess workers could be transformed to America to become productive within the colonies. ...
Unit 1 Review Sheet
... Did Christopher Columbus the famous explorer discover America? Not really. Many other explorers came before him, but Columbus landing in the Caribbean in 1492 was very important because his travel led to the colonization of the New World (North, Central, and South America) by European countries. Col ...
... Did Christopher Columbus the famous explorer discover America? Not really. Many other explorers came before him, but Columbus landing in the Caribbean in 1492 was very important because his travel led to the colonization of the New World (North, Central, and South America) by European countries. Col ...
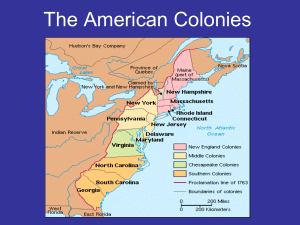
The American Colonies
... this worke wee have undertaken and soe cause him to withdrawe his present help from us” City Upon A Hill, 1630 ...
... this worke wee have undertaken and soe cause him to withdrawe his present help from us” City Upon A Hill, 1630 ...
PP British North America, Seven Years War, Pontiac`s War
... that Britain imposed and France accepted • American Indians fought for their independence against the British and compelled them to think seriously about the place of Native peoples in the British Empire • The Royal Proclamation - established the Appalachian as the boundary line between Indian and c ...
... that Britain imposed and France accepted • American Indians fought for their independence against the British and compelled them to think seriously about the place of Native peoples in the British Empire • The Royal Proclamation - established the Appalachian as the boundary line between Indian and c ...
Chapter 5: Europeans Settle throughout North America Lesson One
... Hooker believed a government should be based on the will of its people. Fundamental Orders were adopted; this was the first written system of government in North America. ...
... Hooker believed a government should be based on the will of its people. Fundamental Orders were adopted; this was the first written system of government in North America. ...
All of the Colonies
... Not originally British Colonies: New Netherlands: the region was originally controlled by the Dutch and other non-British groups like the Swedes and Germans. New Netherlands founded in the Hudson River area (NY) between 1623-1624. Netherlands was interested for the fur trade with Native American ...
... Not originally British Colonies: New Netherlands: the region was originally controlled by the Dutch and other non-British groups like the Swedes and Germans. New Netherlands founded in the Hudson River area (NY) between 1623-1624. Netherlands was interested for the fur trade with Native American ...
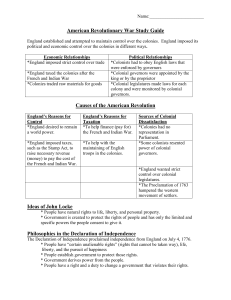
Revolution Study Guide
... Boston Tea Party: Samuel Adams and Paul Revere led patriots in throwing tea into Boston Harbor to protest tea taxes. First Continental Congress: Delegates from all colonies except Georgia met to discuss problems with England and to promote independence. Battle of Lexington and Concord: This was the ...
... Boston Tea Party: Samuel Adams and Paul Revere led patriots in throwing tea into Boston Harbor to protest tea taxes. First Continental Congress: Delegates from all colonies except Georgia met to discuss problems with England and to promote independence. Battle of Lexington and Concord: This was the ...
New World Beginnings
... Jamestown in 1610 with supplies and military. Strained relations with the Native Americans resulted in the First Anglo-Powhatan War. The Indians were again defeated in the Second Anglo-Powhatan War in 1644. By 1685, the English considered the Powhatan people to be extinct. ...
... Jamestown in 1610 with supplies and military. Strained relations with the Native Americans resulted in the First Anglo-Powhatan War. The Indians were again defeated in the Second Anglo-Powhatan War in 1644. By 1685, the English considered the Powhatan people to be extinct. ...