MS Word version
... Sidereal Time is used to describe the rotation of Earth and is needed to accurately point telescopes and keep track of the positions of objects in the sky. A sidereal day is the time needed for one complete rotation of Earth and is approximately 23 hours and 56 minutes long. If Earth were rotating i ...
... Sidereal Time is used to describe the rotation of Earth and is needed to accurately point telescopes and keep track of the positions of objects in the sky. A sidereal day is the time needed for one complete rotation of Earth and is approximately 23 hours and 56 minutes long. If Earth were rotating i ...
Tutorial: Luminosity
... Luminosity (brightness) of a Star However, the “brightness” of a star decreases as one moves farther and farther away. If a sphere of radius d is drawn around the star, it should be clear that the energy/sec through the surface of this sphere is the same as the energy/sec emitted through the surfac ...
... Luminosity (brightness) of a Star However, the “brightness” of a star decreases as one moves farther and farther away. If a sphere of radius d is drawn around the star, it should be clear that the energy/sec through the surface of this sphere is the same as the energy/sec emitted through the surfac ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... form a fascinating and complex part of the ongoing process of stellar evolution, energizing and enriching the interstellar ...
... form a fascinating and complex part of the ongoing process of stellar evolution, energizing and enriching the interstellar ...
norfolk skies - Norfolk Astronomical Society
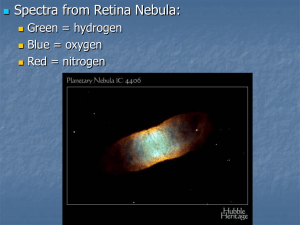
... “emitting” their own light generally look considerably brighter in the telescope when using specific line, or nebula, filters. NGC 2327 does not brighten; therefore I suspect it might be a reflection, rather than emission nebula. When you find it look at the faint star just a bit eastward, in the sa ...
... “emitting” their own light generally look considerably brighter in the telescope when using specific line, or nebula, filters. NGC 2327 does not brighten; therefore I suspect it might be a reflection, rather than emission nebula. When you find it look at the faint star just a bit eastward, in the sa ...
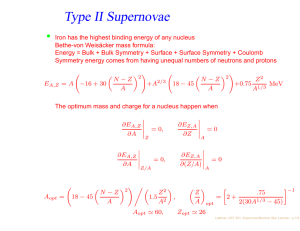
Type II Supernovae
... The inner core plus additional matter falling onto it creates a new neutron star, called a protoneutron star. A protoneutron star differs from a neutron star in having many more protons and electrons as well as being much hotter. ...
... The inner core plus additional matter falling onto it creates a new neutron star, called a protoneutron star. A protoneutron star differs from a neutron star in having many more protons and electrons as well as being much hotter. ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Universal Time (UT) – A time system used by astronomers. Also known as Greenwich Mean Time. USA Eastern Standard Time (for example, New York) is 5 hours behind UT. Variable Star – A star that changes brightness over a period of time. ...
... Universal Time (UT) – A time system used by astronomers. Also known as Greenwich Mean Time. USA Eastern Standard Time (for example, New York) is 5 hours behind UT. Variable Star – A star that changes brightness over a period of time. ...
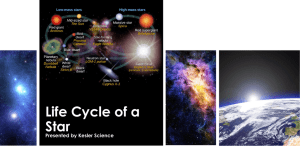
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... • Gravity is 2 billion times that of the gravity on Earth. • Gravity presses the material in on itself so tightly that protons and electrons combine to make neutrons, yielding the name "neutron star”. ...
... • Gravity is 2 billion times that of the gravity on Earth. • Gravity presses the material in on itself so tightly that protons and electrons combine to make neutrons, yielding the name "neutron star”. ...
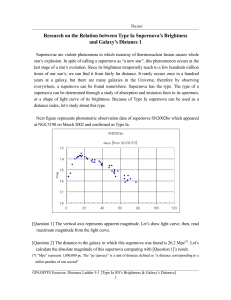
Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
... last stage of a star’s evolution. Since its brightness temporarily reach to a few hundreds million times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supe ...
5. cosmic distance ladder ii: standard candles
... An object of known luminosity is called a standard candle. Most stars are not standard candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequen ...
... An object of known luminosity is called a standard candle. Most stars are not standard candles – their luminosities are not known and consequently their distances cannot be easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequen ...
The Argonauts, background to the constellation Carina Argo Navis
... Keyhole Nebula, imaged by Hubble Space meteor shower, which peaks around January 21 each year. Telescope. The small nebula to the upper left has Eta Carinae's effects on the nebula can be seen directly: been nicknamed "finger of God" or "God's birdie", The dark globules in the image and some other l ...
... Keyhole Nebula, imaged by Hubble Space meteor shower, which peaks around January 21 each year. Telescope. The small nebula to the upper left has Eta Carinae's effects on the nebula can be seen directly: been nicknamed "finger of God" or "God's birdie", The dark globules in the image and some other l ...
Solutions to Homework #4, AST 203, Spring 2012
... Further calculations correctly done based on this erroneous value should be given full credit. However, if the resulting answer is completely ludicrous (e.g., 10−30 seconds for the time to travel to the nearest star, 50 stars in the visible universe), and no mention is made that the value seems wron ...
... Further calculations correctly done based on this erroneous value should be given full credit. However, if the resulting answer is completely ludicrous (e.g., 10−30 seconds for the time to travel to the nearest star, 50 stars in the visible universe), and no mention is made that the value seems wron ...
Explosion and remnants of massive stars
... In single stars of intermediate mass, the degenerate CO core cannot grow to the Chandrasekhar limit because mass loss quickly removes the envelope during the AGB phase (Ch. 10). Even if the Chandrasekhar limit were reached, the remaining H-rich envelope would cause a strong hydrogen signature in the ...
... In single stars of intermediate mass, the degenerate CO core cannot grow to the Chandrasekhar limit because mass loss quickly removes the envelope during the AGB phase (Ch. 10). Even if the Chandrasekhar limit were reached, the remaining H-rich envelope would cause a strong hydrogen signature in the ...
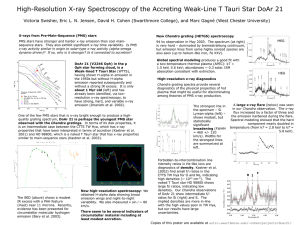
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... Oph star forming cloud, is a Weak-lined T Tauri Star (WTTS), having shown H-alpha in emission in the 1950s but without H-alpha emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to ha ...
... Oph star forming cloud, is a Weak-lined T Tauri Star (WTTS), having shown H-alpha in emission in the 1950s but without H-alpha emission reported subsequently and without a strong IR excess. It is only about 1 Myr old (left) and has already been identified, via lowresolution x-ray spectroscopy, to ha ...
SN 1054

SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 4 July 1054 A.D. (hence its name), and that lasted for a period of around two years. The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a document from the Arab world. Furthermore, there are a number of proposed, but doubtful, references from European sources recorded in the 15th century, and perhaps a pictograph associated with the Ancestral Puebloan culture found near the Peñasco Blanco site in New Mexico.The remnant of SN 1054, which consists of debris ejected during the explosion, is known as the Crab Nebula. It is located in the sky near the star Zeta Tauri (ζ Tauri). The core of the exploding star formed a pulsar, called the Crab Pulsar (or PSR B0531+21). The nebula and the pulsar it contains are the most studied astronomical objects outside the Solar System. It is one of the few Galactic supernovae where the date of the explosion is well known. The two objects are the most luminous in their respective categories. For these reasons, and because of the important role it has repeatedly played in the modern era, SN 1054 is the best known supernova in the history of astronomy.The Crab Nebula is easily observed by amateur astronomers thanks to its brightness, and was also catalogued early on by professional astronomers, long before its true nature was understood and identified. When the French astronomer Charles Messier watched for the return of Halley's Comet in 1758, he confused the nebula for the comet, as he was unaware of the former's existence. Due to this error, he created his catalogue of non-cometary nebulous objects, the Messier Catalogue, to avoid such mistakes in the future. The nebula is catalogued as the first Messier object, or M1.