Characteristics of Stars
... the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
... the lower right when plotted according to luminosity and surface temperature on the Hertzprung-Russell Diagram ...
Foundation 1 - Discovering Astronomy
... become 1 helium nucleus • Since the mass of 4 hydrogen nuclei is greater than the mass of 1 helium nucleus, the leftover mass (0.7%) is converted to energy by Einstein’s equation: E=mc2 ...
... become 1 helium nucleus • Since the mass of 4 hydrogen nuclei is greater than the mass of 1 helium nucleus, the leftover mass (0.7%) is converted to energy by Einstein’s equation: E=mc2 ...
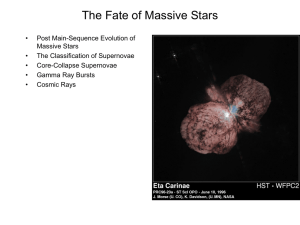
The Fate of Massive Stars
... Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM Massive Stars ability to quench star formation Massive stars rare (1 in 1,000,000) but important role in the evolution of galaxies ...
... Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM Massive Stars ability to quench star formation Massive stars rare (1 in 1,000,000) but important role in the evolution of galaxies ...
How the Universe Works Extreme Stars Name 1. When a star dies
... 4. Eventually, the helium in the core begins to fuse into (oxygen) (iron) (carbon). 5. After the sun blasts away its outer layers, all that remains is an intensely hot, core called a (planetary nebula) (white dwarf) (pulsar). 6. At the core of a white dwarf astronomers believe lies a core of (iron) ...
... 4. Eventually, the helium in the core begins to fuse into (oxygen) (iron) (carbon). 5. After the sun blasts away its outer layers, all that remains is an intensely hot, core called a (planetary nebula) (white dwarf) (pulsar). 6. At the core of a white dwarf astronomers believe lies a core of (iron) ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... • Hottest, most massive stars • Shortest lives: millions of years • Uses hydrogen quickly ...
... • Hottest, most massive stars • Shortest lives: millions of years • Uses hydrogen quickly ...
The Hubble Space Telescope
... and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
... and debris from the disk eventually nuclear fusion occurs and a STAR is BORN Heat and radiation create a stellar wind sweeping away lose matter, but some debris remains eventually clumping together to become ...
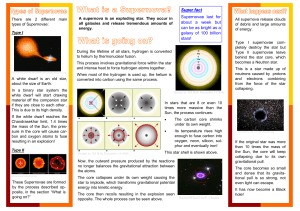
What is a supernova - University of Warwick
... energy into kinetic energy. The core then recoils resulting in the explosion seen opposite. The whole process can be seen above. ...
... energy into kinetic energy. The core then recoils resulting in the explosion seen opposite. The whole process can be seen above. ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
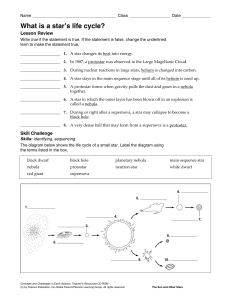
What is a star`s life cycle?
... Write true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined term to make the statement true. ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During ...
... Write true if the statement is true. If the statement is false, change the underlined term to make the statement true. ____________________ 1. A star changes its heat into energy. ____________________ 2. In 1987, a protostar was observed in the Large Magellanic Cloud. ____________________ 3. During ...
Chapter 5 Mid-term Study Guide
... ______11. constellation ______12. Polaris ______13. light-year ______14. Proxima Centauri ______15. nebula ______16. black hole ______17. magnitude ______18. supernova A brightness of a star B measure of distance C nearest star to sun D pattern of stars E largest type of star F cloud of dust and gas ...
... ______11. constellation ______12. Polaris ______13. light-year ______14. Proxima Centauri ______15. nebula ______16. black hole ______17. magnitude ______18. supernova A brightness of a star B measure of distance C nearest star to sun D pattern of stars E largest type of star F cloud of dust and gas ...
SN 1054

SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 4 July 1054 A.D. (hence its name), and that lasted for a period of around two years. The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a document from the Arab world. Furthermore, there are a number of proposed, but doubtful, references from European sources recorded in the 15th century, and perhaps a pictograph associated with the Ancestral Puebloan culture found near the Peñasco Blanco site in New Mexico.The remnant of SN 1054, which consists of debris ejected during the explosion, is known as the Crab Nebula. It is located in the sky near the star Zeta Tauri (ζ Tauri). The core of the exploding star formed a pulsar, called the Crab Pulsar (or PSR B0531+21). The nebula and the pulsar it contains are the most studied astronomical objects outside the Solar System. It is one of the few Galactic supernovae where the date of the explosion is well known. The two objects are the most luminous in their respective categories. For these reasons, and because of the important role it has repeatedly played in the modern era, SN 1054 is the best known supernova in the history of astronomy.The Crab Nebula is easily observed by amateur astronomers thanks to its brightness, and was also catalogued early on by professional astronomers, long before its true nature was understood and identified. When the French astronomer Charles Messier watched for the return of Halley's Comet in 1758, he confused the nebula for the comet, as he was unaware of the former's existence. Due to this error, he created his catalogue of non-cometary nebulous objects, the Messier Catalogue, to avoid such mistakes in the future. The nebula is catalogued as the first Messier object, or M1.