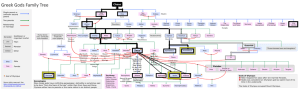
Greek Mythology
... moody and greedy Olympian gods. He was known to be vengeful when insulted. Poseidon was moody by nature: his temperament was unstable at best, and his emotional fluctuations often resulted in violence. He was similar to Zeus in that he liked to exert power over women and flaunt his rugged masculinit ...
... moody and greedy Olympian gods. He was known to be vengeful when insulted. Poseidon was moody by nature: his temperament was unstable at best, and his emotional fluctuations often resulted in violence. He was similar to Zeus in that he liked to exert power over women and flaunt his rugged masculinit ...
hades - HoffmanWorldLit
... Greek mythology. Hades was the son of Cronus and Rhea. Cronus and Rhea were the rulers of the world in the golden age. Cronus and Rhea produced many gods and goddesses on Mt. Olympia. Although these gods were brothers and sisters they did not all have the best relationships. For example; Hades was t ...
... Greek mythology. Hades was the son of Cronus and Rhea. Cronus and Rhea were the rulers of the world in the golden age. Cronus and Rhea produced many gods and goddesses on Mt. Olympia. Although these gods were brothers and sisters they did not all have the best relationships. For example; Hades was t ...
Answers Study Guide for Greek Mythology
... and Corn; Hestia: Goddess of Home and Family; Artemis: Goddess of Hunting and Wilderness; Persephone: Queen of Underworld and Goddess of Spring 2. Why was Mount Olympus important to the Greeks? That is where the gods lived. 3. Were the Greeks polytheistic or monotheistic? What does each mean? Th ...
... and Corn; Hestia: Goddess of Home and Family; Artemis: Goddess of Hunting and Wilderness; Persephone: Queen of Underworld and Goddess of Spring 2. Why was Mount Olympus important to the Greeks? That is where the gods lived. 3. Were the Greeks polytheistic or monotheistic? What does each mean? Th ...
Ch. 19 – We Find out the Truth, Sort Of, p.300-319
... The Asphodel Meadows is a section of the Ancient Greek underworld where ordinary souls were sent to live after death. The Asphodel Meadows is most probably where the souls of people who lived average lives remain, however its relationship to other places in the Greek afterlife remains uncertain. ...
... The Asphodel Meadows is a section of the Ancient Greek underworld where ordinary souls were sent to live after death. The Asphodel Meadows is most probably where the souls of people who lived average lives remain, however its relationship to other places in the Greek afterlife remains uncertain. ...
The Afterlife - People Server at UNCW
... on some poor landholder’s farm, a man who is landless and hungry himself, than here to be ruler of all these shriveled-up dead.” ...
... on some poor landholder’s farm, a man who is landless and hungry himself, than here to be ruler of all these shriveled-up dead.” ...
Greek Gods And Goddesses
... to the world. Demeter persuaded Hades to release Persephone but before she left, Demeter's daughter ate the food of the underworld which meant that she could not leave. Eventually she was forced to spend only part of the year in the underworld and that time is what we know as winter, the season of d ...
... to the world. Demeter persuaded Hades to release Persephone but before she left, Demeter's daughter ate the food of the underworld which meant that she could not leave. Eventually she was forced to spend only part of the year in the underworld and that time is what we know as winter, the season of d ...
Study Guide for Greek Mythology Test 2
... and Corn; Hestia: Goddess of Home and Family; Artemis: Goddess of Hunting and Wilderness; Persephone: Queen of Underworld and Goddess of Spring 2. Why was Mount Olympus important to the Greeks? That is where the gods lived. 3. Were the Greeks polytheistic or monotheistic? What does each mean? Th ...
... and Corn; Hestia: Goddess of Home and Family; Artemis: Goddess of Hunting and Wilderness; Persephone: Queen of Underworld and Goddess of Spring 2. Why was Mount Olympus important to the Greeks? That is where the gods lived. 3. Were the Greeks polytheistic or monotheistic? What does each mean? Th ...
Slide 1 - Teacherpage
... collecting flowers on the plain of Enna, the earth suddenly opened and Hades rose up from the gap and abducted her. None but Zeus, and the all-seeing sun, Helios, had noticed it. Broken-hearted, Demeter wandered the earth, looking for her daughter until Helios revealed what had happened. Demeter was ...
... collecting flowers on the plain of Enna, the earth suddenly opened and Hades rose up from the gap and abducted her. None but Zeus, and the all-seeing sun, Helios, had noticed it. Broken-hearted, Demeter wandered the earth, looking for her daughter until Helios revealed what had happened. Demeter was ...
Greek Gods and Goddesses
... and sisters so Gaea replaced the baby Zeus with a stone=Zeus lived • Zeus later poisoned Coronus and Coronus barfed up all of the other Olympians! • Given the lightening/thunder bolt by the Cyclopes as his special weapon ...
... and sisters so Gaea replaced the baby Zeus with a stone=Zeus lived • Zeus later poisoned Coronus and Coronus barfed up all of the other Olympians! • Given the lightening/thunder bolt by the Cyclopes as his special weapon ...
Greek Gods and Goddesses Song
... Ares and Athena, wars they always won. Artemis loved to hunt by the light of the moon Persephone came in springtime, flowers began to bloom. Aphrodite she was cute, Goddess of love and beauty. King of Gods that was Zeus, Married Hera, wife was her duty. Demeter, she loved the harvest, Dionysus loved ...
... Ares and Athena, wars they always won. Artemis loved to hunt by the light of the moon Persephone came in springtime, flowers began to bloom. Aphrodite she was cute, Goddess of love and beauty. King of Gods that was Zeus, Married Hera, wife was her duty. Demeter, she loved the harvest, Dionysus loved ...
The Olympian Gods
... Zeus’s wife and sister Known to be very Goddess of heaven, jealous: she’s always marriage, home Depicted in all stages of life spying and hunting down Zeus and his (girl, wife, mother, widow) ladies, often catching Stately, regal, beautiful, them! queenly (depicted on a ...
... Zeus’s wife and sister Known to be very Goddess of heaven, jealous: she’s always marriage, home Depicted in all stages of life spying and hunting down Zeus and his (girl, wife, mother, widow) ladies, often catching Stately, regal, beautiful, them! queenly (depicted on a ...
Greek Mythology PowerPoint Project
... Hades: Son of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. His wife was Persephone. He abducted her from her mother and took her with him down to the underworld. He was the god of the underworld; hell and hatred. He had a beard and dark hair falling over his brow. His helmet which was his sacred symbol helped him st ...
... Hades: Son of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. His wife was Persephone. He abducted her from her mother and took her with him down to the underworld. He was the god of the underworld; hell and hatred. He had a beard and dark hair falling over his brow. His helmet which was his sacred symbol helped him st ...
Apollo and Daphne
... Demeter was the goddess of agriculture. She had a very lovely daughter, Persephone, who was in charge of flowers for her mother and was as beautiful as a flower. One day, when Persephone was out in the field, she was spotted by Hades, god of the Underworld. Hades immediately fell in love with Persep ...
... Demeter was the goddess of agriculture. She had a very lovely daughter, Persephone, who was in charge of flowers for her mother and was as beautiful as a flower. One day, when Persephone was out in the field, she was spotted by Hades, god of the Underworld. Hades immediately fell in love with Persep ...
Jennifer Thomas Sheena Sarfine Ms. Burke Junior Communication
... Junior Communication Arts 29 January 2009 Persephone Throughout Greek mythology there are many different gods and goddesses. The one we found most interesting is Persephone. Just about all of the gods and goddesses have Roman names as well. Persephone’s Roman name was Preserpina. Persephone was one ...
... Junior Communication Arts 29 January 2009 Persephone Throughout Greek mythology there are many different gods and goddesses. The one we found most interesting is Persephone. Just about all of the gods and goddesses have Roman names as well. Persephone’s Roman name was Preserpina. Persephone was one ...
greek mythology - Brett Jennings|Ed Tech
... A closer look at two myths—a Nature myth and a Trickster myth—shows how the ancient Greeks explained the natural world and the role their gods and goddesses played in their daily lives. Nature Myth: Persephone. Persephone was the daughter of Demeter, the sister of Zeus and goddess of the harvest. On ...
... A closer look at two myths—a Nature myth and a Trickster myth—shows how the ancient Greeks explained the natural world and the role their gods and goddesses played in their daily lives. Nature Myth: Persephone. Persephone was the daughter of Demeter, the sister of Zeus and goddess of the harvest. On ...
Zeus is the father of Persephone. Demeter is the mother of
... duties as goddess of the harvest and this caused a famine on the Earth. To make Demeter happy again, Zeus set Hermes to get Persephone out of the Underworld. Hades, though, tricked Persephone into eating some pomegranate seeds. Once she did her fate was sealed and Persephone was bound to return to t ...
... duties as goddess of the harvest and this caused a famine on the Earth. To make Demeter happy again, Zeus set Hermes to get Persephone out of the Underworld. Hades, though, tricked Persephone into eating some pomegranate seeds. Once she did her fate was sealed and Persephone was bound to return to t ...
Zeus, Demeter, Persephone
... Rich haired, golden tresses, slender feet, wears light cloak, holds torch. ...
... Rich haired, golden tresses, slender feet, wears light cloak, holds torch. ...
INTRODUCTION TO GREEK MYTHOLOGY
... Two Main Divisions of the Underworld: Erebus: where the dead ...
... Two Main Divisions of the Underworld: Erebus: where the dead ...
INTRODUCTION TO GREEK MYTHOLOGY
... Two Main Divisions of the Underworld: Erebus: where the dead ...
... Two Main Divisions of the Underworld: Erebus: where the dead ...
Greek underworld

The Greek underworld, in mythology, was an otherworld where souls went after death and was the Greek idea of afterlife. At the moment of death the soul was separated from the corpse, taking on the shape of the former person, and was transported to the entrance of Hades. Hades itself was described as being either at the outer bounds of the ocean or beneath the depths or ends of the earth. It was considered the dark counterpart to the brightness of Mount Olympus, and was the kingdom of the dead that corresponded to the kingdom of the gods. Hades was a realm invisible to the living and it was made solely for the dead.