The Central Nervous System
... • Involve temporary modifications in the function of preexisting synapses • Two types – Habituation • Decreased responsiveness to a repetitive indifferent stimulus • Ca2+ channels do not readily open ...
... • Involve temporary modifications in the function of preexisting synapses • Two types – Habituation • Decreased responsiveness to a repetitive indifferent stimulus • Ca2+ channels do not readily open ...
Nervous System - Emery
... Cells of the Nervous System Two major cell types: 1. neurons conduct electrical signals ...
... Cells of the Nervous System Two major cell types: 1. neurons conduct electrical signals ...
Week 2
... Formed in part by endothelial cells that surround the capillary Endothelial cells are in turn surrounded by the basement membrane: outside this membrane are Astrocytes Junctions between endothelial cells act as active gates, allowing only certain molecules to penetrate Therapeutic drugs mean ...
... Formed in part by endothelial cells that surround the capillary Endothelial cells are in turn surrounded by the basement membrane: outside this membrane are Astrocytes Junctions between endothelial cells act as active gates, allowing only certain molecules to penetrate Therapeutic drugs mean ...
9-1_BrainStemNeurons_BujtarZs
... Brain stem is a part of the brain. It has several important rule in the nervous system. It contains specialized parts which have important rules in the vital life processes. It has processing centres of most cranial nerves, reticular formation controlling respiratory and circulatory mechanisms, subc ...
... Brain stem is a part of the brain. It has several important rule in the nervous system. It contains specialized parts which have important rules in the vital life processes. It has processing centres of most cranial nerves, reticular formation controlling respiratory and circulatory mechanisms, subc ...
Central Nervous System
... Which type of neuron conducts the message when… Seeing a picture Feeling pain from skinning your knee Moving your arm to catch a ball ...
... Which type of neuron conducts the message when… Seeing a picture Feeling pain from skinning your knee Moving your arm to catch a ball ...
The Nervous System
... In the CNS, a collection of neuron cell bodies that share a particular function is called a center A center with a a discrete anatomical boundary is called a nucleus. Portions of the brain surface are covered by a thick layer of gray matter called the neural cortex ...
... In the CNS, a collection of neuron cell bodies that share a particular function is called a center A center with a a discrete anatomical boundary is called a nucleus. Portions of the brain surface are covered by a thick layer of gray matter called the neural cortex ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron membrane A.Physiology – neurons have two major functional properties: 1.Irritability – the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into a nerve impulse (electrochemical event) ...
... wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron membrane A.Physiology – neurons have two major functional properties: 1.Irritability – the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into a nerve impulse (electrochemical event) ...
Week 4 homework
... associated tissue that is enclosed in the spine and connects nearly all the parts of the body to the brain, with which it forms the Central Nervous System. Paraplegia: Paralysis of the legs and lower body, typically caused by spinal injury or disease. Quadriplegia: Paralysis of all four limbs. Paral ...
... associated tissue that is enclosed in the spine and connects nearly all the parts of the body to the brain, with which it forms the Central Nervous System. Paraplegia: Paralysis of the legs and lower body, typically caused by spinal injury or disease. Quadriplegia: Paralysis of all four limbs. Paral ...
nervous system
... The brain stem is like a flower stem. T stem of a flower carries nutrients from t roots to the leaves and petals. The stem the brain is composed of nerve tiss carrying information from the cerebrum a spinal cord. The brain stem handl functions that do not require conscio thought or action such as ci ...
... The brain stem is like a flower stem. T stem of a flower carries nutrients from t roots to the leaves and petals. The stem the brain is composed of nerve tiss carrying information from the cerebrum a spinal cord. The brain stem handl functions that do not require conscio thought or action such as ci ...
Cells, Tissue, Organ, System
... • A group of one type of cells working together is tissue. • Here is nerve tissue. Here you see a group of nerve cells. ...
... • A group of one type of cells working together is tissue. • Here is nerve tissue. Here you see a group of nerve cells. ...
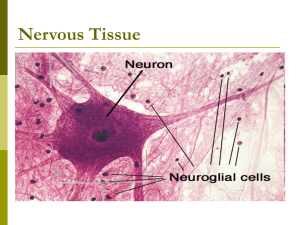
Nervous Tissue
... • In developing NS, form structural framework to guide migration of developing neurons • In developed NS, form structural scaffolding for more specialized neural elements • Clear ECM of by-products of neural activity and contain glycogen reserves • Extend foot processes around blood capillaries ...
... • In developing NS, form structural framework to guide migration of developing neurons • In developed NS, form structural scaffolding for more specialized neural elements • Clear ECM of by-products of neural activity and contain glycogen reserves • Extend foot processes around blood capillaries ...
BRAINS!!! A Presentation on the Nervous System
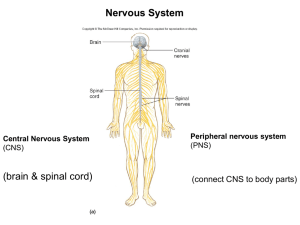
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM • System in an animal that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions. • Two main parts • Central Nervous System (CNS)= brain and spinal chord • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)= nerves and ganglia (nerve cells and tissue) outside of the brain ...
... THE NERVOUS SYSTEM • System in an animal that coordinates voluntary and involuntary actions. • Two main parts • Central Nervous System (CNS)= brain and spinal chord • Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)= nerves and ganglia (nerve cells and tissue) outside of the brain ...
Chapter 11: The Nervous System
... (A) Structure: cell body with nucleus, axon (transmission), dendrite(s) (reception). Some axons with myelin sheaths for faster, saltatory (leaping) conduction. Myelin forms white matter. Other structures form gray matter. Neurons surrounded by neuroglia = supporting cells. (B) Communication: -1- imp ...
... (A) Structure: cell body with nucleus, axon (transmission), dendrite(s) (reception). Some axons with myelin sheaths for faster, saltatory (leaping) conduction. Myelin forms white matter. Other structures form gray matter. Neurons surrounded by neuroglia = supporting cells. (B) Communication: -1- imp ...
nerves and glials - Central Connecticut State University
... • Yes, but their path is blocked by CNS Glial Cells. • CNS Glial cells (Oligodendrocytes) form scar tissue. • Pathway is blocked by scar tissue. scar ...
... • Yes, but their path is blocked by CNS Glial Cells. • CNS Glial cells (Oligodendrocytes) form scar tissue. • Pathway is blocked by scar tissue. scar ...
LAB 7 Practical Histology Nervous Tissue Definition: is highly
... c. Bipolar neurons: single axon and dendrite arise at opposite poles of the cell body. Found only in sensory neurons, such as in the retina, olfactory and auditory systems. d. Multipolar neurons: More than two dendrites just one axon ; found in brain, peripheral autonomic nervous system and spinal c ...
... c. Bipolar neurons: single axon and dendrite arise at opposite poles of the cell body. Found only in sensory neurons, such as in the retina, olfactory and auditory systems. d. Multipolar neurons: More than two dendrites just one axon ; found in brain, peripheral autonomic nervous system and spinal c ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SPECIAL SENSES
... -Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces -Axon arises from the cell body and can be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma -Either multipolar, bipolar, or unipolar ...
... -Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces -Axon arises from the cell body and can be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma -Either multipolar, bipolar, or unipolar ...
Development of the central nervous system
... B. B. In the spinal cordoligodendroglia cells surround the ventral rootlet; outside the spinal cord, Schwann cells begin to surround the rootlet. C. C. In the spinal cord the myelin sheath is formed by oligodendroglia cells; outside the spinal cord the sheath is formed by Schwann cells. ...
... B. B. In the spinal cordoligodendroglia cells surround the ventral rootlet; outside the spinal cord, Schwann cells begin to surround the rootlet. C. C. In the spinal cord the myelin sheath is formed by oligodendroglia cells; outside the spinal cord the sheath is formed by Schwann cells. ...
Astrocyte

For the cell in the gastrointestinal tract, see Interstitial cell of Cajal.Astrocytes (Astro from Greek astron = star and cyte from Greek ""kyttaron"" = cell), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined. Depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. They perform many functions, including biochemical support of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injuries.Research since the mid-1990s has shown that astrocytes propagate intercellular Ca2+ waves over long distances in response to stimulation, and, similar to neurons, release transmitters (called gliotransmitters) in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Data suggest that astrocytes also signal to neurons through Ca2+-dependent release of glutamate. Such discoveries have made astrocytes an important area of research within the field of neuroscience.