
Gene: Usually, a section of DNA long enough to code for a protein
... substance is sequentially altered until a desired product is produced. Each step in the pathway is assisted by a specific enzyme. Chromosome: A tightly coiled piece of DNA long enough to include up to about 1000 genes. Recessive gene: An inactive gene. Alleles: Paired genes. Example: you inherited a ...
... substance is sequentially altered until a desired product is produced. Each step in the pathway is assisted by a specific enzyme. Chromosome: A tightly coiled piece of DNA long enough to include up to about 1000 genes. Recessive gene: An inactive gene. Alleles: Paired genes. Example: you inherited a ...
14-3 Human Molecular Genetics
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
... is replaced by a normal, working gene. - This way the body can make the correct protein or enzyme it needs, which eliminates the cause of the disorder. ...
Players in the protein game
... proteins. They are built inside cells using Dna code however it folds that’s the what it does. ...
... proteins. They are built inside cells using Dna code however it folds that’s the what it does. ...
Introduction to DNA webquest: Name http://learn.genetics.utah.
... 1. What are genes needed for? ...
... 1. What are genes needed for? ...
Linked Genes and Crossing Over
... 2. Thomas Hunt Morgan discovered that the expected 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in a dihybrid cross did not always occur when examining some traits. When he mated wild type ( gray body and normal wings) with a double mutant type (black body and vestigal wings(stumpy)), all of the offspring had normal bo ...
... 2. Thomas Hunt Morgan discovered that the expected 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio in a dihybrid cross did not always occur when examining some traits. When he mated wild type ( gray body and normal wings) with a double mutant type (black body and vestigal wings(stumpy)), all of the offspring had normal bo ...
Genetics Vocabulary Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a
... Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color or blood type. In an individual, one form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than another form (the ...
... Allele: One of the variant forms of a gene at a particular locus, or location, on a chromosome. Different alleles produce variation in inherited characteristics such as hair color or blood type. In an individual, one form of the allele (the dominant one) may be expressed more than another form (the ...
History of Genetics
... structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from two different species in vitro, then transform it into ...
... structure of the DNA molecule, which leads directly to knowledge of how it replicates • 1966: Marshall Nirenberg solves the genetic code, showing that 3 DNA bases code for one amino acid. • 1972: Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer combine DNA from two different species in vitro, then transform it into ...
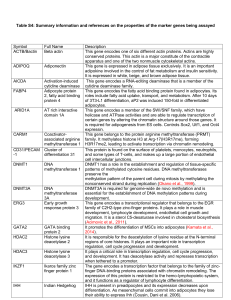
Table S4: Summary information and references on the properties of
... residues of histone H3. KDM4A generates H3K9Me from the di-and trimethylated forms. It regulates the expression of key transcription factors during embryonic development. Plays an important role in maintaining embryonic stem cells, and in preventing their differentiation. It is a histone lysine meth ...
... residues of histone H3. KDM4A generates H3K9Me from the di-and trimethylated forms. It regulates the expression of key transcription factors during embryonic development. Plays an important role in maintaining embryonic stem cells, and in preventing their differentiation. It is a histone lysine meth ...
Chapter 21 Review – Genetic Basis of Development
... Differentiation – cells become specialized in structure and function Morphogenesis – physical process of giving an organism its shape Stem cells – undifferentiated cells, they can become any kind of cell in the organism Induction – signal molecules that induce changes in gene expression in nearby ce ...
... Differentiation – cells become specialized in structure and function Morphogenesis – physical process of giving an organism its shape Stem cells – undifferentiated cells, they can become any kind of cell in the organism Induction – signal molecules that induce changes in gene expression in nearby ce ...
a version - SEA
... widely known as endolysin, internally hydrolyzes the cell wall of the bacterial host, where it targets the peptidoglycan in order to interfere with cell wall structural integrity. By breaking down the cell wall, newly assembled viruses can be released at the end of the lytic cycle. Holin is a group ...
... widely known as endolysin, internally hydrolyzes the cell wall of the bacterial host, where it targets the peptidoglycan in order to interfere with cell wall structural integrity. By breaking down the cell wall, newly assembled viruses can be released at the end of the lytic cycle. Holin is a group ...
- U
... • Y-linked genes are found on the Y chromosome, symbolized by X, YR, Yr • Thomas Morgan experimented with the eye color of fruit flies (Drosophilia) to determine Xlinkage ...
... • Y-linked genes are found on the Y chromosome, symbolized by X, YR, Yr • Thomas Morgan experimented with the eye color of fruit flies (Drosophilia) to determine Xlinkage ...
Variations of Mendel`s Law Notes Incomplete
... NOT Blending Hypothesis because … In northeast Minnesota there is a creature know as a wildcat. It comes in three colors, blue, red, and purple. This trait is controlled by a single locus gene with incomplete dominance. A homozygous (BB) individual is blue, a homozygous (bb) individual is red, and a ...
... NOT Blending Hypothesis because … In northeast Minnesota there is a creature know as a wildcat. It comes in three colors, blue, red, and purple. This trait is controlled by a single locus gene with incomplete dominance. A homozygous (BB) individual is blue, a homozygous (bb) individual is red, and a ...
linked genes
... contradiction of Mendel’s law of Independent Assortment, would it not?!) As a matter of fact – some genes are linked in this manner. William Bateson was the famous scientist who “rediscovered” Mendel, who invented the term “Genetics” and was the first to recognize that some genes are linked. Numerou ...
... contradiction of Mendel’s law of Independent Assortment, would it not?!) As a matter of fact – some genes are linked in this manner. William Bateson was the famous scientist who “rediscovered” Mendel, who invented the term “Genetics” and was the first to recognize that some genes are linked. Numerou ...
Name_______________________ Period
... What is a Barr body? Why do human females show a Barr body in their cells? ...
... What is a Barr body? Why do human females show a Barr body in their cells? ...
Genetics
... Gregor Mendel If the two alleles are different, One is dominant and one is recessive ...
... Gregor Mendel If the two alleles are different, One is dominant and one is recessive ...
TEKS 5C – describe the roles of DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA), and
... TEKS 5C – describe the roles of DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA), and environmental factors in cell differentiation 1. Unicellular organisms carry out all the necessary life processes in one cell. In multicellular organisms, each cell is specialized to perform a specific function. How do the cells in mul ...
... TEKS 5C – describe the roles of DNA, ribonucleic acid (RNA), and environmental factors in cell differentiation 1. Unicellular organisms carry out all the necessary life processes in one cell. In multicellular organisms, each cell is specialized to perform a specific function. How do the cells in mul ...
No Slide Title
... For analysis of gene profiling data such methods are useful in their ability to represent varying degrees of similarity and more distant relationships among groups of closely related genes, as well as in requiring few assumptions about the nature of the data. The computed trees can be used to order ...
... For analysis of gene profiling data such methods are useful in their ability to represent varying degrees of similarity and more distant relationships among groups of closely related genes, as well as in requiring few assumptions about the nature of the data. The computed trees can be used to order ...
Biology Professor, Robert Osuna, Receives National Science
... gene regulator, plays an essential role in the regulation of the transcription of ribosomal RNA (necessary for the synthesis of proteins in the cell) and of numerous other genes involved in a variety of important cellular processes. DksA differs from most bacterial gene regulators in that it functio ...
... gene regulator, plays an essential role in the regulation of the transcription of ribosomal RNA (necessary for the synthesis of proteins in the cell) and of numerous other genes involved in a variety of important cellular processes. DksA differs from most bacterial gene regulators in that it functio ...
Nutrition and Gene Expression Jan 29, 2015
... Complete human chromosomes (Male), as seen during MITOSIS. The banding patterns are very distinctive, and allow each chromosome to be identified. ...
... Complete human chromosomes (Male), as seen during MITOSIS. The banding patterns are very distinctive, and allow each chromosome to be identified. ...
GENE EXPRESSION - Doctor Jade Main
... • others remain quiescent • some function at all times • 30,000 are expressed in nearly all cell types • housekeeping genes – carry out basic metabolic processes • called constitutive • other genes are regulated – turned on or off as needed ...
... • others remain quiescent • some function at all times • 30,000 are expressed in nearly all cell types • housekeeping genes – carry out basic metabolic processes • called constitutive • other genes are regulated – turned on or off as needed ...
m10-expression
... Diagnostic / prognostic biomarker for human (or other) sample outcomes. Microarrays were originally developed for sequencing. Array one or more known sequences per gene in preassigned locations. Extract RNA from condition(s) of interest, reverse transcribe with fluorescent label. Quantify the amount ...
... Diagnostic / prognostic biomarker for human (or other) sample outcomes. Microarrays were originally developed for sequencing. Array one or more known sequences per gene in preassigned locations. Extract RNA from condition(s) of interest, reverse transcribe with fluorescent label. Quantify the amount ...





















![Gene Regulation Powerpoint[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008316551_1-1ebe12542f6d355f67fcc596db1be2d3-300x300.png)
