black holes are created when stars collapse and die from burning its
... •Swiss astrophysicist Fritz Zwicky first proposed dark matter existed •dark matter was discovered because of the gravitational forces that it exerts •it was found in the empty spaces that was just thought to be matter of specialized atoms •1930 – discovery of dark matter by Fritz Zwicky •1970 – dis ...
... •Swiss astrophysicist Fritz Zwicky first proposed dark matter existed •dark matter was discovered because of the gravitational forces that it exerts •it was found in the empty spaces that was just thought to be matter of specialized atoms •1930 – discovery of dark matter by Fritz Zwicky •1970 – dis ...
solutions
... 8 If the Universe continues to expand forever, what will eventually become of the cosmic background radiation? Recall that the frequency of photons decreases inversely with the expansion factor, R. Therefore as the Universe expands, the temperature of the cosmic background radiation decreases accord ...
... 8 If the Universe continues to expand forever, what will eventually become of the cosmic background radiation? Recall that the frequency of photons decreases inversely with the expansion factor, R. Therefore as the Universe expands, the temperature of the cosmic background radiation decreases accord ...
1.5 physics beyond the Standard Model
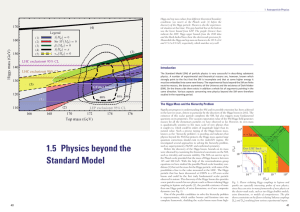
... in the last two years, driven in particular by the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. The existence of this scalar particle completes the SM, but also triggers many fundamental questions on its properties. The vacuum expectation value of the SM Higgs field generates masses for all the elementary ...
... in the last two years, driven in particular by the discovery of the Higgs boson in 2012. The existence of this scalar particle completes the SM, but also triggers many fundamental questions on its properties. The vacuum expectation value of the SM Higgs field generates masses for all the elementary ...
Higgs Portal VDM and Indirect Signature
... • Phenomenology – Relic density, direct detection, indirect signatures,… ...
... • Phenomenology – Relic density, direct detection, indirect signatures,… ...
ASTR 1120-001 Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
... 27. Which kind of rotation curve provides the most convincing evidence for dark matter in spiral galaxies such as the Milky Way? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
... 27. Which kind of rotation curve provides the most convincing evidence for dark matter in spiral galaxies such as the Milky Way? (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) ...
Dark matter

Dark matter is a hypothetical kind of matter that cannot be seen with telescopes but would account for most of the matter in the universe. The existence and properties of dark matter are inferred from its gravitational effects on visible matter, on radiation, and on the large-scale structure of the universe. Dark matter has not been detected directly, making it one of the greatest mysteries in modern astrophysics.Dark matter neither emits nor absorbs light or any other electromagnetic radiation at any significant level. According to the Planck mission team, and based on the standard model of cosmology, the total mass–energy of the known universe contains 4.9% ordinary matter, 26.8% dark matter and 68.3% dark energy. Thus, dark matter is estimated to constitute 84.5% of the total matter in the universe, while dark energy plus dark matter constitute 95.1% of the total mass–energy content of the universe.Astrophysicists hypothesized the existence of dark matter to account for discrepancies between the mass of large astronomical objects determined from their gravitational effects, and their mass as calculated from the observable matter (stars, gas, and dust) that they can be seen to contain. Their gravitational effects suggest that their masses are much greater than the observable matter survey suggests. Dark matter was postulated by Jan Oort in 1932, albeit based upon insufficient evidence, to account for the orbital velocities of stars in the Milky Way. In 1933, Fritz Zwicky was the first to use the virial theorem to infer the existence of unseen matter, which he referred to as dunkle Materie 'dark matter'. More robust evidence from galaxy rotation curves was discovered by Horace W. Babcock in 1939, but was not attributed to dark matter. The first hypothesis to postulate ""dark matter"" based upon robust evidence was formulated by Vera Rubin and Kent Ford in the 1960s–1970s, using galaxy rotation curves. Subsequently, many other observations have indicated the presence of dark matter in the universe, including gravitational lensing of background objects by galaxy clusters such as the Bullet Cluster, the temperature distribution of hot gas in galaxies and clusters of galaxies and, more recently, the pattern of anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background. According to consensus among cosmologists, dark matter is composed primarily of a not yet characterized type of subatomic particle.The search for this particle, by a variety of means, is one of the major efforts in particle physics today.Although the existence of dark matter is generally accepted by the mainstream scientific community, some alternative theories of gravity have been proposed, such as MOND and TeVeS, which try to account for the anomalous observations without requiring additional matter. However, these theories cannot account for the properties of galaxy clusters.