mendel I
... A backcross involves mating the F1 hybrid to one of the parental types. There are 2 possible backcrosses in the system we are examining. Pp x PP. Back crossing to the dominant parent. The Pp plant will produce 1/2 P gametes and 1/2 p gametes. The PP plant will produce only P gametes. The offspring w ...
... A backcross involves mating the F1 hybrid to one of the parental types. There are 2 possible backcrosses in the system we are examining. Pp x PP. Back crossing to the dominant parent. The Pp plant will produce 1/2 P gametes and 1/2 p gametes. The PP plant will produce only P gametes. The offspring w ...
AP Biology Unit 4: Genetics - Chapter 14
... • An organism with two identical alleles for a character is said to be homozygous for the gene controlling that character • An organism that has two different alleles for a gene is said to be heterozygous for the gene controlling that character • Unlike homozygotes, heterozygotes are not true-breedi ...
... • An organism with two identical alleles for a character is said to be homozygous for the gene controlling that character • An organism that has two different alleles for a gene is said to be heterozygous for the gene controlling that character • Unlike homozygotes, heterozygotes are not true-breedi ...
Studies That Use Samples From the Michigan Neonatal Biobank
... All forms of SMA are inherited as autosomal recessive traits, although 1/3 of SMA3 patients show an autosomal dominant pattern. De-identified dried blood spots are being provided by the Michigan Neonatal Biobank for development of a reliable test suitable for newborn screening programs. ...
... All forms of SMA are inherited as autosomal recessive traits, although 1/3 of SMA3 patients show an autosomal dominant pattern. De-identified dried blood spots are being provided by the Michigan Neonatal Biobank for development of a reliable test suitable for newborn screening programs. ...
Timeline
... • a rare few have been found with thirty genes in them. • cells can have anywhere from a couple to fifty or more plasmids in them. • some pop into the bacterial chromosome = episomes. ...
... • a rare few have been found with thirty genes in them. • cells can have anywhere from a couple to fifty or more plasmids in them. • some pop into the bacterial chromosome = episomes. ...
PCB5065 Exam 2 - UF Plant Pathology
... a) mitotic recombination results in crossing over half the time. F b) mitotic recombination is usually the result of gene conversion T c) in Drosophila and most organisms, mitotic recombination differs from meiotic in that the homology search during mitotic recombination must cover the whole genome. ...
... a) mitotic recombination results in crossing over half the time. F b) mitotic recombination is usually the result of gene conversion T c) in Drosophila and most organisms, mitotic recombination differs from meiotic in that the homology search during mitotic recombination must cover the whole genome. ...
Meiosis The main reason we have meiosis is for sexual reproduction
... Suppose we have a gene for coat color and eye color on the same gene. There may be different versions of these genes (alleles) on these homologous chromosomes. Suppose we have the set up as in the figure (one tetrad). Meiosis will yield four cells, each with a single chromosome. Two cells would have ...
... Suppose we have a gene for coat color and eye color on the same gene. There may be different versions of these genes (alleles) on these homologous chromosomes. Suppose we have the set up as in the figure (one tetrad). Meiosis will yield four cells, each with a single chromosome. Two cells would have ...
Unifying Learning with Evolution Through
... Individuals survive based on their ability to adapt to the pressures of their environment, so that individuals better suited to the environment tend to have more offsprings and thus drive the population towards favourable traits. The traits of offsprings are partially inherited from their parents an ...
... Individuals survive based on their ability to adapt to the pressures of their environment, so that individuals better suited to the environment tend to have more offsprings and thus drive the population towards favourable traits. The traits of offsprings are partially inherited from their parents an ...
Pathchat no 32 Paternity (rev)
... coding regions are genes, which have protein-coding regions and intervening regions. These intervening regions contain repeated DNA sequences. The number of repeats varies among individuals. Variability in these regions can be used to distinguish one DNA profile from another. The markers used in pat ...
... coding regions are genes, which have protein-coding regions and intervening regions. These intervening regions contain repeated DNA sequences. The number of repeats varies among individuals. Variability in these regions can be used to distinguish one DNA profile from another. The markers used in pat ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Mammalian X
... In Drosophila, it is the number of X's that determine sex while in mammals it is the presence or absence of a Y chromosome that determines sex. Homogametic sex- Producing gametes that contain one type of chromosome (females in mammals and insects, males in birds and reptiles) Heterogametic sex- Prod ...
... In Drosophila, it is the number of X's that determine sex while in mammals it is the presence or absence of a Y chromosome that determines sex. Homogametic sex- Producing gametes that contain one type of chromosome (females in mammals and insects, males in birds and reptiles) Heterogametic sex- Prod ...
Epigenetics concerns changes in gene expression states that are
... The two active X chromosomes in female ESCs block exit from the pluripotent state by modulating the ESC signaling network. Cell stem cell : 203-16 : DOI : 10.1016/j.stem.2013.11.022 Year of publication 2011 ...
... The two active X chromosomes in female ESCs block exit from the pluripotent state by modulating the ESC signaling network. Cell stem cell : 203-16 : DOI : 10.1016/j.stem.2013.11.022 Year of publication 2011 ...
Unit 4 Part II Review
... A. Student – Ww; sister – ww B. Student – WW; sister – Ww C. Student – ww; sister – Ww D. Student – ww; sister – ww E. Student – Ww; sister - Ww Answer: C ...
... A. Student – Ww; sister – ww B. Student – WW; sister – Ww C. Student – ww; sister – Ww D. Student – ww; sister – ww E. Student – Ww; sister - Ww Answer: C ...
Example 13.2
... Biologists wish to mate two fruit flies having genetic makeup RrCc, indicating that it has one dominant gene (R) and one recessive gene (r) for eye color, along with one dominant (C) and one recessive (c) gene for wing type. Each offspring will receive one gene for each of the two traits from both p ...
... Biologists wish to mate two fruit flies having genetic makeup RrCc, indicating that it has one dominant gene (R) and one recessive gene (r) for eye color, along with one dominant (C) and one recessive (c) gene for wing type. Each offspring will receive one gene for each of the two traits from both p ...
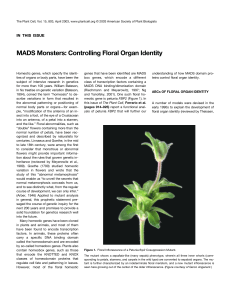
MADS Monsters: Controlling Floral Organ Identity
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
熊本大学学術リポジトリ Kumamoto University Repository System
... expression and its potential involvement in gastrulation processes. In the mouse, goosecoid is expressed in the developing primitive streak, more specifically in those cells that are undergoing anterior migration – one of the earliest features of gastrulation. The fate of these cells has been demons ...
... expression and its potential involvement in gastrulation processes. In the mouse, goosecoid is expressed in the developing primitive streak, more specifically in those cells that are undergoing anterior migration – one of the earliest features of gastrulation. The fate of these cells has been demons ...
Ch13Exampl13_2
... Biologists wish to mate two fruit flies having genetic makeup RrCc, indicating that it has one dominant gene (R) and one recessive gene (r) for eye color, along with one dominant (C) and one recessive (c) gene for wing type. Each offspring will receive one gene for each of the two traits from both p ...
... Biologists wish to mate two fruit flies having genetic makeup RrCc, indicating that it has one dominant gene (R) and one recessive gene (r) for eye color, along with one dominant (C) and one recessive (c) gene for wing type. Each offspring will receive one gene for each of the two traits from both p ...
Selection Purpose change over a period of several generations the
... 3. Disruptive selection Favours both phenotypic extremes less common in livestock. These three could be artificial or natural selection. Methods of selection 1. Tandem selection Selection of one trait at a time for several generations before taking on another for several generations. It’s a single f ...
... 3. Disruptive selection Favours both phenotypic extremes less common in livestock. These three could be artificial or natural selection. Methods of selection 1. Tandem selection Selection of one trait at a time for several generations before taking on another for several generations. It’s a single f ...
Sickle Cell PPT - Dr. Annette M. Parrott
... • /1pt Protein Affected (How are primary through quaternary structure affected? How is enzyme activity affected? normal vs abnormal expression) • /1pt Cellular, Tissue & Organ effects (What signal transduction pathways are interrupted? What morphological changes in cells, tissues and organs result?) ...
... • /1pt Protein Affected (How are primary through quaternary structure affected? How is enzyme activity affected? normal vs abnormal expression) • /1pt Cellular, Tissue & Organ effects (What signal transduction pathways are interrupted? What morphological changes in cells, tissues and organs result?) ...
B-Thalassemia - Cloudfront.net
... that could be thalassemia as much as it would if Susan’s familythey waspair of up in the harmful The vastifmajority of children offspring. If Susan you’re Mediterranean decent because the likelihood carries the born tothat first cousinsunrelated, are the odds for these thalassemia gene is about 1 in ...
... that could be thalassemia as much as it would if Susan’s familythey waspair of up in the harmful The vastifmajority of children offspring. If Susan you’re Mediterranean decent because the likelihood carries the born tothat first cousinsunrelated, are the odds for these thalassemia gene is about 1 in ...
Guo, Ming: Biological Pathways - A pathway to explore diseases mechanism
... More and more genome-wide association studies of diseases have revealed possible connections between DNA sequence variants and various diseases. However, it is common that, only a small proportion of the disease risk is explainable by the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified in these st ...
... More and more genome-wide association studies of diseases have revealed possible connections between DNA sequence variants and various diseases. However, it is common that, only a small proportion of the disease risk is explainable by the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified in these st ...
THE BITHORAX COMPLEX: THE FIRST FIFTY YEARS
... causing the halteres to become partially wing-like. Body segments and structures of the wild-type adult are correlated with those of the late embryo in Fig 2. bx was the first example of a mutant that exhibited homeosis, a term Bateson had first coined for conversion of one structure into an homolog ...
... causing the halteres to become partially wing-like. Body segments and structures of the wild-type adult are correlated with those of the late embryo in Fig 2. bx was the first example of a mutant that exhibited homeosis, a term Bateson had first coined for conversion of one structure into an homolog ...
Probability and Punnet Squares
... carried on the X-chromosome. Because boys only have one Xchromosome, they are more likely to get color blindness. If they only get one bad copy of the gene, they have the disorder. Girls have to get two bad copies of the gene to have the disorder. ...
... carried on the X-chromosome. Because boys only have one Xchromosome, they are more likely to get color blindness. If they only get one bad copy of the gene, they have the disorder. Girls have to get two bad copies of the gene to have the disorder. ...
Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention What Are the Risk Factors for
... types of cancer. Researchers are studying families that have many cases of WM to try to find the genes that might cause this disorder in some people. The DNA changes found in WM cells are usually acquired after birth (not passed on from a parent). Some of these acquired changes may have outside caus ...
... types of cancer. Researchers are studying families that have many cases of WM to try to find the genes that might cause this disorder in some people. The DNA changes found in WM cells are usually acquired after birth (not passed on from a parent). Some of these acquired changes may have outside caus ...