What_Is_Ontology_Mia.. - Buffalo Ontology Site
... in an organism that constitutes an increased risk of the organism’s subsequently developing the disease X. HNPCC is caused by a disorder (mutation) in a DNA mismatch repair gene that disposes to the acquisition of additional mutations from defective DNA repair processes, and thus is a predispo ...
... in an organism that constitutes an increased risk of the organism’s subsequently developing the disease X. HNPCC is caused by a disorder (mutation) in a DNA mismatch repair gene that disposes to the acquisition of additional mutations from defective DNA repair processes, and thus is a predispo ...
mutations, and several investigators have characterized eight
... A frequent etiology of congenital lactic acidosis is disturbed mitochondrial energy metabolism. Affected children generally present with neurologic symptoms, such as myopathy and epilepsy. Parents who have lost a child to mitochondrial disease often ask for prenatal diagnosis in subsequent pregnanci ...
... A frequent etiology of congenital lactic acidosis is disturbed mitochondrial energy metabolism. Affected children generally present with neurologic symptoms, such as myopathy and epilepsy. Parents who have lost a child to mitochondrial disease often ask for prenatal diagnosis in subsequent pregnanci ...
Nucleolar Dominance - Indiana University Bloomington
... in X. laevis and X. borealis rRNA genes results in the preferential transcription of X. laevis rRNA genes, presumably due to preferential recruitment of one or more transcription factors. Based on indirect evidence, this `enhancer imbalance' hypothesis was also proposed as a possible explanation for ...
... in X. laevis and X. borealis rRNA genes results in the preferential transcription of X. laevis rRNA genes, presumably due to preferential recruitment of one or more transcription factors. Based on indirect evidence, this `enhancer imbalance' hypothesis was also proposed as a possible explanation for ...
Introduction to Genetic Algorithms - computer science
... algorithms based on the mechanics of the natural selection process (biological evolution). The most basic concept is that the strong tend to adapt and survive while the weak tend to die out. That is, optimization is based on evolution, and the "Survival of the fittest" concept. _ GAs have the abilit ...
... algorithms based on the mechanics of the natural selection process (biological evolution). The most basic concept is that the strong tend to adapt and survive while the weak tend to die out. That is, optimization is based on evolution, and the "Survival of the fittest" concept. _ GAs have the abilit ...
Heredity Study Guide
... ◦ Sex-linked trait: genes that are only in the X or Y chromosomes ◦ Sex influenced trait: traits that are influenced by hormones in the body ◦ Pedigree: diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over generations ◦ Karyotype: a picture of chromosomes that can show the sex and chromosomal disorders ...
... ◦ Sex-linked trait: genes that are only in the X or Y chromosomes ◦ Sex influenced trait: traits that are influenced by hormones in the body ◦ Pedigree: diagram that shows how a trait is inherited over generations ◦ Karyotype: a picture of chromosomes that can show the sex and chromosomal disorders ...
Going Multicellular >> Out of the Oort Cloud BK Channel
... and the multicellular Volvox, which diverged from one another 50 to 200 million years ago. Prochnik et al. (p. 223) compared the Volvox genome with that of Chlamydomonas to identify any genomic innovations that might have been associated with the transition to multicellularity. Size changes were obs ...
... and the multicellular Volvox, which diverged from one another 50 to 200 million years ago. Prochnik et al. (p. 223) compared the Volvox genome with that of Chlamydomonas to identify any genomic innovations that might have been associated with the transition to multicellularity. Size changes were obs ...
13 Genetics Part 1
... Discuss how a testcross is performed to determine the genotype of an organism. ...
... Discuss how a testcross is performed to determine the genotype of an organism. ...
Genetics - Mendelian Inheritance & Heredity Lecture PowerPoint
... - In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation. - Offspring that are hybrid for a trait will have only the dominant trait in the phenotype. ...
... - In a cross of parents that are pure for contrasting traits, only one form of the trait will appear in the next generation. - Offspring that are hybrid for a trait will have only the dominant trait in the phenotype. ...
Exam #3 Part of Ch. 13, Ch.14-17 and Ch. 20 Supplement to notes
... Chromosomal theory of inheritance, loci, Morgan’s notation for symbolizing alleles in Drosophila, wild type, mutant (non-wild type) for wing and body color For example: b+ vg+ wild type for both body color and wing shape (phenotype gray and normal wing) 15.2 Linked genes tend to be inherited togethe ...
... Chromosomal theory of inheritance, loci, Morgan’s notation for symbolizing alleles in Drosophila, wild type, mutant (non-wild type) for wing and body color For example: b+ vg+ wild type for both body color and wing shape (phenotype gray and normal wing) 15.2 Linked genes tend to be inherited togethe ...
Warren, ST: Trinucleotide repetition and fragile X syndrome. Hospital Practice 32:73 - 98 (1997). cover illustration.
... containing a perfect run of more than, say, 25 repeats may be predisposed alleles. Such a surmise at least accords with what is now known of other tripletexpansion-related disorders. In Huntington disease, the culprit CAG tract does not show cryptic interruptions even in normal alleles, but normal a ...
... containing a perfect run of more than, say, 25 repeats may be predisposed alleles. Such a surmise at least accords with what is now known of other tripletexpansion-related disorders. In Huntington disease, the culprit CAG tract does not show cryptic interruptions even in normal alleles, but normal a ...
University of Sydney Institutional Biosafety Committee This form is to
... species and strain or organ/tissue as applicable. Include the specific genes to be involved in the dealing. ...
... species and strain or organ/tissue as applicable. Include the specific genes to be involved in the dealing. ...
Goals of Genetic Enginnering - ASAB-NUST
... block infection. More specifically, it’s a monoclonal antibody made from immune cells for one specific role. ...
... block infection. More specifically, it’s a monoclonal antibody made from immune cells for one specific role. ...
Microbial growth requirements Chemical growth factors
... Mechanisms of Gene Transfer: 1- Conjugation. 2- Transduction (is a phage-mediated genetic transfer). 3- Transformation. Conjugation: is a mechanism of gene transfer by which plasmids will be transferred from one bacterial cell to another by a mean of Sex pili. Hospital-dwelling bacteria resist antib ...
... Mechanisms of Gene Transfer: 1- Conjugation. 2- Transduction (is a phage-mediated genetic transfer). 3- Transformation. Conjugation: is a mechanism of gene transfer by which plasmids will be transferred from one bacterial cell to another by a mean of Sex pili. Hospital-dwelling bacteria resist antib ...
F 1
... Instead, some genes for body color and wing shape were inherited together. Morgan theorized that the two loci were linked on the same chromosome and ...
... Instead, some genes for body color and wing shape were inherited together. Morgan theorized that the two loci were linked on the same chromosome and ...
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes NOTES Cancer
... leads to problems. This is in contrast to oncogenes which often have gained functions (or lost the ability to be controlled) in their mutant form. ...
... leads to problems. This is in contrast to oncogenes which often have gained functions (or lost the ability to be controlled) in their mutant form. ...
Oncogenes And Tumor Suppressor Genes NOTES
... leads to problems. This is in contrast to oncogenes which often have gained functions (or lost the ability to be controlled) in their mutant form. Unlike oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes generally follow the "two-hit hypothesis", meaning that both alleles that code for a particular protein must be ...
... leads to problems. This is in contrast to oncogenes which often have gained functions (or lost the ability to be controlled) in their mutant form. Unlike oncogenes, tumor suppressor genes generally follow the "two-hit hypothesis", meaning that both alleles that code for a particular protein must be ...
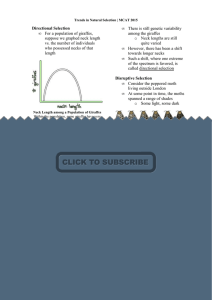
Directional Selection • For a population of giraffes, suppose we
... programmed to lay a given number of eggs might look like this: ...
... programmed to lay a given number of eggs might look like this: ...
Wings, Horns, and Butterfly Eyespots: How Do Complex Traits Evolve?
... have evolved numerous complex morphological, physiological, and behavioral adaptations to increase their chances of survival and reproduction. Insects have evolved wings and flight, which allowed them to better disperse [2], beetles have grown horns to fight over females [3], and moths and butterfli ...
... have evolved numerous complex morphological, physiological, and behavioral adaptations to increase their chances of survival and reproduction. Insects have evolved wings and flight, which allowed them to better disperse [2], beetles have grown horns to fight over females [3], and moths and butterfli ...
Document
... Males have a square, females a circle, if the square or circle is completely filled in, that individual is affected with the trait, on some pedigrees-if half the circle or square colored in represents a carrier. Remember, sex linked traits can not have males as carriers but the other autosomes (chro ...
... Males have a square, females a circle, if the square or circle is completely filled in, that individual is affected with the trait, on some pedigrees-if half the circle or square colored in represents a carrier. Remember, sex linked traits can not have males as carriers but the other autosomes (chro ...
Rethinking Gene Expression and Evolution (Nobel Lecture)
... cell division. These remarkably stable differentiation events can be maintained for the entire life of an organism without any underlying changes in the DNA sequence. The germline cells, which in C. elegans inherit PIE-1 protein, are the only cells that retain the potential to launch the development ...
... cell division. These remarkably stable differentiation events can be maintained for the entire life of an organism without any underlying changes in the DNA sequence. The germline cells, which in C. elegans inherit PIE-1 protein, are the only cells that retain the potential to launch the development ...
Mendelian Genetics
... 9. What phenotypic and genotypic ratios can be expected in the F1 and F2 generations from a dihybrid cross between homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive individuals in the P generation (for both traits)? (WWRR x wwrr) Show the ratios by using a Punnett Square. ...
... 9. What phenotypic and genotypic ratios can be expected in the F1 and F2 generations from a dihybrid cross between homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive individuals in the P generation (for both traits)? (WWRR x wwrr) Show the ratios by using a Punnett Square. ...
Case Study Learning via Simulations of Molecular Biology Techniques
... The disease is multifactorial and inheritance patterns are complex. Some forms of familial Alzheimer disease appear to be inherited as autosomal dominant traits, while others are recessive. Spontaneous Alzheimer disease also can occur in the absence of inherited factors. Mutations in at least four g ...
... The disease is multifactorial and inheritance patterns are complex. Some forms of familial Alzheimer disease appear to be inherited as autosomal dominant traits, while others are recessive. Spontaneous Alzheimer disease also can occur in the absence of inherited factors. Mutations in at least four g ...
Genetic analysis of TTF2 gene in congenital hypothyroid infants with
... is caused by an alteration in the morphogenesis of the thyroid which is called thyroid dysgenesis, TD.6 These anomalies including thyroid (hemi) agenesis (the thyroid gland is absent so called ‘athyrosis’ and ‘hemithyroidoea’), ectopic thyroid tissue (the thyroid gland is abnormally located in a sub ...
... is caused by an alteration in the morphogenesis of the thyroid which is called thyroid dysgenesis, TD.6 These anomalies including thyroid (hemi) agenesis (the thyroid gland is absent so called ‘athyrosis’ and ‘hemithyroidoea’), ectopic thyroid tissue (the thyroid gland is abnormally located in a sub ...
X-linked Coffin-Lowry syndrome (CLS, MIM 303600, RPS6KA3 gene
... the RSK2 gene. (a) Note the hypertelorism, the broad based nose, the downwards slanting of the palpetral fissures and the large mouth with full lips and missing and abnormal shaped teeth. (b) Note the thickened tapered digits. hypotonia together with the facial gestalt including hypertelorism, ptosi ...
... the RSK2 gene. (a) Note the hypertelorism, the broad based nose, the downwards slanting of the palpetral fissures and the large mouth with full lips and missing and abnormal shaped teeth. (b) Note the thickened tapered digits. hypotonia together with the facial gestalt including hypertelorism, ptosi ...