Lab I: Three-Point Mapping in Drosophila melanogaster
... The experiment began with the use of two fly stocks: wild type males (+++) and fully mutant females (wfm). The white (w) locus was identified by red (+) or white (w) eye color, the forked (f) locus was identified by straight (+) or the presence of forked/bent (f) bristles along the posterior a ...
... The experiment began with the use of two fly stocks: wild type males (+++) and fully mutant females (wfm). The white (w) locus was identified by red (+) or white (w) eye color, the forked (f) locus was identified by straight (+) or the presence of forked/bent (f) bristles along the posterior a ...
TGAC * Sequence Polymorphisms Module
... Q.44: What disease(s) has the gene been found associated with? Various cancers Q.45: Would you anticipate a change in phenotype/health if a small (ca. 300 bp) transposon is being inserted into the PV92 locus? Mutations in introns have generally no phenotypic effects. However, this is not always the ...
... Q.44: What disease(s) has the gene been found associated with? Various cancers Q.45: Would you anticipate a change in phenotype/health if a small (ca. 300 bp) transposon is being inserted into the PV92 locus? Mutations in introns have generally no phenotypic effects. However, this is not always the ...
... Based on a sequence comparison between the mutant and wild type alleles of cot-5 (amplified with primers GGTACCATGATGATGATGAGGC and GGAGACGCAAGCGGCTATG), the mutation responsible for the cot-5 phenotype resides in codon 37 of cot-5. The C to T transition in the mutant changes the wild type CAG codon ...
Cilantro Genetics - MisterSyracuse.com
... from a very young age may grow to like them, simply because of chemical changes in their brains through environmental stimuli. This is all well and good, but why might some people have a different amount of chemicals in their brains than others? The obvious answer is either their genes or their envi ...
... from a very young age may grow to like them, simply because of chemical changes in their brains through environmental stimuli. This is all well and good, but why might some people have a different amount of chemicals in their brains than others? The obvious answer is either their genes or their envi ...
Genetics Unit Review and Problem Set
... 14. One type of baldness is a sex-influenced trait. The gene for baldness (B = has hair, b = bald) is NOT on a sex chromosome, but the person’s sex does influence the expression of this trait. All BB individuals have hair, and all bb individuals go bald, but (due to hormonal differences) Bb women ha ...
... 14. One type of baldness is a sex-influenced trait. The gene for baldness (B = has hair, b = bald) is NOT on a sex chromosome, but the person’s sex does influence the expression of this trait. All BB individuals have hair, and all bb individuals go bald, but (due to hormonal differences) Bb women ha ...
The Evolution of Genetic Architecture
... by Cheverud & Routman (1995), who developed an explicit model of “physiological” epistasis defined without regard to allele frequencies and showed how this physiological epistasis differed from the Fisherian notion of statistical epistasis and even contributed to the additive genetic variance. The Fi ...
... by Cheverud & Routman (1995), who developed an explicit model of “physiological” epistasis defined without regard to allele frequencies and showed how this physiological epistasis differed from the Fisherian notion of statistical epistasis and even contributed to the additive genetic variance. The Fi ...
Grade 10 SC.F.1.4.1 BENCHMARK SC.F.1.4.1 Strand F Processes
... The student understands the mechanisms of change (e.g., mutation and natural selection) that lead to adaptations in a species and their ability to survive naturally in changing conditions and to increase species diversity. This benchmark also assesses SC.D.1.4.413 and SC.F.1.4.2.14 ...
... The student understands the mechanisms of change (e.g., mutation and natural selection) that lead to adaptations in a species and their ability to survive naturally in changing conditions and to increase species diversity. This benchmark also assesses SC.D.1.4.413 and SC.F.1.4.2.14 ...
My favourite flowering image: a cob of pod corn
... he started reading frantically a wide variety of books. One of these books (Grebenscikov, 1959) was about the domestication of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays). In contrast to the strange novels my father was reading, it immediately caught my interest. I was impressed by the enormous agronomic and religio ...
... he started reading frantically a wide variety of books. One of these books (Grebenscikov, 1959) was about the domestication of maize (Zea mays ssp. mays). In contrast to the strange novels my father was reading, it immediately caught my interest. I was impressed by the enormous agronomic and religio ...
Mendel 2014
... Assortment Chromosomes from any parent have a 50/50 chance of lining up on any side. This increases the variation in the gametes. Mom gives one and Dad give the other chromatid. ...
... Assortment Chromosomes from any parent have a 50/50 chance of lining up on any side. This increases the variation in the gametes. Mom gives one and Dad give the other chromatid. ...
Mendelian Dynamics and Sturtevant`s Paradigm
... A possible mechanism was suggested by Gregor Mendel in his paper ”Versuche über Pflanzen-Hybriden” that appeared in Verhandlungen des naturforschenden Vereines, Abhandlungen, Brunn 4, pp. 3-47 (1866) (seven years after Charles Darwin’s Origin of Species) where Mendel writes in the introduction: ”Th ...
... A possible mechanism was suggested by Gregor Mendel in his paper ”Versuche über Pflanzen-Hybriden” that appeared in Verhandlungen des naturforschenden Vereines, Abhandlungen, Brunn 4, pp. 3-47 (1866) (seven years after Charles Darwin’s Origin of Species) where Mendel writes in the introduction: ”Th ...
Lecture 8
... In this case, the donor parent will be the recessive and usually it is taken as the male parent. In the first season, the dominant x recessive cross is made and F1 seeds are collected. In the second season, the F1 is grown and backcrossed with the recurrent (dominant) parent and the BC1 seeds are co ...
... In this case, the donor parent will be the recessive and usually it is taken as the male parent. In the first season, the dominant x recessive cross is made and F1 seeds are collected. In the second season, the F1 is grown and backcrossed with the recurrent (dominant) parent and the BC1 seeds are co ...
Study Guide for the Genetics Unit
... Like blood types, sometimes there can be more than two alleles possible for a gene, which leads to a wider spectrum of possible outcomes Explain how the sex of an individual is determined. The sex chromosomes determine the sex of the offspring (XX = female, XY = male) Define the term “autosome”. ...
... Like blood types, sometimes there can be more than two alleles possible for a gene, which leads to a wider spectrum of possible outcomes Explain how the sex of an individual is determined. The sex chromosomes determine the sex of the offspring (XX = female, XY = male) Define the term “autosome”. ...
Factors modifying the yield of radiation
... FISH painted chromosomes. By PCC technique, it is possible to visualize the breaks and exchanges induced immediately and after different times following irradiation of human lymphocytes. By combining PCC with FISH it was possible to study the process of exchange ...
... FISH painted chromosomes. By PCC technique, it is possible to visualize the breaks and exchanges induced immediately and after different times following irradiation of human lymphocytes. By combining PCC with FISH it was possible to study the process of exchange ...
Demography, life tables and survivorship curves
... Rates of dispersal between populations Sex ratio Population size Number of individuals that contribute to a population’s gene pool Can be determined by Capture-Recapture Method for mobile species Capture-recapture method Sample small number and extrapolate Capture, mark, and release indi ...
... Rates of dispersal between populations Sex ratio Population size Number of individuals that contribute to a population’s gene pool Can be determined by Capture-Recapture Method for mobile species Capture-recapture method Sample small number and extrapolate Capture, mark, and release indi ...
Novel Molecular Methods for Discovery and Engineering of
... general, involves four main steps. First, a metagenomic library containing a pool of biocatalyst-encoding genes is constructed from a marine environment, which can be done by various methods, including cloning of enzymatically-digested DNA, uncut DNA, and PCR-amplified products. Second, the metageno ...
... general, involves four main steps. First, a metagenomic library containing a pool of biocatalyst-encoding genes is constructed from a marine environment, which can be done by various methods, including cloning of enzymatically-digested DNA, uncut DNA, and PCR-amplified products. Second, the metageno ...
Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics of Bone and Soft
... Both tumors with specific translocations and those without (Table II) have been shown to have numerous cytogenetic and molecular changes. In the case of the former tumors, this may be indicative of biologic tumor progression; in the case of the latter tumors, some of the changes may be primary and c ...
... Both tumors with specific translocations and those without (Table II) have been shown to have numerous cytogenetic and molecular changes. In the case of the former tumors, this may be indicative of biologic tumor progression; in the case of the latter tumors, some of the changes may be primary and c ...
Essentials of Genetics 6/e - Greenville Technical College
... Quantitative Traits Can Be Explained in Mendelian Terms • Multiple genes individually behave in ...
... Quantitative Traits Can Be Explained in Mendelian Terms • Multiple genes individually behave in ...
Regulation of biosynthesis and transport of aromatic amino acids in
... Genes forming one candidate operon (with spacer less than 100 bp) are separated by dashes ‘-’. Larger spacers between genes are marked by ‘^’. Operons from di¡erent loci, if shown in one column, are separated by a semicolon ‘ ;’. Known and predicted regulatory elements (PCE, TRAP, T-trp, T-tyr and T ...
... Genes forming one candidate operon (with spacer less than 100 bp) are separated by dashes ‘-’. Larger spacers between genes are marked by ‘^’. Operons from di¡erent loci, if shown in one column, are separated by a semicolon ‘ ;’. Known and predicted regulatory elements (PCE, TRAP, T-trp, T-tyr and T ...
National 5 Biology Unit 2 – Multicellular Organisms
... specialised cells in plants I can state that meristems are involved in plant growth I can state that meristems produce cells that can become specialised into any plant cell type I can state that meristems are the only points in plants where cell division happens ...
... specialised cells in plants I can state that meristems are involved in plant growth I can state that meristems produce cells that can become specialised into any plant cell type I can state that meristems are the only points in plants where cell division happens ...
The true ramifications of genetic criminality research
... knowledge’13, propositions about genetic causation would have to tend towards (1), (2) or (3). Such contentions would be akin, for instance, to former Science editor Daniel Koshland saying: the brain is an organ like other organs… it can go wrong not only as the result of abuse, but also because of ...
... knowledge’13, propositions about genetic causation would have to tend towards (1), (2) or (3). Such contentions would be akin, for instance, to former Science editor Daniel Koshland saying: the brain is an organ like other organs… it can go wrong not only as the result of abuse, but also because of ...
Click
... mber of probes to the gene RNA. RNA-seq gene expression as the fraction of aligned reads that can be assigned to the before expression e Expression estimator value ...
... mber of probes to the gene RNA. RNA-seq gene expression as the fraction of aligned reads that can be assigned to the before expression e Expression estimator value ...
Chromosome number 2
... a threshold number of copies is reached. ◦ iv.Amplification of CGG repeats occurs only in females, perhaps during a slipped mispairing process during DNA replication. ◦ v. The FMR-1 product (FMRP) is an RNA-binding protein. The triplet repeat expansion in FMR-1 affects expression of certain mRNAs, b ...
... a threshold number of copies is reached. ◦ iv.Amplification of CGG repeats occurs only in females, perhaps during a slipped mispairing process during DNA replication. ◦ v. The FMR-1 product (FMRP) is an RNA-binding protein. The triplet repeat expansion in FMR-1 affects expression of certain mRNAs, b ...
super bug
... implications are uncertain. Multi drug-resistant bacteria have been around for decades. In fact, the so called “super bug” is not actually a bug at all. Instead, the drug resistance comes from a gene called NDM-1 that gets passed from one kind of bacteria to another. These genes have sparked even mo ...
... implications are uncertain. Multi drug-resistant bacteria have been around for decades. In fact, the so called “super bug” is not actually a bug at all. Instead, the drug resistance comes from a gene called NDM-1 that gets passed from one kind of bacteria to another. These genes have sparked even mo ...
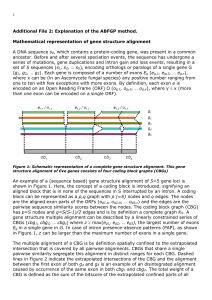
Abstract - BioMed Central
... Figure 3d: Position Specific Scoring Matrix representation of the canonical translational start site in fungi (WebLogo) Intron identification is performed by looking at intron PAPs and at splice sites that are positionally conserved. The nodes in splice site graphs are putative donor- and acceptor s ...
... Figure 3d: Position Specific Scoring Matrix representation of the canonical translational start site in fungi (WebLogo) Intron identification is performed by looking at intron PAPs and at splice sites that are positionally conserved. The nodes in splice site graphs are putative donor- and acceptor s ...