DETERMINING THE LOCATION OF GENES IN DROSOPHILA
... Genetics is the branch of biology concerned with heredity and variation (Cumming and Klug, 2000, p.5). Heredity is the passing of traits from a parent to an offspring. For example, handedness, the preference of using one hand over the other, is a trait that can be passed down from parents to their o ...
... Genetics is the branch of biology concerned with heredity and variation (Cumming and Klug, 2000, p.5). Heredity is the passing of traits from a parent to an offspring. For example, handedness, the preference of using one hand over the other, is a trait that can be passed down from parents to their o ...
Dual-Tagging Gene Trap of Novel Genes in Drosophila
... gene-trap vectors). Therefore, unless a reliable detection method for gene-trap events is available, more studies need to be carried out to obtain a comparable number of positive lines. To overcome this problem, we use two independent markers, mini-white (w) and Gal4 genes, as a “dual tag” for the t ...
... gene-trap vectors). Therefore, unless a reliable detection method for gene-trap events is available, more studies need to be carried out to obtain a comparable number of positive lines. To overcome this problem, we use two independent markers, mini-white (w) and Gal4 genes, as a “dual tag” for the t ...
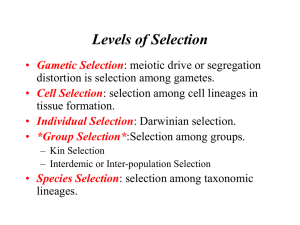
Slide 1
... Selection of diseases and training genes for the cross-validation: • For the cross-validation experiment, diseases in OMIM, to which at least 8 causative genes were assigned, were included. Automated HUGO-to-Ensembl mapping reduced the number of genes for a few diseases. The smallest gene set (ALS) ...
... Selection of diseases and training genes for the cross-validation: • For the cross-validation experiment, diseases in OMIM, to which at least 8 causative genes were assigned, were included. Automated HUGO-to-Ensembl mapping reduced the number of genes for a few diseases. The smallest gene set (ALS) ...
Lab Investigation: Examining a Single Gene
... 1. Label the PCR tube so that you can distinguish DNA from the Amp plates with glowing bacteria, or DNA from the Amp plates with nonglowing bacteria. 2. Add 5µl primer of each primer to each tube. If necessary, gently tap you tube on the counter to get all of the liquid to the bottom of the tube. 3. ...
... 1. Label the PCR tube so that you can distinguish DNA from the Amp plates with glowing bacteria, or DNA from the Amp plates with nonglowing bacteria. 2. Add 5µl primer of each primer to each tube. If necessary, gently tap you tube on the counter to get all of the liquid to the bottom of the tube. 3. ...
Mitosis and Meiosis
... in metaphase and anaphase of mitosis. In the metaphase cell, there are 4 chromosomes (8 chromatids) total and two sets of homologous chromosomes that are duplicated. In the anaphase cell, there are 8 chromosomes. The resulting daughter cells will also be diploid and genetically identical to the moth ...
... in metaphase and anaphase of mitosis. In the metaphase cell, there are 4 chromosomes (8 chromatids) total and two sets of homologous chromosomes that are duplicated. In the anaphase cell, there are 8 chromosomes. The resulting daughter cells will also be diploid and genetically identical to the moth ...
Ancient Structure in Africa Unlikely to Explain Neanderthal and Non
... between the ancestors of present-day Africans and nonAfricans would be sufficiently high until the out-of-Africa event, thus making the Africans and non-Africans more genetically similar to one another than either is to Neanderthals. In this model, no later interbreeding between Neanderthals and ear ...
... between the ancestors of present-day Africans and nonAfricans would be sufficiently high until the out-of-Africa event, thus making the Africans and non-Africans more genetically similar to one another than either is to Neanderthals. In this model, no later interbreeding between Neanderthals and ear ...
Meiosis - My Haiku
... Haploid – 1 copy of each chromosome (N) Diploid – 2 copies of each chromosome (2N) ...
... Haploid – 1 copy of each chromosome (N) Diploid – 2 copies of each chromosome (2N) ...
Guidelines for genetic studies in single patients
... Further, at least 1,500 Mendelian conditions lack a defined genetic etiology. Purely sporadic conditions in non-consanguineous families may also be caused by familial single-gene defects (of incomplete penetrance) or by de novo mutations (of complete penetrance) causing disease by various mechanism ...
... Further, at least 1,500 Mendelian conditions lack a defined genetic etiology. Purely sporadic conditions in non-consanguineous families may also be caused by familial single-gene defects (of incomplete penetrance) or by de novo mutations (of complete penetrance) causing disease by various mechanism ...
guidelines for usage of the vetgen dna marker
... dark about JRD1 (B or B allele) we must test but use the information wisely. Clearly we need a Marker for the different JRD2 alleles also. This will allow greater flexibility for different mating combinations and ensuring we do not produce affected offspring. Recommendations 1) Test all individuals ...
... dark about JRD1 (B or B allele) we must test but use the information wisely. Clearly we need a Marker for the different JRD2 alleles also. This will allow greater flexibility for different mating combinations and ensuring we do not produce affected offspring. Recommendations 1) Test all individuals ...
Haemoglobinopathies in Southeast Asia
... and β-thalassaemia/Hb E; Hb H-CS (α-thalassaemia 1/Hb CS) and homozygous Hb E; and Hb H-CS (α-thalassaemia 1/Hb CS) and β-thalassaemia/Hb E. Among these, Hb H-CS (a-thalassaemia 1/Hb CS) and homozygous Hb E patients are most common. A possible reason is that the presence of Hb CS leads to a more s ...
... and β-thalassaemia/Hb E; Hb H-CS (α-thalassaemia 1/Hb CS) and homozygous Hb E; and Hb H-CS (α-thalassaemia 1/Hb CS) and β-thalassaemia/Hb E. Among these, Hb H-CS (a-thalassaemia 1/Hb CS) and homozygous Hb E patients are most common. A possible reason is that the presence of Hb CS leads to a more s ...
Lesson Plans
... sexual reproduction. When the single alleles that each parent can contribute are written along the top and side of the table (see Figure 1 on page D-41 in the Student Book), the formation of sex cells is implied. When one allele from each parent is transferred to a box within the table (see Figure 2 ...
... sexual reproduction. When the single alleles that each parent can contribute are written along the top and side of the table (see Figure 1 on page D-41 in the Student Book), the formation of sex cells is implied. When one allele from each parent is transferred to a box within the table (see Figure 2 ...
Genetics and Probability Practice Problems
... 3. True-breeding tall red-flowered plants are crossed with dwarf white-flowered plants. The resulting F1 generation consists of all tall pink-flowered plants. Assuming that height and flower color are each determined by a single gene locus, predict the results of an F1 cross of the TtRr plants. List ...
... 3. True-breeding tall red-flowered plants are crossed with dwarf white-flowered plants. The resulting F1 generation consists of all tall pink-flowered plants. Assuming that height and flower color are each determined by a single gene locus, predict the results of an F1 cross of the TtRr plants. List ...
Direct measurement of electrical transport through DNA molecules
... states7,8, which could, for example, be associated with the base pairs. The hopping process could be either unidirectional or involve one-dimensional diffusion. It can be argued that the back-and-forth diffusive hopping8 is less likely in our case due to the high electric ®elds used, which will tilt ...
... states7,8, which could, for example, be associated with the base pairs. The hopping process could be either unidirectional or involve one-dimensional diffusion. It can be argued that the back-and-forth diffusive hopping8 is less likely in our case due to the high electric ®elds used, which will tilt ...
Cognitvie Psychology
... an immediate “calming” effect on baby rats in the first week after birth a long-term reduction in stress responsiveness ...
... an immediate “calming” effect on baby rats in the first week after birth a long-term reduction in stress responsiveness ...
A Modified Genetic Algorithm for Matching Building Sets with the
... in a database of polygon features, represented in the coordinate system of the scene. From this information, we calculate the HoF between any two buildings. As the size of the search area increases, the number of possible building pairs grows at a rate of !. To limit our search space, we only calcul ...
... in a database of polygon features, represented in the coordinate system of the scene. From this information, we calculate the HoF between any two buildings. As the size of the search area increases, the number of possible building pairs grows at a rate of !. To limit our search space, we only calcul ...
The role of humans in facilitating and sustaining coat
... determining coat colour and more than 300 genes have been identified that have an effect on pigmentation either directly or indirectly [11]. Most of these genes act on either the production or the regulation of two pigments, pheomelanin and eumelanin [8]. Both MC1R and ASIP act like switches, while K ...
... determining coat colour and more than 300 genes have been identified that have an effect on pigmentation either directly or indirectly [11]. Most of these genes act on either the production or the regulation of two pigments, pheomelanin and eumelanin [8]. Both MC1R and ASIP act like switches, while K ...
fog-1, a Regulatory Gene Required for Specification of
... make sperm continuously and never make oocytes (Figure 2, A and B ) , homozygous fog-l males make oocytes continuously and never make sperm (Figure 2, C and D).Similarly, whereas wild-type hermaphrodites make some sperm (about 160 per ovotestis) and then make oocytes continuously (Figure 3, A and B ...
... make sperm continuously and never make oocytes (Figure 2, A and B ) , homozygous fog-l males make oocytes continuously and never make sperm (Figure 2, C and D).Similarly, whereas wild-type hermaphrodites make some sperm (about 160 per ovotestis) and then make oocytes continuously (Figure 3, A and B ...
Topic To Know For Chapter 15
... 10. Know what is meant by multiple alleles. Use the ABO blood group as an example and illustrate how it works. Be able to give examples of how the different blood types are brought about. 11. Know what is meant by pleiotropy, epistasis, polygenic inheretance, and carriers. Also give examples of each ...
... 10. Know what is meant by multiple alleles. Use the ABO blood group as an example and illustrate how it works. Be able to give examples of how the different blood types are brought about. 11. Know what is meant by pleiotropy, epistasis, polygenic inheretance, and carriers. Also give examples of each ...
A GO annotation is
... • The Gene Ontology is always changing and GO annotations are continually being created - always use a current version of both - if publishing your analyses please report the versions/dates you used http://www.geneontology.org/GO.cite.shtml ...
... • The Gene Ontology is always changing and GO annotations are continually being created - always use a current version of both - if publishing your analyses please report the versions/dates you used http://www.geneontology.org/GO.cite.shtml ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The pace of Dr. Taub`s lectures have been
... • D: Recombination takes place at a high rate between two alleles ...
... • D: Recombination takes place at a high rate between two alleles ...
Copenhagen1 - Buffalo Ontology Site
... GDB: a gene is a DNA fragment that can be transcribed and translated into a protein Genbank: a gene is a DNA region of biological interest with a name and that carries a genetic trait or phenotype GO does not tell us which of these is correct, or indeed whether either is correct, and it does not tel ...
... GDB: a gene is a DNA fragment that can be transcribed and translated into a protein Genbank: a gene is a DNA region of biological interest with a name and that carries a genetic trait or phenotype GO does not tell us which of these is correct, or indeed whether either is correct, and it does not tel ...























