Human Genetics - Chapter 10
... • Explain how microRNAs control transcription • Explain how division of genes into exons and introns maximizes the number of encoded proteins • Discuss how viral DNA, noncoding RNAs and repeated sequences account for large proportions of the human genome ...
... • Explain how microRNAs control transcription • Explain how division of genes into exons and introns maximizes the number of encoded proteins • Discuss how viral DNA, noncoding RNAs and repeated sequences account for large proportions of the human genome ...
Evidence for massive gene exchange between archaeal and
... and have been retained owing to the specific selective advantage they provided by enabling the bacterium to thrive in high-temperature habitats. The presence of the same set of genes of apparent archaeal origin in the genomes of two or more ...
... and have been retained owing to the specific selective advantage they provided by enabling the bacterium to thrive in high-temperature habitats. The presence of the same set of genes of apparent archaeal origin in the genomes of two or more ...
Time Dependency of Molecular Rate Estimates and Systematic
... broadly uniform, with rates hovering around 0.01 substitutions per site per million years corresponding to the traditional sequence divergence rate of 2% per million years. This residual rate, which appears to stay constant over long periods of time, is probably due to two processes that are not mut ...
... broadly uniform, with rates hovering around 0.01 substitutions per site per million years corresponding to the traditional sequence divergence rate of 2% per million years. This residual rate, which appears to stay constant over long periods of time, is probably due to two processes that are not mut ...
MMG 232: Methods In Bioinformatics Spring 2016, 3 credits
... BLAST searches and Protein visualization Amplicon sequencing & OTU identification Inferring evolutionary history Metagenomics: the complete picture What have you learned so far? Structural changes & DNA integration: inversion/translocation & viral insertion The effects of differential gene expressio ...
... BLAST searches and Protein visualization Amplicon sequencing & OTU identification Inferring evolutionary history Metagenomics: the complete picture What have you learned so far? Structural changes & DNA integration: inversion/translocation & viral insertion The effects of differential gene expressio ...
Biology EOC Review
... 6. The gene for tallness (T) is dominant over the gene for shortness (t) in pea plants. A homozygous dominant pea plant is crossed with a heterozygous pea plant, and 200 seeds are produced. Approximately how many of these seeds can be expected to produce plants that are homozygous dominant? ...
... 6. The gene for tallness (T) is dominant over the gene for shortness (t) in pea plants. A homozygous dominant pea plant is crossed with a heterozygous pea plant, and 200 seeds are produced. Approximately how many of these seeds can be expected to produce plants that are homozygous dominant? ...
Milestone2
... The GC content of a genome is the percentage of nucleotides in the genome that are either guanines or cytosines. Different genomes have widely varying GC contents. For example, the genomes of the bacteria Anaeromyxobacter have a GC content of about 75%, whereas the genomes of the bacteria Buchnera h ...
... The GC content of a genome is the percentage of nucleotides in the genome that are either guanines or cytosines. Different genomes have widely varying GC contents. For example, the genomes of the bacteria Anaeromyxobacter have a GC content of about 75%, whereas the genomes of the bacteria Buchnera h ...
A novel gene encoding a 54 kDa polypeptide is
... method takes time and can cover only limited types of bacteria, and selection, being a growth-dependent process, may miss out organisms which require different media or temperatures. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies have proved to be more reliable and easy to use for detection of target organism ...
... method takes time and can cover only limited types of bacteria, and selection, being a growth-dependent process, may miss out organisms which require different media or temperatures. Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies have proved to be more reliable and easy to use for detection of target organism ...
et al - International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary
... these proteins was previously available from only a limited number of actinobacteria, whose genomes have been sequenced. One possible signature for actinobacteria, consisting of a large insert in the 23S rRNA, has previously been described (Roller et al., 1992). However, the validity and specificity ...
... these proteins was previously available from only a limited number of actinobacteria, whose genomes have been sequenced. One possible signature for actinobacteria, consisting of a large insert in the 23S rRNA, has previously been described (Roller et al., 1992). However, the validity and specificity ...
DCW11, Down-Regulated Gene 11 in CW-Type
... DCW11 is involved in pollen germination DCW11 encodes PP2C targeted to mitochondria. The function of DCW11 or an ortholog of Arabidopsis has not yet been elucidated. We have analyzed the expressional and functional characters of DCW11 in wild-type rice. Knockdown of DCW11 resulted in reduced seed se ...
... DCW11 is involved in pollen germination DCW11 encodes PP2C targeted to mitochondria. The function of DCW11 or an ortholog of Arabidopsis has not yet been elucidated. We have analyzed the expressional and functional characters of DCW11 in wild-type rice. Knockdown of DCW11 resulted in reduced seed se ...
Document
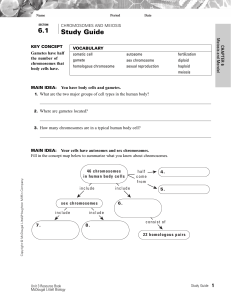
... KEY CONCEPT Genes encode proteins that produce a diverse range of traits. A gene is a segment of DNA that tells the cell how to make a particular polypeptide. The location of a gene on a chromosome is called a locus. A gene has the same locus on both chromosomes in a pair of homologous chromosomes. ...
... KEY CONCEPT Genes encode proteins that produce a diverse range of traits. A gene is a segment of DNA that tells the cell how to make a particular polypeptide. The location of a gene on a chromosome is called a locus. A gene has the same locus on both chromosomes in a pair of homologous chromosomes. ...
Principle of TAIL-PCR
... indicating that these were non-specific type II products Specific products were not always seen in the primary reactions due to their low concentration. However, these specific products becomes visible after the subsequent secondary reaction ...
... indicating that these were non-specific type II products Specific products were not always seen in the primary reactions due to their low concentration. However, these specific products becomes visible after the subsequent secondary reaction ...
Foundations of Biology
... Syndrome, extra chromosome 21, tends to be the most viable Down’s Syndrome is more common in children of mothers who gave birth after age 40 ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
... Syndrome, extra chromosome 21, tends to be the most viable Down’s Syndrome is more common in children of mothers who gave birth after age 40 ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
1 MendelHandout
... Mendelian Analysis • branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation. • explains life at the level of molecules, organisms, and the populations. • relationship between genes and traits. • This course will take us from Mendel’s observations that led to the basic laws of genetics, to the n ...
... Mendelian Analysis • branch of biology that deals with heredity and variation. • explains life at the level of molecules, organisms, and the populations. • relationship between genes and traits. • This course will take us from Mendel’s observations that led to the basic laws of genetics, to the n ...
How to optimize carotenoid production. David D. Perkins Background
... 1996), gene silencing (Romano and Macino 1992), carotenoid biosynthesis (Harding and Turner 1981, Perkins et al. 2001), and readily visualized allelic variation (Perkins 1989). Alterations in both external conditions (Harding 1974) and genotype (Shrode et al. 2001) can be used to intensify the pigme ...
... 1996), gene silencing (Romano and Macino 1992), carotenoid biosynthesis (Harding and Turner 1981, Perkins et al. 2001), and readily visualized allelic variation (Perkins 1989). Alterations in both external conditions (Harding 1974) and genotype (Shrode et al. 2001) can be used to intensify the pigme ...
Import of genetically modified carnation `Moonaqua`
... This carnation variety is admitted and has already gone into commercial production in Colombia and Ecuador. A similar transgenic carnation variety, named ‘Moondust’ has already been approved for commercial production within the EU. In the environmental risk assessment the probability of gene dispers ...
... This carnation variety is admitted and has already gone into commercial production in Colombia and Ecuador. A similar transgenic carnation variety, named ‘Moondust’ has already been approved for commercial production within the EU. In the environmental risk assessment the probability of gene dispers ...
*************P*********************************************** *I***J***K
... Independent Assortment The Principle of Independent Assortment: The alleles of different genes segregate, or as we sometimes say, assort, independently of each other. Principios de Mendel: - Dominancia - Segregación - Sorteo Objetivos ...
... Independent Assortment The Principle of Independent Assortment: The alleles of different genes segregate, or as we sometimes say, assort, independently of each other. Principios de Mendel: - Dominancia - Segregación - Sorteo Objetivos ...
Mendel and his Peas Sept.1, 2010 Lecture Learning Objectives: You
... 2. Consider a hypothetical flowering plant that can have red or green flowers and tall or short stems. For the flower color, green is dominant to red, and tall stems are dominant to short stems. Predict the phenotypic ratios for the following crosses a. Green tall (GGTT) x red short (ggtt) ...
... 2. Consider a hypothetical flowering plant that can have red or green flowers and tall or short stems. For the flower color, green is dominant to red, and tall stems are dominant to short stems. Predict the phenotypic ratios for the following crosses a. Green tall (GGTT) x red short (ggtt) ...
Trachemys scripta elegans Red-Eared Turtle ( Fc)
... (encoded by the g and ε genes, respectively) expressed only by mammals. Because of the functional similarities and relatively high levels of sequence homology between y, g and ε genes, the y gene is thought to be the evolutionary precursor of the mammalian g and ε genes and may have diversified thro ...
... (encoded by the g and ε genes, respectively) expressed only by mammals. Because of the functional similarities and relatively high levels of sequence homology between y, g and ε genes, the y gene is thought to be the evolutionary precursor of the mammalian g and ε genes and may have diversified thro ...
Chromosomal Clustering of Periodically Expressed Genes
... noted that some of the oligonucleotides in the training sample had PVE values less than 0.7, which explains why the number of oligonucleotides in the combined training and testing samples does not equal the number of periodically expressed oligonucleotides selected). We built pairwise binary SVM cla ...
... noted that some of the oligonucleotides in the training sample had PVE values less than 0.7, which explains why the number of oligonucleotides in the combined training and testing samples does not equal the number of periodically expressed oligonucleotides selected). We built pairwise binary SVM cla ...
Semiconservative Replication in the Quasispecies Model
... mismatch probability ǫ{σ,σ̄} (a base-pair-independent mismatch probability is certainly a simplification, but it is an initial starting point). Different genomes may have different replication fidelities, due to various replication error correction mechanisms which may or may not be functioning. For ...
... mismatch probability ǫ{σ,σ̄} (a base-pair-independent mismatch probability is certainly a simplification, but it is an initial starting point). Different genomes may have different replication fidelities, due to various replication error correction mechanisms which may or may not be functioning. For ...
... the mutation of the p53 gene is an early event in head and neck carcinogenesis, preceding signs of overt neoplasia, and that different p53 mutations in multiple foci may be the molecular basis for the development of multiple tumours. The relationship between the point mutations of the p53 gene and c ...
Sex Determination
... Syndrome, extra chromosome 21, tends to be the most viable Down’s Syndrome is more common in children of mothers who gave birth after age 40 ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
... Syndrome, extra chromosome 21, tends to be the most viable Down’s Syndrome is more common in children of mothers who gave birth after age 40 ©2000 Timothy G. Standish ...
Messenger RNA
... 1c. Infer Why is it important for a single gene to be able to produce hundreds or thousands of the same RNA molecules? Proteins must be continuously synthesized in the cell, so the instructions coded in genes must be used over and over again. A single gene must be able to produce hundreds or thousa ...
... 1c. Infer Why is it important for a single gene to be able to produce hundreds or thousands of the same RNA molecules? Proteins must be continuously synthesized in the cell, so the instructions coded in genes must be used over and over again. A single gene must be able to produce hundreds or thousa ...
PersPecTIves - Ralf Sommer
... Particularly in the animal kingdom, with its deep branches and vast diversity of form and species, one can always look at new taxa and investigate their molecular inventory. If species are selected from a phylogenetic perspective, such studies can increase our understanding of the molecular evolutio ...
... Particularly in the animal kingdom, with its deep branches and vast diversity of form and species, one can always look at new taxa and investigate their molecular inventory. If species are selected from a phylogenetic perspective, such studies can increase our understanding of the molecular evolutio ...