Influence of Mutation Type and Location on Phenotype
... Rett syndrome (RTT) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that almost exclusively affects girls. It is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene that encodes the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). In this study we correlated mutation type and location with the severity of the phenotype in 123 girls with R ...
... Rett syndrome (RTT) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that almost exclusively affects girls. It is caused by mutations in the MECP2 gene that encodes the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MeCP2). In this study we correlated mutation type and location with the severity of the phenotype in 123 girls with R ...
Example - Hivebench
... stability. Primers with melting temperatures in the range of 52-58 oC generally produce the best results. Primers with melting temperatures above 65oC have a tendency for secondary annealing. The GC content of the sequence gives a fair indication of the Tm. 3. Primer annealing temperature: The prime ...
... stability. Primers with melting temperatures in the range of 52-58 oC generally produce the best results. Primers with melting temperatures above 65oC have a tendency for secondary annealing. The GC content of the sequence gives a fair indication of the Tm. 3. Primer annealing temperature: The prime ...
msc_botnay_pre_pap1_bl2
... Nucleus controls cellular differentiation by regulating differential gene expression ...
... Nucleus controls cellular differentiation by regulating differential gene expression ...
Dentinogenesis imperfecta type II
... Types of dentinogenesis imperfecta with similar dental formalities usually an autosomal dominant trait with variable expressivity but can be recessive if the associated osteogenesis imperfecta is of recessive type. This is type l. Type II : Occurs in people without other inherited disorders (i.e. Os ...
... Types of dentinogenesis imperfecta with similar dental formalities usually an autosomal dominant trait with variable expressivity but can be recessive if the associated osteogenesis imperfecta is of recessive type. This is type l. Type II : Occurs in people without other inherited disorders (i.e. Os ...
Distinguishing Different DNA Heterozygotes by
... them. In our study, high-resolution melting of small amplicons distinguished all heterozygotes studied. This included 21 pairwise comparisons, suggesting that most randomly selected heterozygotes within small amplicons can be distinguished. The power of melting analysis to distinguish multiple seque ...
... them. In our study, high-resolution melting of small amplicons distinguished all heterozygotes studied. This included 21 pairwise comparisons, suggesting that most randomly selected heterozygotes within small amplicons can be distinguished. The power of melting analysis to distinguish multiple seque ...
16 • Bad species
... not conform to criteria used to delimit species. The advent of numerical taxonomy and cladistics has upset earlier taxonomic certainty and two different consensuses seem to be building among evolutionary biologists. The species concept either (a) takes the form of a minimal, Darwinian, definition whi ...
... not conform to criteria used to delimit species. The advent of numerical taxonomy and cladistics has upset earlier taxonomic certainty and two different consensuses seem to be building among evolutionary biologists. The species concept either (a) takes the form of a minimal, Darwinian, definition whi ...
A-level Biology B Question paper Unit 4 - Energy, Control and
... (b) On the diagram, use label lines and letters to show (i) with E, where electron transport chains are found (ii) with K, where the Krebs cycle occurs. (2 marks) (c) Cyanide prevents oxygen acting as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Explain how cyanide stops ATP producti ...
... (b) On the diagram, use label lines and letters to show (i) with E, where electron transport chains are found (ii) with K, where the Krebs cycle occurs. (2 marks) (c) Cyanide prevents oxygen acting as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. Explain how cyanide stops ATP producti ...
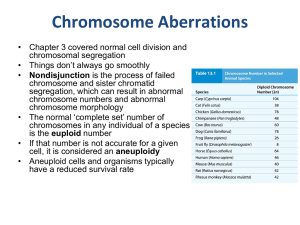
Chromosome Aberrations
... viable but infertile • Chromosome pairs sets are not homologous and cannot synapse properly in meiosis • Chromosome nondisjunction can resolve this problem, the doubled chromosomes have homologs for pairing during synapsis hybrid is fertile ...
... viable but infertile • Chromosome pairs sets are not homologous and cannot synapse properly in meiosis • Chromosome nondisjunction can resolve this problem, the doubled chromosomes have homologs for pairing during synapsis hybrid is fertile ...
Revisiting the Impact of Inversions in Evolution
... where the interacting loci reside (Nei 1967, Pepper 2003). Because inversion polymorphisms generate low recombination rates among the standard (noninverted) and inverted arrangements, they facilitate the spread of the coadapted alleles. Inversions carrying favorable alleles then spread to fixation un ...
... where the interacting loci reside (Nei 1967, Pepper 2003). Because inversion polymorphisms generate low recombination rates among the standard (noninverted) and inverted arrangements, they facilitate the spread of the coadapted alleles. Inversions carrying favorable alleles then spread to fixation un ...
Identification of genes involved in the same
... Ravasz and Barabási, 2002; Ravasz et al., 2002). Detecting these functional modules, learning how functions are carried out in detail and how individual functional modules relate to each other, are current research topics in this field (Barabási and Oltavi, 2004; Wu et al., 2005). Modularity is reco ...
... Ravasz and Barabási, 2002; Ravasz et al., 2002). Detecting these functional modules, learning how functions are carried out in detail and how individual functional modules relate to each other, are current research topics in this field (Barabási and Oltavi, 2004; Wu et al., 2005). Modularity is reco ...
Difference Mechanisms - Philsci-Archive
... generates a causal explanation for the phenomenon under investigation (Bechtel and Richardson 1993; Glennan 2002; Little 1990; Machamer, Darden, and Craver 2000; Schaffner 1993; Woodward 2002). There are differences between the various accounts of a mechanism.3 But the accounts hold in common the ba ...
... generates a causal explanation for the phenomenon under investigation (Bechtel and Richardson 1993; Glennan 2002; Little 1990; Machamer, Darden, and Craver 2000; Schaffner 1993; Woodward 2002). There are differences between the various accounts of a mechanism.3 But the accounts hold in common the ba ...
UNIVERSITAT ROVIRA I VIRGILI MOLECUAR COMPUTING METHODS FOR NATURAL LANGUAGE SYNTAX ISBN:978-84-691-1896-2/D.L:T-352-2008
... The first step from DNA to RNA consists simply of a monoenchainment of the information. Two strings become one by means of a process that does not entail any interpretation. The second step, whose physic basis is the RNA, transforms RNA into a new information, by means of a semantic mechanism of mea ...
... The first step from DNA to RNA consists simply of a monoenchainment of the information. Two strings become one by means of a process that does not entail any interpretation. The second step, whose physic basis is the RNA, transforms RNA into a new information, by means of a semantic mechanism of mea ...
Identification of Potential Corynebacterium ammoniagenes Purine
... Regulation of purE-lacZ and purF-lacZ Reporters by C. ammoniagenes gDNA Clones in E. coli The dependence of purines in the regulation of purE-lacZ and purF-lacZ was characterized by the candidate C. ammoniagenes gDNA clones involved in pur reporter repression. The 3 candidate clones (“E-7”, “E-32”, ...
... Regulation of purE-lacZ and purF-lacZ Reporters by C. ammoniagenes gDNA Clones in E. coli The dependence of purines in the regulation of purE-lacZ and purF-lacZ was characterized by the candidate C. ammoniagenes gDNA clones involved in pur reporter repression. The 3 candidate clones (“E-7”, “E-32”, ...
PREIMPLANTATION GENETIC DIAGNOSIS
... from a donor who is not a carrier of the disorder. In most countries, sperm donation is more easily available than egg donation owing to the difficulty in recruiting egg donors and to the rigours of ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval (see below for details). For X-linked disorders, there is the p ...
... from a donor who is not a carrier of the disorder. In most countries, sperm donation is more easily available than egg donation owing to the difficulty in recruiting egg donors and to the rigours of ovarian stimulation and egg retrieval (see below for details). For X-linked disorders, there is the p ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Chapter 27 Bacteria and Archaea Concept
... Many prokaryotes are decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter. Many prokaryotes are symbiotic, forming crucial relationships with other species. Some prokaryotes are pathogenic and cause illness by producing poisons. Antibiotics are chemicals that can kill prokaryotes. They are NOT effec ...
... Many prokaryotes are decomposers, breaking down dead organic matter. Many prokaryotes are symbiotic, forming crucial relationships with other species. Some prokaryotes are pathogenic and cause illness by producing poisons. Antibiotics are chemicals that can kill prokaryotes. They are NOT effec ...
RRR…Replicate 10
... nucleotides according to the base pairing rule 3)Ligase: “glues” the bases back together ...
... nucleotides according to the base pairing rule 3)Ligase: “glues” the bases back together ...
Document
... sequence. This assumption is reasonable if editing is relatively inexpensive, because in this case most editing sites will be random in nature rather than involve some other biological factors. Comparing our results with the actual codon bias data then reveals if this assumption is true or if there ...
... sequence. This assumption is reasonable if editing is relatively inexpensive, because in this case most editing sites will be random in nature rather than involve some other biological factors. Comparing our results with the actual codon bias data then reveals if this assumption is true or if there ...
PDF - 2.3 MB
... Phage T4 expresses an enzyme tysozyme, which enabtes phage to lyse infected ceils. Mutations in the lysozyme gene can prevent T4 from forming a plaques on a lawn of E. coil. You have isolated two T4 mutants that can not make plaques on wild type (Su-), but that can make plaques on an E. co//strain c ...
... Phage T4 expresses an enzyme tysozyme, which enabtes phage to lyse infected ceils. Mutations in the lysozyme gene can prevent T4 from forming a plaques on a lawn of E. coil. You have isolated two T4 mutants that can not make plaques on wild type (Su-), but that can make plaques on an E. co//strain c ...
PDF
... mutually exclusive expression, with the single expressed var gene determining the antigenic, cytoadherent, and virulence phenotype of the infected cell. The mutually exclusive expression pattern of var genes is imperative for the parasite’s ability to evade the host’s immune response and is similar ...
... mutually exclusive expression, with the single expressed var gene determining the antigenic, cytoadherent, and virulence phenotype of the infected cell. The mutually exclusive expression pattern of var genes is imperative for the parasite’s ability to evade the host’s immune response and is similar ...
PTC Tasting and Evolution
... If AA = homozygous non tasters, then If AP mates with AP, what percent of their children will be – Tasters – Nontasters ...
... If AA = homozygous non tasters, then If AP mates with AP, what percent of their children will be – Tasters – Nontasters ...
- Free Documents
... what is the chance of producing an offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype A B C D E Answer C Topic Concept . one for head shape H and one for tail length T. but the F generation as well. E many of the F progeny died. making statistical analysis difficult. because A he obtained very few F ...
... what is the chance of producing an offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype A B C D E Answer C Topic Concept . one for head shape H and one for tail length T. but the F generation as well. E many of the F progeny died. making statistical analysis difficult. because A he obtained very few F ...
2001-2002
... Code bloat is the phenomena whereby the size of the program is disproportionate to the function it performs. For example, a program might represent X^2 but take a parse tree of depth 10, with a total number of nodes exceeding 1000. 4 marks There are some mechanisms to control code bloat. For example ...
... Code bloat is the phenomena whereby the size of the program is disproportionate to the function it performs. For example, a program might represent X^2 but take a parse tree of depth 10, with a total number of nodes exceeding 1000. 4 marks There are some mechanisms to control code bloat. For example ...
Genome-wide identification and analysis of the SGR
... where it is bound in CHL-protein complexes (Markwell et al., 1979). The protein components of the two photosystems are structurally organized into morphologically distinct membrane subunits (Arntzen, 1978), including photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII) reaction center complexes (Kusaba et ...
... where it is bound in CHL-protein complexes (Markwell et al., 1979). The protein components of the two photosystems are structurally organized into morphologically distinct membrane subunits (Arntzen, 1978), including photosystem I (PSI) and photosystem II (PSII) reaction center complexes (Kusaba et ...
Hemophilia
... attributed to mild or moderate phenotypes but sometimes occur in less than 20% of individuals with severe hemophilia A. Hemophilia B has a mutation at the chromosomal locus Xq27.1-q27.2 which alters the functional protein produced by the factor IX gene, coagulation factor IX. The mutation often resu ...
... attributed to mild or moderate phenotypes but sometimes occur in less than 20% of individuals with severe hemophilia A. Hemophilia B has a mutation at the chromosomal locus Xq27.1-q27.2 which alters the functional protein produced by the factor IX gene, coagulation factor IX. The mutation often resu ...