Slide 1
... • Simplest, fairest and most widely used • Each process is assigned a quantum (time interval) which it is allowed to run • If the process is still running at the end of quantum, the CPU is preempted and given to another process • Also the CPU switches when a process blocks ...
... • Simplest, fairest and most widely used • Each process is assigned a quantum (time interval) which it is allowed to run • If the process is still running at the end of quantum, the CPU is preempted and given to another process • Also the CPU switches when a process blocks ...
03_shells_and_processes
... multiprogramming and multitasking – Multiprogramming systems switch the running process when that process requires I/O. – Multitasking systems periodically switch the running process after some (typically minute) period of time ...
... multiprogramming and multitasking – Multiprogramming systems switch the running process when that process requires I/O. – Multitasking systems periodically switch the running process after some (typically minute) period of time ...
Chapter_7
... -Batch Systems. The programmer does not have any control or interactions during the execution of his Jobs (programs). -Time-Sharing Systems efficiently use computer resources because it allows several programs to share resources. Each program is allowed to use the resource only if it is available a ...
... -Batch Systems. The programmer does not have any control or interactions during the execution of his Jobs (programs). -Time-Sharing Systems efficiently use computer resources because it allows several programs to share resources. Each program is allowed to use the resource only if it is available a ...
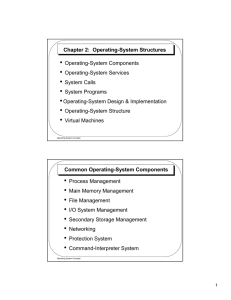
Chapter 2: Operating-System Structures • Operating-System
... compiled, it must be loaded into memory to be executed. The system may provide loaders, linkage editors and debuggers. – Communications: Programs provide mechanism for creating virtual connections among processes, users, and computer systems, such as sending messages and transferring files. Operatin ...
... compiled, it must be loaded into memory to be executed. The system may provide loaders, linkage editors and debuggers. – Communications: Programs provide mechanism for creating virtual connections among processes, users, and computer systems, such as sending messages and transferring files. Operatin ...
Introduction to Operating Systems (continued)
... • The distillation of a complex mechanism into a simple, conceptual model • User of abstraction does not need to worry about details • Implementer of abstraction does not need to worry about how user will use it (within limits) CS-2301 B-term 2008 ...
... • The distillation of a complex mechanism into a simple, conceptual model • User of abstraction does not need to worry about details • Implementer of abstraction does not need to worry about how user will use it (within limits) CS-2301 B-term 2008 ...
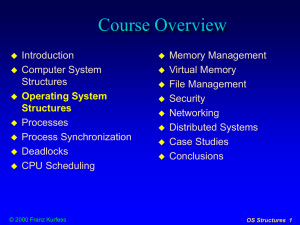
Course Overview
... Files that consist of ASCII characters -> text files All other files -> binary files (e.g., 35 is a part of a ...
... Files that consist of ASCII characters -> text files All other files -> binary files (e.g., 35 is a part of a ...
Operating System Overview
... – File open, close, read and write – Control the CPU, or a single user takes over by doing while ( 1 ) ; ...
... – File open, close, read and write – Control the CPU, or a single user takes over by doing while ( 1 ) ; ...
Chapter03
... • Processor is faster than I/O so all processes could be waiting for I/O • Swap these processes to disk to free up more memory • Blocked state becomes suspend state when swapped to disk • Two new states – Blocked/Suspend – Ready/Suspend ...
... • Processor is faster than I/O so all processes could be waiting for I/O • Swap these processes to disk to free up more memory • Blocked state becomes suspend state when swapped to disk • Two new states – Blocked/Suspend – Ready/Suspend ...
PPT - Defcon
... • Although scheduling code to run is based upon threads, when the kernel reports what is running on the system, it reports based upon EPROCESS blocks which can be modified with no adverse affect. This is what current tools (IDS/IPS’s) rely upon to discover what is running on the system. ...
... • Although scheduling code to run is based upon threads, when the kernel reports what is running on the system, it reports based upon EPROCESS blocks which can be modified with no adverse affect. This is what current tools (IDS/IPS’s) rely upon to discover what is running on the system. ...
How-OS-Works.pdf
... When the computer is turned on, the BIOS locates the operating system on the hard drive, and transfers the core parts into memory, RAM. If a command line is used, a file named autoexec.bat is executed, to configure the system for the user. Steps in most autoexec.bat files @echo off Suppress the disp ...
... When the computer is turned on, the BIOS locates the operating system on the hard drive, and transfers the core parts into memory, RAM. If a command line is used, a file named autoexec.bat is executed, to configure the system for the user. Steps in most autoexec.bat files @echo off Suppress the disp ...
13. Operating Systems
... A hardware platform may support a variety of operating systems An operating system may work on a variety of platforms A standard operating system that works on different hardware Provides program and file portability Enables user efficiency through recognizable interface Is implemented t ...
... A hardware platform may support a variety of operating systems An operating system may work on a variety of platforms A standard operating system that works on different hardware Provides program and file portability Enables user efficiency through recognizable interface Is implemented t ...
Chapter 10 Multiprocessor and Real
... multiprocessor provides the same service as a multiprogrammed uniprocessor because more than one processor is available, average response time to the users will be less ...
... multiprocessor provides the same service as a multiprogrammed uniprocessor because more than one processor is available, average response time to the users will be less ...
Lec3
... – Program Counter (PC) – Registers (Integer, Floating point, others…?) – Save PC and registers in current state block – Load PC and registers from new state block – Timer, voluntary yield, I/O, other things ...
... – Program Counter (PC) – Registers (Integer, Floating point, others…?) – Save PC and registers in current state block – Load PC and registers from new state block – Timer, voluntary yield, I/O, other things ...
Chapter 9
... • Microkernel systems provide better security, easier maintenance, and portability at the expense of execution speed. – Examples are Windows 2000, Mach, and QNX. – Symmetric multiprocessor computers are ideal platforms for microkernel operating systems. ...
... • Microkernel systems provide better security, easier maintenance, and portability at the expense of execution speed. – Examples are Windows 2000, Mach, and QNX. – Symmetric multiprocessor computers are ideal platforms for microkernel operating systems. ...
Chapter 8
... • Microkernel systems provide better security, easier maintenance, and portability at the expense of execution speed. – Examples are Windows 2000, Mach, and QNX. – Symmetric multiprocessor computers are ideal platforms for microkernel operating systems. ...
... • Microkernel systems provide better security, easier maintenance, and portability at the expense of execution speed. – Examples are Windows 2000, Mach, and QNX. – Symmetric multiprocessor computers are ideal platforms for microkernel operating systems. ...
Test1: Spring 2017 (Hint)
... when it fields an interrupt. How does the system handle a second interrupt while it is busy attending the first interrupt? Ans. An interrupt routine is a CPU state changer – whatever a CPU were doing would be first stopped. Upon receiving an interrupt signal, the CPU goes through the following ■ sto ...
... when it fields an interrupt. How does the system handle a second interrupt while it is busy attending the first interrupt? Ans. An interrupt routine is a CPU state changer – whatever a CPU were doing would be first stopped. Upon receiving an interrupt signal, the CPU goes through the following ■ sto ...
Operating System Structures
... is essentially the same a thread shares resources with its peers good ...
... is essentially the same a thread shares resources with its peers good ...
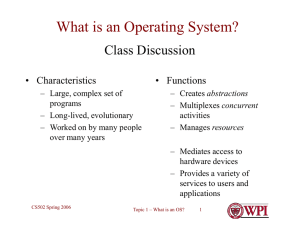
What is an Operating System
... sharing: how are resources shared across users? naming: how are resources named (by users or programs)? security: how is the integrity of the OS and its resources ensured? protection: how is one user/program protected from another? performance: how do we make it all go fast? reliability: what happen ...
... sharing: how are resources shared across users? naming: how are resources named (by users or programs)? security: how is the integrity of the OS and its resources ensured? protection: how is one user/program protected from another? performance: how do we make it all go fast? reliability: what happen ...
Information flow between computer components In this presentation
... old document called WPdoc1? 3. With Windows, user commands are usually entered via a mouse click. How does the user enter a command on a table PC like the iPad or a smartphone like the iPhone? 4. When it is turned on, a computer executes a small bootstrap program that checks to see the hardware is w ...
... old document called WPdoc1? 3. With Windows, user commands are usually entered via a mouse click. How does the user enter a command on a table PC like the iPad or a smartphone like the iPhone? 4. When it is turned on, a computer executes a small bootstrap program that checks to see the hardware is w ...
Slide 10 : Multiprocessor Scheduling
... multiprocessor provides the same service as a multiprogrammed uniprocessor because more than one processor is available, average response time to the users will be less ...
... multiprocessor provides the same service as a multiprogrammed uniprocessor because more than one processor is available, average response time to the users will be less ...
Lecture 2 Processes and Threads
... activity at a time (load a remote file while editing a program, for example), and uniprogramming does not allow this. So DOS and other uniprogrammed systems put in things like memory-resident programs that invoked asynchronously, but still have separation problems. One key problem with DOS is th ...
... activity at a time (load a remote file while editing a program, for example), and uniprogramming does not allow this. So DOS and other uniprogrammed systems put in things like memory-resident programs that invoked asynchronously, but still have separation problems. One key problem with DOS is th ...