The principles and methods formulated by Gregor
... Sexual Reproduction Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exception is sperm or eggs which are produced by a different type of cell division called meiosis. During fertilization the sperm and egg unite to form a single cell called the zygote which contains chromosomes ...
... Sexual Reproduction Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exception is sperm or eggs which are produced by a different type of cell division called meiosis. During fertilization the sperm and egg unite to form a single cell called the zygote which contains chromosomes ...
ECE/PSY171 Chapter 2 Biological Beginnings WHAT IS THE
... Fragile X syndrome—An abnormality in the X chromosome which becomes constricted and often breaks; associated with mental retardation, learning disabilities or a short attention span. This disorder occurs more frequently in males than in females. Turner syndrome—A disorder in which females are missin ...
... Fragile X syndrome—An abnormality in the X chromosome which becomes constricted and often breaks; associated with mental retardation, learning disabilities or a short attention span. This disorder occurs more frequently in males than in females. Turner syndrome—A disorder in which females are missin ...
Lab 6 Prelab Reading
... techniques that were developed for human chromosome study. One tool at the disposal of genetic scientists is a karyotype, which resembles a “family portrait” of all the chromosomes within a cell. By looking at a karyotype, large-scale chromosomal abnormalities can be detected. Before looking at type ...
... techniques that were developed for human chromosome study. One tool at the disposal of genetic scientists is a karyotype, which resembles a “family portrait” of all the chromosomes within a cell. By looking at a karyotype, large-scale chromosomal abnormalities can be detected. Before looking at type ...
Genetics - DNA
... of chromosomes - they are haploid (n). For instance human egg and sperm cells each contain 23 chromosomes. During fertilisation they will fuse together to form a zygote – a single cell with the normal number of chromosomes. This single cell will grow and divide many times, copying it’s set of chromo ...
... of chromosomes - they are haploid (n). For instance human egg and sperm cells each contain 23 chromosomes. During fertilisation they will fuse together to form a zygote – a single cell with the normal number of chromosomes. This single cell will grow and divide many times, copying it’s set of chromo ...
Gregor Mendel used pea plants to study A.flowering. B.gamete
... 11. A phenotype that results from a dominant allele must have at least _____ dominant allele(s) present in the parent(s).(B4.1c) A. one B. two C. three D. four ...
... 11. A phenotype that results from a dominant allele must have at least _____ dominant allele(s) present in the parent(s).(B4.1c) A. one B. two C. three D. four ...
Biology 3201 Chromosomal Mutations Information Table
... from one X chromosome in every cell. In this case they will have the normal number of chromosomes (46) in every cell. Other symptoms include: short with female genitalia but no ovaries or menstrual period, webbed neck, heart defects, kidney and skeletal abnormalities, learning difficulty, and thyroi ...
... from one X chromosome in every cell. In this case they will have the normal number of chromosomes (46) in every cell. Other symptoms include: short with female genitalia but no ovaries or menstrual period, webbed neck, heart defects, kidney and skeletal abnormalities, learning difficulty, and thyroi ...
Biology HW Chapter 14 (Due Apr 29, Test Apr 30)
... ____ 33. What new field is described by the overlap area in the Venn diagram in Figure 14–9? a. biotechnology b. bioinformatics c. gene therapy d. genetic engineering ____ 34. What did scientists in the Human Genome Project look for in DNA to identify the locations of genes? a. promoters b. sex-lin ...
... ____ 33. What new field is described by the overlap area in the Venn diagram in Figure 14–9? a. biotechnology b. bioinformatics c. gene therapy d. genetic engineering ____ 34. What did scientists in the Human Genome Project look for in DNA to identify the locations of genes? a. promoters b. sex-lin ...
Unit 2
... A sex-linked trait is a trait controlled by genes on the X or Y chromosome. Recall, female is XX and male is XY Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. One set is the sex chromosomes, while the other 22 pairs are autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). If an allele is found on an autosome, it is called au ...
... A sex-linked trait is a trait controlled by genes on the X or Y chromosome. Recall, female is XX and male is XY Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. One set is the sex chromosomes, while the other 22 pairs are autosomes (non-sex chromosomes). If an allele is found on an autosome, it is called au ...
X Chromosome
... - Males (XY) express all of their sex linked genes because they only have one X chromosome. - If the X chromosome has the gene, the male has the disorder. - Males can not be carriers because they only have one X chromosome - Examples: Hemophilia and Colorblindness ...
... - Males (XY) express all of their sex linked genes because they only have one X chromosome. - If the X chromosome has the gene, the male has the disorder. - Males can not be carriers because they only have one X chromosome - Examples: Hemophilia and Colorblindness ...
Karyotypes and Sex-Linked Traits
... All moms have the genotype XX. When egg cells are made, they will all carry a single X chromosome. All dads have the genotype XY. When sperm cells are made, 50% will have an X chromosome and 50% will have a Y chromosome. Therefore, males and females are born in roughly a 50:50 ratio ...
... All moms have the genotype XX. When egg cells are made, they will all carry a single X chromosome. All dads have the genotype XY. When sperm cells are made, 50% will have an X chromosome and 50% will have a Y chromosome. Therefore, males and females are born in roughly a 50:50 ratio ...
Karyotypes and Sex-Linked Traits
... All moms have the genotype XX. When egg cells are made, they will all carry a single X chromosome. All dads have the genotype XY. When sperm cells are made, 50% will have an X chromosome and 50% will have a Y chromosome. Therefore, males and females are born in roughly a 50:50 ratio ...
... All moms have the genotype XX. When egg cells are made, they will all carry a single X chromosome. All dads have the genotype XY. When sperm cells are made, 50% will have an X chromosome and 50% will have a Y chromosome. Therefore, males and females are born in roughly a 50:50 ratio ...
Heredity 1)Heredity is the ______ of the qualities that were passed
... Females have_____ X chromosomes and Males have one_____ and one ______ chromosome. The mother has only x chromosomes! Males pass either an ____ or _____ chromosome to the child which determined the gender of the child. 18) _________________________ is affected by the genes you inherit and other fact ...
... Females have_____ X chromosomes and Males have one_____ and one ______ chromosome. The mother has only x chromosomes! Males pass either an ____ or _____ chromosome to the child which determined the gender of the child. 18) _________________________ is affected by the genes you inherit and other fact ...
Chromosome 1
... Find a brown- and a blue-eyed person. Look deep into their eyes & try to figure out the difference ...
... Find a brown- and a blue-eyed person. Look deep into their eyes & try to figure out the difference ...
Grade 9 Science Ch 4 - Answers to Comprehensive Questions
... on from an individual to its offspring. 3. Where is heredity information stored? The nucleus. 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells ...
... on from an individual to its offspring. 3. Where is heredity information stored? The nucleus. 4. Why is the nucleus sometimes called "the control center of the cell"? Because the nucleus is responsible for controlling the functions of the cell. The info contained in the nucleus instructs your cells ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide D6
... 2. The _________________ states that factors for different traits on different genes are independent of one another. 3. A ___________ is a plant pure for a specific trait. 4. A _________________ occurs between individuals with 2 contrasting traits. 5. A ______________ is the actual alleles that are ...
... 2. The _________________ states that factors for different traits on different genes are independent of one another. 3. A ___________ is a plant pure for a specific trait. 4. A _________________ occurs between individuals with 2 contrasting traits. 5. A ______________ is the actual alleles that are ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... Mainly in boys, onset 3-5 yrs, by 12 years can’t walk, and later needs respirator. ...
... Mainly in boys, onset 3-5 yrs, by 12 years can’t walk, and later needs respirator. ...
Gene Expression, Inheritance Patterns, and DNA Technology
... hormones influence the expression of certain human traits: Males and females have different ...
... hormones influence the expression of certain human traits: Males and females have different ...
401Lecture5sp2013post
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
Chromosomes and Mutations Chromosomes and
... • Genes can be mutated when the DNA is mutated or when the chromosomes are mutated • There are two types of DNA (gene) mutations: • Point Mutations: a change in a single base pair • Frameshift Mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA ...
... • Genes can be mutated when the DNA is mutated or when the chromosomes are mutated • There are two types of DNA (gene) mutations: • Point Mutations: a change in a single base pair • Frameshift Mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA ...
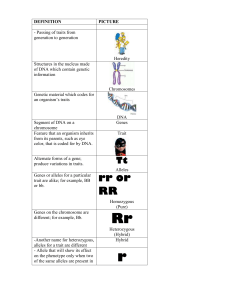
definition - Humble ISD
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
... of DNA which contain genetic information Chromosomes Genetic material which codes for an organism’s traits ...
Keystone Vocabulary 61-70
... 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and c ...
... 63. Homologous Structure: A physical characteristic in different organisms that is similar because it was inherited from a common ancestor. 64. Interphase: The longest lasting phase of the cell cycle in which a cell performs the majority of its functions, such as preparing for nuclear division and c ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.