Name: MEIOSIS MANIPULATIVES Introduction: You are going to
... Note: A chromosome is a tightly coiled strand of DNA and within each chromosome there are many, many genes. The chromosomes within each pair are homologous. Homologous chromosomes are the same in size and function but they do have different alleles. For instance, the homologous chromosome may contai ...
... Note: A chromosome is a tightly coiled strand of DNA and within each chromosome there are many, many genes. The chromosomes within each pair are homologous. Homologous chromosomes are the same in size and function but they do have different alleles. For instance, the homologous chromosome may contai ...
Chromosome Inversions - Birmingham Women`s Hospital
... This means that the ‘middle’ part of the chromosome called the centromere is involved. Pericentric inversions can lead to mistakes being made when the eggs or sperm are made. Some may get extra chromosome material and some may have missing chromosome material. This can lead to an increased chance of ...
... This means that the ‘middle’ part of the chromosome called the centromere is involved. Pericentric inversions can lead to mistakes being made when the eggs or sperm are made. Some may get extra chromosome material and some may have missing chromosome material. This can lead to an increased chance of ...
MECHANISMS OF GENETIC CHANGE
... •Transposable elements or transposons for short are sections of DNA that have the ability to move from one section of a chromosome to another. •Due to this wandering nature, they can insert themselves into genes and disrupt their function. •Here the gene for kernel •They are also nicknamed ‘jumping ...
... •Transposable elements or transposons for short are sections of DNA that have the ability to move from one section of a chromosome to another. •Due to this wandering nature, they can insert themselves into genes and disrupt their function. •Here the gene for kernel •They are also nicknamed ‘jumping ...
meiosis - newmanr
... Independent assortment – each of the 23 pairs of chromosomes segregates (separates) independently. Thus about 8 million gametes with different gene combinations can be produced from the one original cell. ...
... Independent assortment – each of the 23 pairs of chromosomes segregates (separates) independently. Thus about 8 million gametes with different gene combinations can be produced from the one original cell. ...
Genetic Diseases
... cells cannot carry O2 effectively; sickled shape cells cannot travel through small blood vessels (autosomal recessive disorder) Most common in African Americans homozygous recessive= sickle cell disease heterozygous= sickle cell trait; defense against malaria (codominant) ...
... cells cannot carry O2 effectively; sickled shape cells cannot travel through small blood vessels (autosomal recessive disorder) Most common in African Americans homozygous recessive= sickle cell disease heterozygous= sickle cell trait; defense against malaria (codominant) ...
Invited Review: Sex-based differences in gene expression
... that are inherited within the region are not transmitted exclusively to males or females and thus behave as if they were inherited on autosomes (52). Sex-based differences in gene expression may occur from the sex-limited regions of the X or Y chromosomes. Genes within the sex-limited regions of the ...
... that are inherited within the region are not transmitted exclusively to males or females and thus behave as if they were inherited on autosomes (52). Sex-based differences in gene expression may occur from the sex-limited regions of the X or Y chromosomes. Genes within the sex-limited regions of the ...
Genetics
... • Locus – the location of a gene/allele on a chromosome • Homozygous – when both alleles of a gene are the same (ex. aa, AA) • Heterozygous – when both alleles of a gene ...
... • Locus – the location of a gene/allele on a chromosome • Homozygous – when both alleles of a gene are the same (ex. aa, AA) • Heterozygous – when both alleles of a gene ...
Genetic Mutations
... • Red blood cells form an abnormal crescent shape • Hemoglobin (protein) is abnormally shaped • don't move easily through your blood vessels • form clumps and get stuck in the blood vessels ...
... • Red blood cells form an abnormal crescent shape • Hemoglobin (protein) is abnormally shaped • don't move easily through your blood vessels • form clumps and get stuck in the blood vessels ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 10. Explain the difference between a dominant and a recessive characteristic. 11. Every business has an office. Inside the office is a filing cabinet and inside the cabinet are files. Inside each file there is specific information. Compare this to a cell. Which part is equivalent to the office, the ...
... 10. Explain the difference between a dominant and a recessive characteristic. 11. Every business has an office. Inside the office is a filing cabinet and inside the cabinet are files. Inside each file there is specific information. Compare this to a cell. Which part is equivalent to the office, the ...
Human Chromosomes
... This individual is female in appearance but does not develop the female sex organs during puberty and is ____________. Klinefelter’s Syndrome: Nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes in which an extra ____ ____________________ is present. They have the chromosome makeup of ___________. They are ______ ...
... This individual is female in appearance but does not develop the female sex organs during puberty and is ____________. Klinefelter’s Syndrome: Nondisjunction of the sex chromosomes in which an extra ____ ____________________ is present. They have the chromosome makeup of ___________. They are ______ ...
Chapter 8: Variations in Chromosome Number and
... lost during mitosis. A deletion does not have to be large to cause harmful effects (cri-du-chat). The more genetic information that is lost, the more likely the effects become lethal. 8.8 A duplication is a repeated segment of the genetic material When any part of the genetic material is present m ...
... lost during mitosis. A deletion does not have to be large to cause harmful effects (cri-du-chat). The more genetic information that is lost, the more likely the effects become lethal. 8.8 A duplication is a repeated segment of the genetic material When any part of the genetic material is present m ...
Genetics Notes HONORS
... has been turned off. White is just the absence of any color on hair. This results in three different colors. – Male calico cats only have one X either orange and white or black and white… depending on which color is turned off in the X inactivationmales cannot be all three colors. ...
... has been turned off. White is just the absence of any color on hair. This results in three different colors. – Male calico cats only have one X either orange and white or black and white… depending on which color is turned off in the X inactivationmales cannot be all three colors. ...
Ch - TeacherWeb
... B. Nondisjunction: cell division during which sister chromatids fails to separate properly; occurs in any organism where gametes are produced through meiosis 1. nondisjunction in meiosis I or II results in gametes that have the incorrect number of chromosomes 2. when one of these gametes fertilizes ...
... B. Nondisjunction: cell division during which sister chromatids fails to separate properly; occurs in any organism where gametes are produced through meiosis 1. nondisjunction in meiosis I or II results in gametes that have the incorrect number of chromosomes 2. when one of these gametes fertilizes ...
Genetics Exam 5
... A. exhibit altered mitosis B. are unable to asexually reproduce C. exhibit altered growth D. have low fertility E. are not viable _____ Pollen from one species germinates on the stigma of another related species and sexually fertilizes the ovule. Most of the resulting plants are sterile but some of ...
... A. exhibit altered mitosis B. are unable to asexually reproduce C. exhibit altered growth D. have low fertility E. are not viable _____ Pollen from one species germinates on the stigma of another related species and sexually fertilizes the ovule. Most of the resulting plants are sterile but some of ...
File
... vision, all located on the X chromosome. In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness, an inability to distinguish certain colors. The most common form, red-green colorblindness, occurs in about 1 in 12 males. Among females, however, colorblindness affects only about ...
... vision, all located on the X chromosome. In males, a defective allele for any of these genes results in colorblindness, an inability to distinguish certain colors. The most common form, red-green colorblindness, occurs in about 1 in 12 males. Among females, however, colorblindness affects only about ...
I. Introduction
... 8. X-linked characteristics affect males much more than females. 9. Recessive conditions can skip a generation because a person most likely inherits a recessive condition from two healthy parents who are each heterozygotes. 10. Dominant conditions do not skip generations because a person who inheri ...
... 8. X-linked characteristics affect males much more than females. 9. Recessive conditions can skip a generation because a person most likely inherits a recessive condition from two healthy parents who are each heterozygotes. 10. Dominant conditions do not skip generations because a person who inheri ...
click here
... DNA molecule will be: 1/4 x1/4 x 1/2 x 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/512; or it will cut once every 512 base pairs. The haploid genome of the fish is (3.8 x 106); expecting a cut every 512 nucleotides would produce (3.8 x 106)/512 or 7.4 x 105 fragments. Ans: (c). 2. Inserting a foreign DNA fragment into the BglI s ...
... DNA molecule will be: 1/4 x1/4 x 1/2 x 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/512; or it will cut once every 512 base pairs. The haploid genome of the fish is (3.8 x 106); expecting a cut every 512 nucleotides would produce (3.8 x 106)/512 or 7.4 x 105 fragments. Ans: (c). 2. Inserting a foreign DNA fragment into the BglI s ...
Genetic Basis of Development
... Cell expresses a particular set of genes that forces it to develop into a particular cell These tissue-specific genes are located on euchromatin (expressed/loosely wound portion of DNA) within the given cell ...
... Cell expresses a particular set of genes that forces it to develop into a particular cell These tissue-specific genes are located on euchromatin (expressed/loosely wound portion of DNA) within the given cell ...
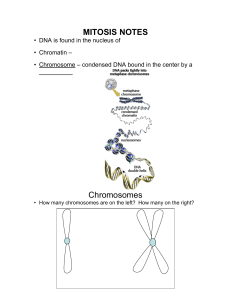
Mitosis Notes
... MITOSIS NOTES • DNA is found in the nucleus of • Chromatin – • Chromosome – condensed DNA bound in the center by a __________ ...
... MITOSIS NOTES • DNA is found in the nucleus of • Chromatin – • Chromosome – condensed DNA bound in the center by a __________ ...
Review for exam 1
... During another round of cell division, the sister chromatids finally separate; four haploid daughter cells result, containing single chromosomes ...
... During another round of cell division, the sister chromatids finally separate; four haploid daughter cells result, containing single chromosomes ...
Ch 2: Heredity Worksheet 1. Chromosomes are found in the the cell
... 4. ___________________exists in every cell of our body. 5. How many chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the human cell? 6. Chromosomes are made of long strand of _____________________ 7. Sperm collected from the father and then injected into the mother’s reproductive system for fertilization is ...
... 4. ___________________exists in every cell of our body. 5. How many chromosomes are found in the nucleus of the human cell? 6. Chromosomes are made of long strand of _____________________ 7. Sperm collected from the father and then injected into the mother’s reproductive system for fertilization is ...
RevShtFinalBio160
... A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. (Note: if the correct answer below is more than one letter long, like “ae.”, mark both a AND e on your answer sheet for that questio ...
... A cell which has a diploid (2n) number of 6 undergoes either mitosis or meiosis. Use the pictures below to answer questions about the stages of division for this cell. (Note: if the correct answer below is more than one letter long, like “ae.”, mark both a AND e on your answer sheet for that questio ...
Identify the three parts of cell theory All living things are made of
... life. Cells come from other cells. ...
... life. Cells come from other cells. ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.