Human Genetics and Linked Genes
... Rate of miscarriage due to amniocentesis: 1970s data 0.5%, or 1 in 200 pregnancies 2006 data <0.1%, or 1 in 1600 pregnancies ...
... Rate of miscarriage due to amniocentesis: 1970s data 0.5%, or 1 in 200 pregnancies 2006 data <0.1%, or 1 in 1600 pregnancies ...
Fill-in-Notes - Pearland ISD
... human body. (3 Billion nucleotides and 20,000-25,000 genes) This was completed in _____________ Pharmacogenomics The study of how genetic inheritance _____________the body’s response to drugs is called ______________________. Gene therapy Gene therapy is a technique aimed at ___________mutated ...
... human body. (3 Billion nucleotides and 20,000-25,000 genes) This was completed in _____________ Pharmacogenomics The study of how genetic inheritance _____________the body’s response to drugs is called ______________________. Gene therapy Gene therapy is a technique aimed at ___________mutated ...
AP & Regents Biology
... Rate of miscarriage due to amniocentesis: 1970s data 0.5%, or 1 in 200 pregnancies 2006 data <0.1%, or 1 in 1600 pregnancies ...
... Rate of miscarriage due to amniocentesis: 1970s data 0.5%, or 1 in 200 pregnancies 2006 data <0.1%, or 1 in 1600 pregnancies ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Males have XY. Females have XX. In female cells, most of the genes in 1 X are randomly switched off (called Barr bodies). Ex: female calico cats ...
... Males have XY. Females have XX. In female cells, most of the genes in 1 X are randomly switched off (called Barr bodies). Ex: female calico cats ...
Drosophila-Mega-Review
... Caveat for using flp/frt or MARCM system: only half of the cells are marked/become homozygous mutant because mitotic recombination needed to induce clones Flp-out system doesn’t rely on mitotic recombination so has better chance of marking all/most cells (greater clonal induction) Components: o Fr ...
... Caveat for using flp/frt or MARCM system: only half of the cells are marked/become homozygous mutant because mitotic recombination needed to induce clones Flp-out system doesn’t rely on mitotic recombination so has better chance of marking all/most cells (greater clonal induction) Components: o Fr ...
must have half the number of chromosomes
... is in serious trouble since all of its cells will be affected. ...
... is in serious trouble since all of its cells will be affected. ...
Genetics
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
No Slide Title
... The probability that a gamete will contain the genes “Ry” if the diploid cells contain the “Rryy” ...
... The probability that a gamete will contain the genes “Ry” if the diploid cells contain the “Rryy” ...
Genetics - Dave Brodbeck
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
... – Does not mean that a complex behavioural sequence is caused by a single gene • Many other genes contribute to behaviour • Some difference must be caused by genetic differences ...
Heredity and Environment
... By puberty, males begin producing many thousands of sperm cells on an ongoing basis, and they continue to do so through out their life span ...
... By puberty, males begin producing many thousands of sperm cells on an ongoing basis, and they continue to do so through out their life span ...
Genetics
... If an individual is heterozygous there will be one copy of each on “opposite” chromosomes. Kpa is then said to be antithetical to antigen Kpb ...
... If an individual is heterozygous there will be one copy of each on “opposite” chromosomes. Kpa is then said to be antithetical to antigen Kpb ...
genetics Study Guide(fall 2014 for old book)
... How does asexual and sexual reproduction differ? What are the 2 key processes involved in sexual reproduction? The names of the stages of meiosis and describe what is happening at each stage Why is it important that the daughter cells resulting in meiosis are haploid? What are homologous chromosomes ...
... How does asexual and sexual reproduction differ? What are the 2 key processes involved in sexual reproduction? The names of the stages of meiosis and describe what is happening at each stage Why is it important that the daughter cells resulting in meiosis are haploid? What are homologous chromosomes ...
word play - Discovery Education
... 6. An organism's inherited physical appearance. 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules ...
... 6. An organism's inherited physical appearance. 8. A rod-shaped structure of tightly coiled DNA found in the cell nucleus of plants and animals. 11. A combination of atoms, and also the basic building-block of DNA and RNA. Each molecule has its own shape and attaches only to certain other molecules ...
Biology Final Exam Vocabulary Review
... 2. __________________ is the term that refers to DNA that is loosely wrapped around histone proteins during interphase. 3. The region that holds the two sister chromatids together in a condensed chromosome is called the __________________. 4. __________________ is the process that divides the cell c ...
... 2. __________________ is the term that refers to DNA that is loosely wrapped around histone proteins during interphase. 3. The region that holds the two sister chromatids together in a condensed chromosome is called the __________________. 4. __________________ is the process that divides the cell c ...
Ch 15b
... • Alterations of chromosome number and structure are associated with some serious disorders • Some types of aneuploidy appear to upset the genetic balance less than others, resulting in individuals surviving to birth and beyond • These surviving individuals have a set of symptoms, or syndrome, chara ...
... • Alterations of chromosome number and structure are associated with some serious disorders • Some types of aneuploidy appear to upset the genetic balance less than others, resulting in individuals surviving to birth and beyond • These surviving individuals have a set of symptoms, or syndrome, chara ...
Point Mutation
... Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome The disease is caused by a small point mutation on a single gene known as LMNA. Almost all cases are caused by the substitution of only one base pair out of the approximate 25 000 DNA base pairs that compose the LMNA gene. This gene codes for the protein lamin A ...
... Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome The disease is caused by a small point mutation on a single gene known as LMNA. Almost all cases are caused by the substitution of only one base pair out of the approximate 25 000 DNA base pairs that compose the LMNA gene. This gene codes for the protein lamin A ...
The process of meiosis - Deans Community High School
... Cells which contain one set of chromosomes are known as haploid cells e.g. Cells which contain two sets of chromosomes are known as ……………… cells e.g. ...
... Cells which contain one set of chromosomes are known as haploid cells e.g. Cells which contain two sets of chromosomes are known as ……………… cells e.g. ...
Chromosome Mutations
... chromosome is subject to mutation, which will most likely occur during crossing over at meiosis. There are a number of ways in which the chromosome structure can change, as indicated below, which will detrimentally change the genotype and phenotype of the organism. However, if the chromosome mutatio ...
... chromosome is subject to mutation, which will most likely occur during crossing over at meiosis. There are a number of ways in which the chromosome structure can change, as indicated below, which will detrimentally change the genotype and phenotype of the organism. However, if the chromosome mutatio ...
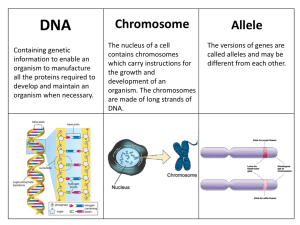
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
Non Mendelian Genetics - Warren County Schools
... – The ABO blood types result from codominant alleles. ...
... – The ABO blood types result from codominant alleles. ...
doc Summer 2010 Lecture 3
... BIOL 202 5.5 Genetic Mapping There are a number of genes in the mtDNA - many involved with energy production - some play roles in heredity - chromosomal inheritance is 50% male and 50% female - organelle DNA: male contribution is low o random distribution—no spindle dividing it get a segregation o ...
... BIOL 202 5.5 Genetic Mapping There are a number of genes in the mtDNA - many involved with energy production - some play roles in heredity - chromosomal inheritance is 50% male and 50% female - organelle DNA: male contribution is low o random distribution—no spindle dividing it get a segregation o ...
X-inactivation

X-inactivation (also called lyonization) is a process by which one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by its being packaged in such a way that it has a transcriptionally inactive structure called heterochromatin. As nearly all female mammals have two X chromosomes, X-inactivation prevents them from having twice as many X chromosome gene products as males, who only possess a single copy of the X chromosome (see dosage compensation). The choice of which X chromosome will be inactivated is random in placental mammals such as humans, but once an X chromosome is inactivated it will remain inactive throughout the lifetime of the cell and its descendants in the organism. Unlike the random X-inactivation in placental mammals, inactivation in marsupials applies exclusively to the paternally derived X chromosome.