Social_life
... difficult to predict how they are going to behave in other situations If someone behaves according to a set of internal principles and values, we can better predict their behaviour across situations. We like to believe that we can pigeon hole or stereotype others. When do we not tend to make the ...
... difficult to predict how they are going to behave in other situations If someone behaves according to a set of internal principles and values, we can better predict their behaviour across situations. We like to believe that we can pigeon hole or stereotype others. When do we not tend to make the ...
Lecture 1 () - Faculty of Computer Science and Information
... All forms of technology applied to processing, storing, and transmitting information in electronic form. Physical equipments – fax, computers, PDAs, scanners etc. Information systems – organized procedures that process and/or communicate information. Information system processed data to turn into an ...
... All forms of technology applied to processing, storing, and transmitting information in electronic form. Physical equipments – fax, computers, PDAs, scanners etc. Information systems – organized procedures that process and/or communicate information. Information system processed data to turn into an ...
RoboCup
... Football strategies search for RoboCup Information Retrieval Course Project Project Group: Stanislav Semakin Vyacheslav Shirikov Yaroslav Karulin Igor Razumny ...
... Football strategies search for RoboCup Information Retrieval Course Project Project Group: Stanislav Semakin Vyacheslav Shirikov Yaroslav Karulin Igor Razumny ...
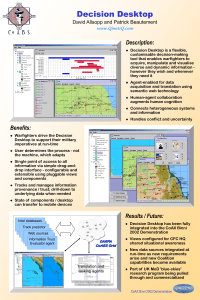
Decision support system
... as not to lose sales and disappoint customers. CDs that are not sold for some time, go on the sale table, and are sold at below cost, if they sell at all. She wants to design a DSS to try and predict how many copies of each future CD she should order, and for how long she should keep them on a rack, ...
... as not to lose sales and disappoint customers. CDs that are not sold for some time, go on the sale table, and are sold at below cost, if they sell at all. She wants to design a DSS to try and predict how many copies of each future CD she should order, and for how long she should keep them on a rack, ...
Objective 2.02: Acquire a foundational knowledge of information
... What is involved in robotics activities? It involves mechanical devices programmed to do routine tasks, such as those seen on an assembly line in factories. Robots are also used in dangerous situations where it is not safe for people to go. Example: Assembly line work that requires repeated task ...
... What is involved in robotics activities? It involves mechanical devices programmed to do routine tasks, such as those seen on an assembly line in factories. Robots are also used in dangerous situations where it is not safe for people to go. Example: Assembly line work that requires repeated task ...
Chapter 10
... 2. Neural Network – attempts to emulate the way the human brain works – Fuzzy logic – a mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective information ...
... 2. Neural Network – attempts to emulate the way the human brain works – Fuzzy logic – a mathematical method of handling imprecise or subjective information ...
KTH-CSC-TCS/DDT
... KTH-CSC-TCS/DDT - Theory Group Development Plan - 2008-06-22 The theory group (TCS) is a strong research environment. Its mission is to carry the culture of Theoretical Computer Science, including developing and disseminating new, interesting and useful knowledge in the area. Our judgment is that ou ...
... KTH-CSC-TCS/DDT - Theory Group Development Plan - 2008-06-22 The theory group (TCS) is a strong research environment. Its mission is to carry the culture of Theoretical Computer Science, including developing and disseminating new, interesting and useful knowledge in the area. Our judgment is that ou ...
Classnotes chapter 3: Cognitive foundations of entrepreneurship
... structures that allow us to store—and use—information. Why do some persons generate ideas for new products or services? The answer seems to involve having just the right combination of past experiences. Because everyone’s experience is unique, the information they have at their disposal, too, is uni ...
... structures that allow us to store—and use—information. Why do some persons generate ideas for new products or services? The answer seems to involve having just the right combination of past experiences. Because everyone’s experience is unique, the information they have at their disposal, too, is uni ...
Information, Life and Evolutionary Robots: a systemic approach
... in terms of self-organizing patterns (Haken, 2000) that are available to a receiver. This characterization is further developed in order to contemplate the notion of meaning. Based upon Gibson’s conception of mutuality, we conceive meaningful information as an evolutionary, self-organizing process o ...
... in terms of self-organizing patterns (Haken, 2000) that are available to a receiver. This characterization is further developed in order to contemplate the notion of meaning. Based upon Gibson’s conception of mutuality, we conceive meaningful information as an evolutionary, self-organizing process o ...
Jose Marie`s questions and Gio`s responses:
... their acquisition, search, analysis, discovery and dissemination in broad areas spanning proteomics, genetics, neurology, medicine, zoology, botany, … to populations, and ecosystems. The goal of bioinformatics efforts is to provide an effective information-rich environment that will support endeavor ...
... their acquisition, search, analysis, discovery and dissemination in broad areas spanning proteomics, genetics, neurology, medicine, zoology, botany, … to populations, and ecosystems. The goal of bioinformatics efforts is to provide an effective information-rich environment that will support endeavor ...
Cognitive Information Processing
... Cognitive Process- any internal mental event and includes such phenomena as perceiving, attention, interpretation, understanding and remembering Learning vs. Memory - learning is viewed as the acquisition of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previo ...
... Cognitive Process- any internal mental event and includes such phenomena as perceiving, attention, interpretation, understanding and remembering Learning vs. Memory - learning is viewed as the acquisition of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previo ...
Artificial Intelligence
... Artificial Intelligence I. seeks to simulate or imitate human intelligence, such as reasoning and learning, by using computer science and computer systems A. Computers are far more efficient than people in storing information, solving complex numerical problems and doing large-scale repetitive tasks ...
... Artificial Intelligence I. seeks to simulate or imitate human intelligence, such as reasoning and learning, by using computer science and computer systems A. Computers are far more efficient than people in storing information, solving complex numerical problems and doing large-scale repetitive tasks ...
Some Applications of Fuzzy Logic in Data Mining and Information
... Abstract: Data mining and information retrieval are two domains difficult to cope with for various reasons. First, most of the databases are complex, large, and contain heterogeneous, imprecise, vague, uncertain, incomplete data. Furthermore, the queries may be imprecise or subjective in the case of ...
... Abstract: Data mining and information retrieval are two domains difficult to cope with for various reasons. First, most of the databases are complex, large, and contain heterogeneous, imprecise, vague, uncertain, incomplete data. Furthermore, the queries may be imprecise or subjective in the case of ...
Chapter 9 - Missouri State University
... • Transaction processing system (TPS) - the basic business system that serves the operational level (analysts) in an organization • Online transaction processing (OLTP) – the capturing of transaction and event information using technology to (1) process the information according to defined business ...
... • Transaction processing system (TPS) - the basic business system that serves the operational level (analysts) in an organization • Online transaction processing (OLTP) – the capturing of transaction and event information using technology to (1) process the information according to defined business ...
Abstract
... acquired remarkable progress and many application fields. The increasing demand on it brought forth the concept of automatic text categorization, by the help of machine learning, and some implementation algorithms for text categorizer systems, employing the machine learning approach, appeared. The m ...
... acquired remarkable progress and many application fields. The increasing demand on it brought forth the concept of automatic text categorization, by the help of machine learning, and some implementation algorithms for text categorizer systems, employing the machine learning approach, appeared. The m ...
Lecture 2
... Chapter 9- Enabling the organization- Decision making Reasons for growth of decision making information system: 1. People need to analyze large amounts of information- Improvements in technology itself, innovations in communication, and globalization have resulted in dramatic increase in the alterna ...
... Chapter 9- Enabling the organization- Decision making Reasons for growth of decision making information system: 1. People need to analyze large amounts of information- Improvements in technology itself, innovations in communication, and globalization have resulted in dramatic increase in the alterna ...
Redalyc.Special Issue on Innovative Applications of AI
... diagnosis systems, planning systems and decision support systems. They were all developed for Comisión Federal de Electricity, a company of the Mexican government that generates, transmits, distributes and commercialises almost 80% of the power energy in Mexico. Téllez et al. present an approach bas ...
... diagnosis systems, planning systems and decision support systems. They were all developed for Comisión Federal de Electricity, a company of the Mexican government that generates, transmits, distributes and commercialises almost 80% of the power energy in Mexico. Téllez et al. present an approach bas ...
Webquest webprojects situated cognition
... process normally includes higher order thinking: analysis, synthesis, problem-solving, judgment and creativity. standard set of steps that learners go through in doing a webquest. The steps include: ...
... process normally includes higher order thinking: analysis, synthesis, problem-solving, judgment and creativity. standard set of steps that learners go through in doing a webquest. The steps include: ...
Chapter 1
... An organization is a nexus of decisions with information needs supplied by an Information System Information, Decisions, and Management – the type of information required by decision makers is directly related to the level of management decision making and the amount of structure in the decision ...
... An organization is a nexus of decisions with information needs supplied by an Information System Information, Decisions, and Management – the type of information required by decision makers is directly related to the level of management decision making and the amount of structure in the decision ...
Artificial Intelligence - AIM - Automated Information Management Corp.
... The 1st. Full time research group was started in 1954 at Carnegie Mellon University by Allen Newell and Herbert Simon; It all started in the Dartmouth conference where ten young researchers had the same dream of using a computer to model the ways humans think; Their hypothesis was that mechani ...
... The 1st. Full time research group was started in 1954 at Carnegie Mellon University by Allen Newell and Herbert Simon; It all started in the Dartmouth conference where ten young researchers had the same dream of using a computer to model the ways humans think; Their hypothesis was that mechani ...
Chapter_3_ID2e_slides
... • Icons and other graphical representations should enable users to readily distinguish their meaning • Bordering and spacing are effective visual ways of grouping information • Sounds should be audible and distinguishable • Speech output should enable users to distinguish between the set of spoken w ...
... • Icons and other graphical representations should enable users to readily distinguish their meaning • Bordering and spacing are effective visual ways of grouping information • Sounds should be audible and distinguishable • Speech output should enable users to distinguish between the set of spoken w ...
Chap13.doc
... ___ 3. Operational decisions should be consistent with and support the tactical decisions made by middle management. ___ 4. The same information is meaningful to every individual and group within an organization. ___ 5. New management methods and structures have had no impact on information systems. ...
... ___ 3. Operational decisions should be consistent with and support the tactical decisions made by middle management. ___ 4. The same information is meaningful to every individual and group within an organization. ___ 5. New management methods and structures have had no impact on information systems. ...