KINETIC AND POTENTIAL ENERGY
... body uses to do things like move, think, and stay warm Gasoline has chemical potential energy that engines turn into heat energy in order to do work ...
... body uses to do things like move, think, and stay warm Gasoline has chemical potential energy that engines turn into heat energy in order to do work ...
Unit 4: Energy
... A 2-kg rock falls off a 20 m cliff. When it is halfway down, it is traveling at 14 m/s. Kinetic energy and potential energy at the ...
... A 2-kg rock falls off a 20 m cliff. When it is halfway down, it is traveling at 14 m/s. Kinetic energy and potential energy at the ...
Energy and Forms of Energy
... This type of energy stores potential energy in the nucleus of the atoms. It is released during a nuclear reaction. Power plants use nuclear fission, the splitting of atoms, to produce electricity. However, there is a much more destructive use of nuclear power. ...
... This type of energy stores potential energy in the nucleus of the atoms. It is released during a nuclear reaction. Power plants use nuclear fission, the splitting of atoms, to produce electricity. However, there is a much more destructive use of nuclear power. ...
Energy - Learning While Doing
... •Radiant energy is also called electromagnetic energy. •Radiant energy is the movement of photons. •All life on earth is dependent on radiant energy from the sun. •Examples of radiant energy include radio ...
... •Radiant energy is also called electromagnetic energy. •Radiant energy is the movement of photons. •All life on earth is dependent on radiant energy from the sun. •Examples of radiant energy include radio ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. All states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) contain energy. A state is the form in which matter exists. Heat + to a system= the temp. of substances in the system ...
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. All states of matter (solid, liquid, and gas) contain energy. A state is the form in which matter exists. Heat + to a system= the temp. of substances in the system ...
Management of Different Energy Storage Devices
... always satisfied—being the Hessian matrix of the Lagrangian function positive definite (F+λH = 2Q > 0)—the solutions of (10) identify the minimum value of f . It is worth noting that this minimization is carried out on a continuous basis, i.e., for every value of u the algorithm sets the values of the ...
... always satisfied—being the Hessian matrix of the Lagrangian function positive definite (F+λH = 2Q > 0)—the solutions of (10) identify the minimum value of f . It is worth noting that this minimization is carried out on a continuous basis, i.e., for every value of u the algorithm sets the values of the ...
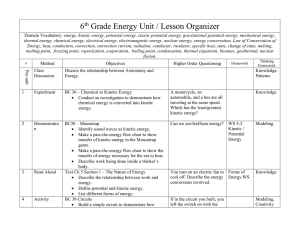
6th Grade Energy Unit / Lesson Organizer Domain Vocabulary
... Explain how fossil fuels contain energy that comes from the sun. Describe the conversion of chemical energy in fossil fuels to other forms of energy. Fossil Fuel Cookie Extraction Understand the positive and negative effects of fossil fuels, vs. renewable energy sources. BC72 Nuclear Power I ...
... Explain how fossil fuels contain energy that comes from the sun. Describe the conversion of chemical energy in fossil fuels to other forms of energy. Fossil Fuel Cookie Extraction Understand the positive and negative effects of fossil fuels, vs. renewable energy sources. BC72 Nuclear Power I ...
Energy and its importance script
... Potential energy is the energy of position. When an object is raised to a higher position, it gains potential energy. For example, a lift, and the passengers inside it, gains potential energy when they move upwards. The higher the position of an object is, the more potential energy it has. When an e ...
... Potential energy is the energy of position. When an object is raised to a higher position, it gains potential energy. For example, a lift, and the passengers inside it, gains potential energy when they move upwards. The higher the position of an object is, the more potential energy it has. When an e ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Calculating Mechanical Energy pg. 297 • An object’s mechanical energy is a combination of its potential energy and its kinetic energy. How do you find an object’s mechanical energy ?? You can find an object’s mechanical energy by adding the object’s kinetic energy and potential energy. (Mechanical ...
... Calculating Mechanical Energy pg. 297 • An object’s mechanical energy is a combination of its potential energy and its kinetic energy. How do you find an object’s mechanical energy ?? You can find an object’s mechanical energy by adding the object’s kinetic energy and potential energy. (Mechanical ...
TYPES OF ENERGY
... determines how active its atoms are. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement. ...
... determines how active its atoms are. A hot object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A cooler object's molecules and atoms will show less movement. ...
Name
... 9. Thermal energy is energy stored by things that stretch or compress. 10. A slanted surface used to raise an object is called an inclined plane. 11. Two copies of the same book are in a book case. One book is twice as high as the other. They have the same potential energy. 12. A toaster uses chemic ...
... 9. Thermal energy is energy stored by things that stretch or compress. 10. A slanted surface used to raise an object is called an inclined plane. 11. Two copies of the same book are in a book case. One book is twice as high as the other. They have the same potential energy. 12. A toaster uses chemic ...
Potential and Kinetic Energy
... Learning Scale for Energy … I can 4 – All of 3, 2, & 1 + Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 – All of 2 & 1 + Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 – All of 1 + Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identif ...
... Learning Scale for Energy … I can 4 – All of 3, 2, & 1 + Cite evidence to support the Law of Conservation of Energy. 3 – All of 2 & 1 + Investigate and describe the transformation of energy that occurs in given examples. 2 – All of 1 + Differentiate between kinetic and potential energy. 1 - Identif ...
Kinetic Energy Lab - Owen County Schools
... As we know, kinetic energy is related to mass and speed of an object. Potential energy is related to the mass and height of an object with an influence from the acceleration due to gravity. When this unit began, you may have thought that an object at rest has no energy. While I stationary object has ...
... As we know, kinetic energy is related to mass and speed of an object. Potential energy is related to the mass and height of an object with an influence from the acceleration due to gravity. When this unit began, you may have thought that an object at rest has no energy. While I stationary object has ...
energy - Petervaldivia
... we have a heavier nucleus and the release of energy • Scientists are working on creating fusion energy, so that someday there might be fusion power plants. ...
... we have a heavier nucleus and the release of energy • Scientists are working on creating fusion energy, so that someday there might be fusion power plants. ...
Energy storage

Energy storage is accomplished by devices or physical media that store energy to perform useful processes at a later time. A device that stores energy is sometimes called an accumulator.Many forms of energy produce useful work, heating or cooling to meet societal needs. These energy forms include chemical energy, gravitational potential energy, electrical potential, electricity, temperature differences, latent heat, and kinetic energy. Energy storage involves converting energy from forms that are difficult to store (electricity, kinetic energy, etc.) to more conveniently or economically storable forms. Some technologies provide only short-term energy storage, and others can be very long-term such as power to gas using hydrogen or methane and the storage of heat or cold between opposing seasons in deep aquifers or bedrock. A wind-up clock stores potential energy (in this case mechanical, in the spring tension), a rechargeable battery stores readily convertible chemical energy to operate a mobile phone, and a hydroelectric dam stores energy in a reservoir as gravitational potential energy. Ice storage tanks store ice (thermal energy in the form of latent heat) at night to meet peak demand for cooling. Fossil fuels such as coal and gasoline store ancient energy derived from sunlight by organisms that later died, became buried and over time were then converted into these fuels. Even food (which is made by the same process as fossil fuels) is a form of energy stored in chemical form.