Answers
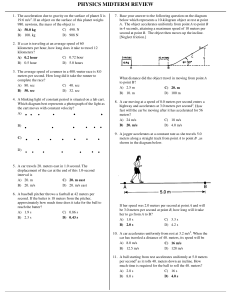
... 3.2.2C – Use the principle of Conservation of Energy to determine changes in potential energy; kinetic energy; internal energy; speed; and/or height. A 2.0 kilogram object at rest at the top of a frictionless 4.0 meter high hill is allowed to slide to the bottom. What speed will the object reach at ...
... 3.2.2C – Use the principle of Conservation of Energy to determine changes in potential energy; kinetic energy; internal energy; speed; and/or height. A 2.0 kilogram object at rest at the top of a frictionless 4.0 meter high hill is allowed to slide to the bottom. What speed will the object reach at ...
Part B: Force, Acceleration and Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... k. Force can be measured in kilograms or Newtons depending upon the system of measurement (metric or otherwise). 7. Consider Newton's second law of motion to determine which of the following statements are true? List all that apply. a. If an object is accelerating to the right, the net force on the ...
... k. Force can be measured in kilograms or Newtons depending upon the system of measurement (metric or otherwise). 7. Consider Newton's second law of motion to determine which of the following statements are true? List all that apply. a. If an object is accelerating to the right, the net force on the ...
Wednesday, February 13, 2008
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintaine ...
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frames Aristotle (384-322BC): A natural state of a body is rest. Thus force is required to move an object. To move faster, ones needs larger forces. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintaine ...
RP 1P1 Force and Motion - NC Science Wiki
... Motion is as much a part of the physical world as matter and energy are. Everything moves—atoms and molecules; the stars, planets, and moons; the earth and its surface and everything on its surface; all living things, and every part of living things. Nothing in the universe is at rest. Since everyth ...
... Motion is as much a part of the physical world as matter and energy are. Everything moves—atoms and molecules; the stars, planets, and moons; the earth and its surface and everything on its surface; all living things, and every part of living things. Nothing in the universe is at rest. Since everyth ...
Document
... However, the Earth is always rotating, so the projectile also has a component of velocity that is directed eastward. As the projectile travels, the eastward component of its velocity remains constant (ignoring wind resistance). However, the Earth that the projectile is traveling over will have a sma ...
... However, the Earth is always rotating, so the projectile also has a component of velocity that is directed eastward. As the projectile travels, the eastward component of its velocity remains constant (ignoring wind resistance). However, the Earth that the projectile is traveling over will have a sma ...
AP Physics notes volume #3
... For ohmic materials, the ratio of the current density and the electric field, which gives rise to the current is equal to a constant, σ, which is the conductivity of the material. The reciprocal of the conductivity is called the resistivity, p. Each ohmic material has a characteristic resistivity th ...
... For ohmic materials, the ratio of the current density and the electric field, which gives rise to the current is equal to a constant, σ, which is the conductivity of the material. The reciprocal of the conductivity is called the resistivity, p. Each ohmic material has a characteristic resistivity th ...
Test 3 Preparation Questions
... B10. An electron is placed in a region of space where there is a uniform electric field which is in the +y direction as shown. The magnitude of the electric field is 51.0 V/m. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on the electron. ...
... B10. An electron is placed in a region of space where there is a uniform electric field which is in the +y direction as shown. The magnitude of the electric field is 51.0 V/m. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force on the electron. ...