A space-time geometric interpretation of the beta factor in Special
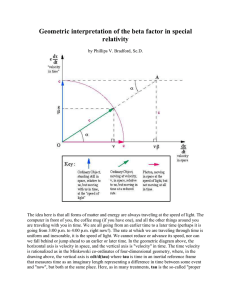
... the common reference frame in which the distances and time between the events is measured. We may select a reference frame that recognizes x = y = z = t = 0 where and when the first flash bulb pops. Then we can measure the values of x, y, z, and t when and where the second flash bulb pops. We can al ...
... the common reference frame in which the distances and time between the events is measured. We may select a reference frame that recognizes x = y = z = t = 0 where and when the first flash bulb pops. Then we can measure the values of x, y, z, and t when and where the second flash bulb pops. We can al ...
Force and Acceleration
... For example, when we are traveling in a bus, and bus is going at fast speed. The driver suddenly applies the brake and we are unable to control ourselves and our body plunges forward. It is because the bus and our body are moving at constant velocity. That is why in cars etc. we use seat belts. So t ...
... For example, when we are traveling in a bus, and bus is going at fast speed. The driver suddenly applies the brake and we are unable to control ourselves and our body plunges forward. It is because the bus and our body are moving at constant velocity. That is why in cars etc. we use seat belts. So t ...
Force and Acceleration
... For example, when we are traveling in a bus, and bus is going at fast speed. The driver suddenly applies the brake and we are unable to control ourselves and our body plunges forward. It is because the bus and our body are moving at constant velocity. That is why in cars etc. we use seat belts. So t ...
... For example, when we are traveling in a bus, and bus is going at fast speed. The driver suddenly applies the brake and we are unable to control ourselves and our body plunges forward. It is because the bus and our body are moving at constant velocity. That is why in cars etc. we use seat belts. So t ...
File
... “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” These are interaction pairs. Ex. A ball hits a bat. The ball exerts a force on the bat. The bat exerts a forces on the ball equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Outcome: The ball changed direction and accelerates. The bat is slowe ...
... “For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.” These are interaction pairs. Ex. A ball hits a bat. The ball exerts a force on the bat. The bat exerts a forces on the ball equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Outcome: The ball changed direction and accelerates. The bat is slowe ...
Laws of Motion Powerpoint
... • Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
... • Gravity is the force of attraction between two objects. • The strength of gravity depends on an object’s mass and distance. • For example, the moon’s gravity is 1/6 of the Earth’s gravity because it is much smaller. • Where would gravity be less, at sea level or on top of a mountain? ...
Forces - Solon City Schools
... Which of Newton’s law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion at a constant velocity will remain in motion at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force? Newton’s First Law of Motion What do we call the speed of a free falling object when ...
... Which of Newton’s law of motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion at a constant velocity will remain in motion at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force? Newton’s First Law of Motion What do we call the speed of a free falling object when ...
Newton`s Laws
... object in free fall? How does Newton’s 2nd Law relate to what a weight scale would read as you move up and down on an elevator? ...
... object in free fall? How does Newton’s 2nd Law relate to what a weight scale would read as you move up and down on an elevator? ...
![Forces-part2 [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008777900_1-5d589672d0a73f66816cf69cd76bbed3-300x300.png)