Law of Conservation of Energy
... You may have heard that it’s important to conserve energy. What this means is it’s important to lower the consumption of energy sources like, electricity/ fuel oil/ natural gas/ etc. The Law of Conservation of Energy is only stating that energy in= energy out ...
... You may have heard that it’s important to conserve energy. What this means is it’s important to lower the consumption of energy sources like, electricity/ fuel oil/ natural gas/ etc. The Law of Conservation of Energy is only stating that energy in= energy out ...
Thermochemistry ch 16 energy diagrams phase
... • How many Joules are in a bowl of breakfast cereal and milk which contain 340 Calories? ...
... • How many Joules are in a bowl of breakfast cereal and milk which contain 340 Calories? ...
Energy Transformation Poster Rubric
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
... Create a poster of an energy transformation. Your transformation cannot be of one from class. being stored, transformed or transferred at all times. Any device that undergoes an energy conversion where stored energy (potential energy) is changed to active energy (kinetic energy) undergoes an energy ...
Energy - WEB . WHRSD . ORG
... What kinds of energy are there? Mechanical (potential, kinetic) electrical thermal light sound ...
... What kinds of energy are there? Mechanical (potential, kinetic) electrical thermal light sound ...
Forms of Energy Review
... converts electrical energy into light (electromagnetic) energy and heat (thermal) energy ...
... converts electrical energy into light (electromagnetic) energy and heat (thermal) energy ...
Pop Quiz pp. 151-155 What two forms of energy combine to make
... 1. What two forms of energy combine to make mechanical energy? 2. What kind of potential energy does a projectile have? 3. Lava was used as an example of this type of energy. 4. Food and fuels are examples of this type of energy. 5. What form of energy are microwaves? ...
... 1. What two forms of energy combine to make mechanical energy? 2. What kind of potential energy does a projectile have? 3. Lava was used as an example of this type of energy. 4. Food and fuels are examples of this type of energy. 5. What form of energy are microwaves? ...
Energy
... But if you add heat energy or take it away, it causes particles to move faster or slower and thus changes the temp. ...
... But if you add heat energy or take it away, it causes particles to move faster or slower and thus changes the temp. ...
Power
... • W=m (change in v/change in t) d • You do work only when you exert a force on an object and move it. • Work is done only by the part of the force that is in the same direction as the motion. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company ...
... • W=m (change in v/change in t) d • You do work only when you exert a force on an object and move it. • Work is done only by the part of the force that is in the same direction as the motion. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company ...
Resource Page Work, Power, and Energy
... depends on how fast or slow the object vibrates. SC.4.P.10.4 - Describe how moving water and air are sources of energy and can be used to move things. SC.5.P.10.1 - Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. SC.5.P.10.2 - ...
... depends on how fast or slow the object vibrates. SC.4.P.10.4 - Describe how moving water and air are sources of energy and can be used to move things. SC.5.P.10.1 - Investigate and describe some basic forms of energy, including light, heat, sound, electrical, chemical, and mechanical. SC.5.P.10.2 - ...
Chapter 12: Work and Energy
... 3. Describe how a lever can increase the force without changing the amount of work being done. 4. Explain why pulleys are in the lever family. 5. Compare the mechanical advantage of a long thin wedge with a short, wide wedge. ...
... 3. Describe how a lever can increase the force without changing the amount of work being done. 4. Explain why pulleys are in the lever family. 5. Compare the mechanical advantage of a long thin wedge with a short, wide wedge. ...
power
... is converted to another form. To generate electricity, water must be in motion. This is kinetic (moving) energy. When flowing water turns blades in a turbine, the form is changed to mechanical (machine) energy. The turbine turns the generator rotor which then converts this mechanical energy into ano ...
... is converted to another form. To generate electricity, water must be in motion. This is kinetic (moving) energy. When flowing water turns blades in a turbine, the form is changed to mechanical (machine) energy. The turbine turns the generator rotor which then converts this mechanical energy into ano ...
What are the six main forms of energy?
... called atoms that are constantly moving. • The internal motion of atoms = heat/thermal energy. Ex: phase changes ...
... called atoms that are constantly moving. • The internal motion of atoms = heat/thermal energy. Ex: phase changes ...
Energy Conservation Notes Filled-in
... Energy 3. Stored energy. Potential Energy 4. Energy in motion. Kinetic Energy 5. Energy stored in bonds of molecules. Chemical Energy 6. Energy of position or place, especially dealing with height differences. Gravitational Energy 7. Movement of charges through a conductor. Electrical Energy 8. Ener ...
... Energy 3. Stored energy. Potential Energy 4. Energy in motion. Kinetic Energy 5. Energy stored in bonds of molecules. Chemical Energy 6. Energy of position or place, especially dealing with height differences. Gravitational Energy 7. Movement of charges through a conductor. Electrical Energy 8. Ener ...
Energy Vocabulary I
... 11. ____________ Potential energy that is stored by stretching or compressing. 12. ____________ Energy that is transferred from a warm object to a cooler object. 13. ____________ Energy stored due to the mass and height of an object. 14. ____________ Energy can be transferred and or transformed, but ...
... 11. ____________ Potential energy that is stored by stretching or compressing. 12. ____________ Energy that is transferred from a warm object to a cooler object. 13. ____________ Energy stored due to the mass and height of an object. 14. ____________ Energy can be transferred and or transformed, but ...
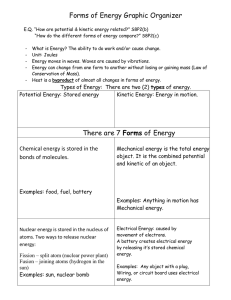
Forms of Energy
... movement of electrons. A battery creates electrical energy by releasing it’s stored chemical energy. Examples: Any object with a plug, Wiring, or circuit board uses electrical energy. ...
... movement of electrons. A battery creates electrical energy by releasing it’s stored chemical energy. Examples: Any object with a plug, Wiring, or circuit board uses electrical energy. ...
Chapter 3 Test – Energy! Name: ______ At its basic level, energy is
... 12. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that ___________________ can neither be created nor destroyed. 13. For example, when using an electric fan, some energy is converted to _________________ energy to turn the fan blades. 14. Some energy is converted into unwanted __________________ energy. ...
... 12. The Law of Conservation of Energy states that ___________________ can neither be created nor destroyed. 13. For example, when using an electric fan, some energy is converted to _________________ energy to turn the fan blades. 14. Some energy is converted into unwanted __________________ energy. ...
Presentation
... Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form into another. ...
... Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form into another. ...
Alternative energy

Alternative energy is any energy source that is an alternative to fossil fuel. These alternatives are intended to address concerns about such fossil fuels.The nature of what constitutes an alternative energy source has changed considerably over time, as have controversies regarding energy use. Today, because of the variety of energy choices and differing goals of their advocates, defining some energy types as ""alternative"" is highly controversial.In a general sense, alternative energy as it is currently conceived, is that which is produced or recovered without the undesirable consequences inherent in fossil fuel use, particularly high carbon dioxide emissions (greenhouse gas), an important factor in global warming.