on-campus manual for Lab 8
... left a gelatinous mass of carbon and hydrogen (hydrocarbons). After being buried under a mile or two of sediment, it formed petroleum (a fossil fuel). Ancient forests did the same thing; however, after they died and got buried, they turned into coal (another fossil fuel). Daily Source of Energy: The ...
... left a gelatinous mass of carbon and hydrogen (hydrocarbons). After being buried under a mile or two of sediment, it formed petroleum (a fossil fuel). Ancient forests did the same thing; however, after they died and got buried, they turned into coal (another fossil fuel). Daily Source of Energy: The ...
Energy Transformations (transformation_of_energy1)
... and potential energies. • Mechanical energy is the total energy of motion and position of an object. • Both kinetic and potential energies are types of mechanical energy. • Mechanical energy can be made up of both kinetic and potential or some of each. ...
... and potential energies. • Mechanical energy is the total energy of motion and position of an object. • Both kinetic and potential energies are types of mechanical energy. • Mechanical energy can be made up of both kinetic and potential or some of each. ...
6.P.3A.1 Properties and Sources of Energy
... Material (wood, candle wax) that is burning, the Sun, and electricity are all examples of sources of thermal energy. ...
... Material (wood, candle wax) that is burning, the Sun, and electricity are all examples of sources of thermal energy. ...
What is energy?
... • This stored energy of position is referred to as potential energy. • Potential energy is the stored energy of position possessed by an object. ...
... • This stored energy of position is referred to as potential energy. • Potential energy is the stored energy of position possessed by an object. ...
Lesson 4- Amusement Parks
... 3) Before allowing students a chance to answer, show them the definitions of their options on visual 4. Ask them to give you three different examples than the ones in the pictures of force in their every day lives. 4) What is gravity? Gravity is force that acts upon earth. It pushes items in a downw ...
... 3) Before allowing students a chance to answer, show them the definitions of their options on visual 4. Ask them to give you three different examples than the ones in the pictures of force in their every day lives. 4) What is gravity? Gravity is force that acts upon earth. It pushes items in a downw ...
06. Dynamics -- Energy 1. Energy
... Claim: In Newtonian physics, mass and energy are different properties. In Special Relativity, mass and energy are different names for the same property. • Objection 1: We use different units to measure mass (kg) and energy (kg⋅m2/s2). Doesn't this mean they're different properties? " No! Can choose ...
... Claim: In Newtonian physics, mass and energy are different properties. In Special Relativity, mass and energy are different names for the same property. • Objection 1: We use different units to measure mass (kg) and energy (kg⋅m2/s2). Doesn't this mean they're different properties? " No! Can choose ...
The Law of Conservation of Energy
... violate the conservation of energy? No, because we're no longer dealing with a closed system. Your car is gaining kinetic energy from the gasoline in its tank, but it's also gaining kinetic energy because it's going downhill. This isn't a closed system so the conservation of energy doesn't apply any ...
... violate the conservation of energy? No, because we're no longer dealing with a closed system. Your car is gaining kinetic energy from the gasoline in its tank, but it's also gaining kinetic energy because it's going downhill. This isn't a closed system so the conservation of energy doesn't apply any ...
P1 - Powerpoint - tonyconnett.com
... The steam is cooled down and turned back into water in the cooling tower ...
... The steam is cooled down and turned back into water in the cooling tower ...
Energy Unit Study Guide
... Be able to use conservation of energy with kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy to find the height or speed of an object at any point. Be able to use conservation of energy to find height or speed of an object at any point along a hill when friction is involved. Be able to calculate the ...
... Be able to use conservation of energy with kinetic energy and gravitational potential energy to find the height or speed of an object at any point. Be able to use conservation of energy to find height or speed of an object at any point along a hill when friction is involved. Be able to calculate the ...
Energy-Transformations-Practice-Quiz
... radiant energy to chemical energy. B. gravitational energy to radiant energy. C. chemical energy to radiant energy. D. kinetic energy to electric energy. ...
... radiant energy to chemical energy. B. gravitational energy to radiant energy. C. chemical energy to radiant energy. D. kinetic energy to electric energy. ...
File - Mrs. burt`s physical science class
... Lesson 12 Objectives Temperature 1. Explain that changes in the position and motion of atoms in a solid, liquid, or gas are the result of temperature increase or decrease. 2. Explain how the kinetic energy of atoms or molecules of different objects varies with their temperature. 3. Describe the dif ...
... Lesson 12 Objectives Temperature 1. Explain that changes in the position and motion of atoms in a solid, liquid, or gas are the result of temperature increase or decrease. 2. Explain how the kinetic energy of atoms or molecules of different objects varies with their temperature. 3. Describe the dif ...
Heat
... Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy can be converted from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed • Energy of the universe is constant • Can convert from one form to another ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy • Energy can be converted from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed • Energy of the universe is constant • Can convert from one form to another ...
ENERGY
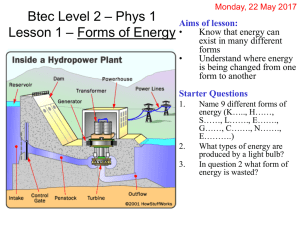
... electricity, it is almost free, there are no waste products, and hydropower does not pollute the water or the air. ...
... electricity, it is almost free, there are no waste products, and hydropower does not pollute the water or the air. ...
multiple choice
... (1) kinetic energy (2) chemical energy (3) potential energy (4) nuclear energy ______ 4- Because of friction? (1) energy is always conserved. (2) energy is not lost. (3) all energy is lost. (4) some potential energy turns into heat ______ 5- What type of energy transformation is represented in the d ...
... (1) kinetic energy (2) chemical energy (3) potential energy (4) nuclear energy ______ 4- Because of friction? (1) energy is always conserved. (2) energy is not lost. (3) all energy is lost. (4) some potential energy turns into heat ______ 5- What type of energy transformation is represented in the d ...
Chapter 5 Energy
... • There are different forms of energy all around us. This energy is moving or transferring from one place to another. ...
... • There are different forms of energy all around us. This energy is moving or transferring from one place to another. ...
File - Mrs. Goodall
... A. Steve throws a ball straight up and notices it slowing down. B. Emily asks for a push to get started on a swing. C. Paula decides to sit in an outside seat of a merry-go-round so that she will have a wilder ride. D. When Dave drops a bowling ball, it does not bounce as high as a basketball droppe ...
... A. Steve throws a ball straight up and notices it slowing down. B. Emily asks for a push to get started on a swing. C. Paula decides to sit in an outside seat of a merry-go-round so that she will have a wilder ride. D. When Dave drops a bowling ball, it does not bounce as high as a basketball droppe ...
Using Vocabulary
... True/False: If the statement is false, change the term or phrase to make the statement true. _____1. Energy in the form of motion is potential energy. ____ 2. The greater mass a moving object has; the more kinetic energy it has. _____ 3. A rock at the edge of a cliff has kinetic energy because of it ...
... True/False: If the statement is false, change the term or phrase to make the statement true. _____1. Energy in the form of motion is potential energy. ____ 2. The greater mass a moving object has; the more kinetic energy it has. _____ 3. A rock at the edge of a cliff has kinetic energy because of it ...
Alternative energy

Alternative energy is any energy source that is an alternative to fossil fuel. These alternatives are intended to address concerns about such fossil fuels.The nature of what constitutes an alternative energy source has changed considerably over time, as have controversies regarding energy use. Today, because of the variety of energy choices and differing goals of their advocates, defining some energy types as ""alternative"" is highly controversial.In a general sense, alternative energy as it is currently conceived, is that which is produced or recovered without the undesirable consequences inherent in fossil fuel use, particularly high carbon dioxide emissions (greenhouse gas), an important factor in global warming.