Nerve Supply
... third of the clavicle. 2. Middle fibers into the medial border of the acromion process of the scapula. 3. Lower fibers into the spine of the scapula. ...
... third of the clavicle. 2. Middle fibers into the medial border of the acromion process of the scapula. 3. Lower fibers into the spine of the scapula. ...
Variation in the Insertion of Brachialis Muscle
... Anatomy: The muscle has two heads. Superficial inserting into ulnar tuberosity innervated by musculocutaneous nerve, the deep head inserts into coronoid process of ulna and supplied by radial nerve. Embryology: Failure of muscle primordia to disappear may account for additional heads. Case report: A ...
... Anatomy: The muscle has two heads. Superficial inserting into ulnar tuberosity innervated by musculocutaneous nerve, the deep head inserts into coronoid process of ulna and supplied by radial nerve. Embryology: Failure of muscle primordia to disappear may account for additional heads. Case report: A ...
l0: fibers from the contralateral pontine nuclei, and the inferior
... hoprioceptive signals are carried ipsilaterally to the spinocerebellum, which consists of vermis, paravermal zones, and interposed nuclei' These nuclei project to the contralateral ventrolateral (VL) thalamic nucleus. The VL projects to the primary motor corto(. The cerebral cortex influences the co ...
... hoprioceptive signals are carried ipsilaterally to the spinocerebellum, which consists of vermis, paravermal zones, and interposed nuclei' These nuclei project to the contralateral ventrolateral (VL) thalamic nucleus. The VL projects to the primary motor corto(. The cerebral cortex influences the co ...
y. - كلية طب الاسنان
... fascia. The investing layer الطبقة المغلقةof deep cervical fascia splits to envelope the gland and the inner leaf صفحةpasses up to the base of the skull. The outer leaf extends superiorly as the parotidomasseteric fascia and reaches up to the zygomatic arch. On the gland, the fascia tends to be ...
... fascia. The investing layer الطبقة المغلقةof deep cervical fascia splits to envelope the gland and the inner leaf صفحةpasses up to the base of the skull. The outer leaf extends superiorly as the parotidomasseteric fascia and reaches up to the zygomatic arch. On the gland, the fascia tends to be ...
muscles involved in respiration
... diaphragm & innervates it from abdominal surface • Action: contraction (descent) of diaphragm increase vertical diameter of thoracic cavity (essential for ...
... diaphragm & innervates it from abdominal surface • Action: contraction (descent) of diaphragm increase vertical diameter of thoracic cavity (essential for ...
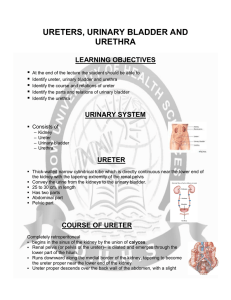
Ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
... External layer, composed of fibers having for the most part a longitudinal arrangement Middle layer, in which the fibers are arranged, more or less, in a circular manner Internal layer, in which the fibers have a general longitudinal arrangement. ...
... External layer, composed of fibers having for the most part a longitudinal arrangement Middle layer, in which the fibers are arranged, more or less, in a circular manner Internal layer, in which the fibers have a general longitudinal arrangement. ...
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS I
... Signal transduction within cells is accomplished by combinations of: 1st Messenger (extracellular signals e.g. epinephrine, acetylcholine) Receptor Effectors (e.g. adenylyl cyclase, phospholipases, kinases, ion channels etc) 2nd messengers (cAMP, cGMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylgycerol, C ...
... Signal transduction within cells is accomplished by combinations of: 1st Messenger (extracellular signals e.g. epinephrine, acetylcholine) Receptor Effectors (e.g. adenylyl cyclase, phospholipases, kinases, ion channels etc) 2nd messengers (cAMP, cGMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylgycerol, C ...
Practice Lecture Exam
... branch of the autonomic system is responsible actions associated with ejaculation rather than erection. c. NO. Erection, in males and females, is stimulated by parasympathetic fibers that originate from the pelvic splanchnic nerves (Spinal cord levels S2-S4). Stimulated parasympathetic neurons rele ...
... branch of the autonomic system is responsible actions associated with ejaculation rather than erection. c. NO. Erection, in males and females, is stimulated by parasympathetic fibers that originate from the pelvic splanchnic nerves (Spinal cord levels S2-S4). Stimulated parasympathetic neurons rele ...
Forelimb or thoracic limb (membra thoracica)
... The scapular region covers the shoulder blade and the scapular cartilage. The dorsal half of the skin is innervated by the dorsal branches of the cervical nerves. These nerves curve around the scapular cartilage or the dorsal margin of the scapula. The cranioventral section of the skin is innervated ...
... The scapular region covers the shoulder blade and the scapular cartilage. The dorsal half of the skin is innervated by the dorsal branches of the cervical nerves. These nerves curve around the scapular cartilage or the dorsal margin of the scapula. The cranioventral section of the skin is innervated ...
Biomechanics Functional Anatomy Human Female Genitalia
... The inner skin of the vulva is hairless and is usually a pinkish color. During sex the color can change to a deep red, purple or blue depending upon the venous structure of the vulva. Women who have been pregnant will often have a more pronounced venous structure of the labia minora, causing it to b ...
... The inner skin of the vulva is hairless and is usually a pinkish color. During sex the color can change to a deep red, purple or blue depending upon the venous structure of the vulva. Women who have been pregnant will often have a more pronounced venous structure of the labia minora, causing it to b ...
Transcriptional mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle
... and cytoskeletal crosslinking proteins such as α‑actinin, myomesin and the kinase titin1,2 (FIG. 1). In vertebrates, striated muscle cells are found in two tissues: skeletal and heart muscle (FIG. 1). Although they both have highly ordered myofibril structures, they have distinct embryonic origins ...
... and cytoskeletal crosslinking proteins such as α‑actinin, myomesin and the kinase titin1,2 (FIG. 1). In vertebrates, striated muscle cells are found in two tissues: skeletal and heart muscle (FIG. 1). Although they both have highly ordered myofibril structures, they have distinct embryonic origins ...
m5zn_1bebf85f2ab3865
... covered by a thin layer of compact bone. • The glenoid fossa is formed only of thin layer of compact bone. • The fibrous covering layer is thin in the g.fossa and thickened rapidly on the posterior slope of the articular eminence. ...
... covered by a thin layer of compact bone. • The glenoid fossa is formed only of thin layer of compact bone. • The fibrous covering layer is thin in the g.fossa and thickened rapidly on the posterior slope of the articular eminence. ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.wordpress.com Yeditepe
... Joints exhibit a variety of forms and functions. Some joints have no movement, such as the epiphysial plates between the epiphysis and diaphysis of a growing long bone; others allow only slight movement, such as teeth within their sockets; and some are freely movable, such as the glenohumeral (shoul ...
... Joints exhibit a variety of forms and functions. Some joints have no movement, such as the epiphysial plates between the epiphysis and diaphysis of a growing long bone; others allow only slight movement, such as teeth within their sockets; and some are freely movable, such as the glenohumeral (shoul ...
Full text (external site)
... by doing so gained extraordinary size (Verkhoshansky & Siff, 2009). This may seem outrageous as far-fetched as this seems, but the story of Milo illustrates a practical principle in human muscular growth and resistance training: The overload principle (Bompa & Haff, 2009). Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) e ...
... by doing so gained extraordinary size (Verkhoshansky & Siff, 2009). This may seem outrageous as far-fetched as this seems, but the story of Milo illustrates a practical principle in human muscular growth and resistance training: The overload principle (Bompa & Haff, 2009). Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) e ...
A Case Report in Thai Cadaver - TU-OSS
... After piercing the coracobrachialis muscle, the MCN runs downward between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles, innervating both muscles. It then divides into two branches, one of them descending inferolaterally behind the biceps brachii which is continuous as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the ...
... After piercing the coracobrachialis muscle, the MCN runs downward between the biceps brachii and brachialis muscles, innervating both muscles. It then divides into two branches, one of them descending inferolaterally behind the biceps brachii which is continuous as the lateral cutaneous nerve of the ...
Practical anatomy equine muscles 2016
... If tight; short choppy sideways or brings the stride and resistance to foreleg and shoulder ...
... If tight; short choppy sideways or brings the stride and resistance to foreleg and shoulder ...
Flexor Digitorum Longus Muscle — an Unusual
... electromyographic study of human foot which showed that FDB is not preferentially recruited over flexor digitorum longus for any normal posture or locomotion. Asomugha et al (6). have reported accessory flexor of the fifth toe. This muscle originated from the tendon of tibialis posterior and inserte ...
... electromyographic study of human foot which showed that FDB is not preferentially recruited over flexor digitorum longus for any normal posture or locomotion. Asomugha et al (6). have reported accessory flexor of the fifth toe. This muscle originated from the tendon of tibialis posterior and inserte ...
201 Practical 2 worksheet BLANK
... 55. Which bone acts as a landmark along the medial side of the forearm? a. Is this bone on the pinky side or thumb side? 56. All muscles with “pollicis” in their name act on which body ...
... 55. Which bone acts as a landmark along the medial side of the forearm? a. Is this bone on the pinky side or thumb side? 56. All muscles with “pollicis” in their name act on which body ...
View ePoster - ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2016
... • The Inferior Gluteal Nerve leaves the pelvis via greater scia0c foramen, inferior and anterior to the Piriformis muscle and lateral to the Scia0c Nerve. • The IGN then divides into branches that pass posteriorly into the deep surface of the Gluteus Maximus Muscle. ...
... • The Inferior Gluteal Nerve leaves the pelvis via greater scia0c foramen, inferior and anterior to the Piriformis muscle and lateral to the Scia0c Nerve. • The IGN then divides into branches that pass posteriorly into the deep surface of the Gluteus Maximus Muscle. ...
Dr. H.A.Jaafar Al-Nahrain University
... • Has a posterior part that is photosensitive; its anterior part, which is not photosensitive, constitutes inner lining of ciliary body and posterior part of iris. 1. Optic disk (blind spot) • Consists of optic nerve fibers formed by axons of ganglion cells. These cells are connected to rods and con ...
... • Has a posterior part that is photosensitive; its anterior part, which is not photosensitive, constitutes inner lining of ciliary body and posterior part of iris. 1. Optic disk (blind spot) • Consists of optic nerve fibers formed by axons of ganglion cells. These cells are connected to rods and con ...
Transcripts/1_12 2
... a. We will be getting a general introduction to cranial nerves (CN) this hour, and then later we will have the opportunity to review them further. He’s giving us the essence and functional deficits of each. II. Considerations [S2] a. When looking at the CNs, look at the embryologic derivations: does ...
... a. We will be getting a general introduction to cranial nerves (CN) this hour, and then later we will have the opportunity to review them further. He’s giving us the essence and functional deficits of each. II. Considerations [S2] a. When looking at the CNs, look at the embryologic derivations: does ...
H1. Coronary artery disease is a frequent cause of myocardial
... very slurred when she tried to answer. He called an ambulance to take her to the nearest hospital. Upon admission, her face appears symmetric, but when asked to protrude her tongue, it deviates toward the left. She is unable to tell if her right toe is moved up or down by the physician when she clo ...
... very slurred when she tried to answer. He called an ambulance to take her to the nearest hospital. Upon admission, her face appears symmetric, but when asked to protrude her tongue, it deviates toward the left. She is unable to tell if her right toe is moved up or down by the physician when she clo ...
Document
... A cutaneous sac consisting of 2 layers: heavily pigmented skin and the closely related dartos fascia, a fat-free fascial layer including smooth muscle fibers (dartos muscle) responsible for the rugose (wrinkled) appearance of the scrotum. Because the dartos muscle attaches to the skin, its contracti ...
... A cutaneous sac consisting of 2 layers: heavily pigmented skin and the closely related dartos fascia, a fat-free fascial layer including smooth muscle fibers (dartos muscle) responsible for the rugose (wrinkled) appearance of the scrotum. Because the dartos muscle attaches to the skin, its contracti ...
Grip and Pinch
... adductor pollicis muscle, the hypothenar muscles (opponens digiti quinti, flexor digiti quinti, abductor digiti quinti), the thenar muscles (abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis), and the lumbricals. The median and ulnar nerves control the performance of the intrinsic ...
... adductor pollicis muscle, the hypothenar muscles (opponens digiti quinti, flexor digiti quinti, abductor digiti quinti), the thenar muscles (abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis), and the lumbricals. The median and ulnar nerves control the performance of the intrinsic ...
Myocyte

A myocyte (also known as a muscle cell) is the type of cell found in muscle tissue. Myocytes are long, tubular cells that develop from myoblasts to form muscles in a process known as myogenesis. There are various specialized forms of myocytes: cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle cells, with various properties. The striated cells of cardiac and skeletal muscles are referred to as muscle fibers. Cardiomyocytes are the muscle fibres that form the chambers of the heart, and have a single central nucleus. Skeletal muscle fibers help support and move the body and tend to have peripheral nuclei. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the stomach.