Chapter 15: Thermodynamics
... 1. You cannot win (that is, you cannot get something for nothing, because matter and energy are conserved). 2. You cannot break even (you cannot return to the same energy state, because there is always an increase in disorder; entropy always increases). 3. You cannot get out of the game (because abs ...
... 1. You cannot win (that is, you cannot get something for nothing, because matter and energy are conserved). 2. You cannot break even (you cannot return to the same energy state, because there is always an increase in disorder; entropy always increases). 3. You cannot get out of the game (because abs ...
any physical system, whether or not it can exchange energy and
... Open system A system, over the border of which both energy and mass can be transmitted. ...
... Open system A system, over the border of which both energy and mass can be transmitted. ...
PS5, Thermo Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be
... Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although in many processes energy is transferred to the environment as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the ...
... Thermodynamics Standards: 3. Energy cannot be created or destroyed, although in many processes energy is transferred to the environment as heat. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know heat flow and work are two forms of energy transfer between systems. b. Students know that the ...
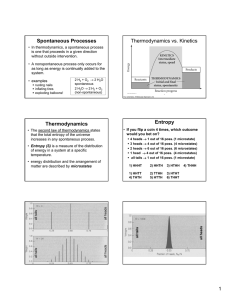
The Four Laws of Thermodynamics
... The conservation of Energy. The change in internal energy of a system dU is equal to the heat added to the system dQ minus the work done by the system dW dU = dQ − dW. For a classical system at constant pressure P where work is mechanical work, and where there are no exotic forms of work such as wor ...
... The conservation of Energy. The change in internal energy of a system dU is equal to the heat added to the system dQ minus the work done by the system dW dU = dQ − dW. For a classical system at constant pressure P where work is mechanical work, and where there are no exotic forms of work such as wor ...
ppt
... Many of you have, no doubt, had differing definitions in different courses (a molecular biologists definition of life is very specific, for example) Neither is this discussion purely academic, it already has significant in the fields of artificial intelligence (where it is tied in intimately with th ...
... Many of you have, no doubt, had differing definitions in different courses (a molecular biologists definition of life is very specific, for example) Neither is this discussion purely academic, it already has significant in the fields of artificial intelligence (where it is tied in intimately with th ...
Entropy And Entropy-based Features In Signal Processing K
... Entropy (or an entropy-based feature) can be computed from any finite set of values, e.g. a parametric vector, a discrete spectral density estimate, or directly from a segment of a digital signal. We used the following algorithms to compute the entropy: ...
... Entropy (or an entropy-based feature) can be computed from any finite set of values, e.g. a parametric vector, a discrete spectral density estimate, or directly from a segment of a digital signal. We used the following algorithms to compute the entropy: ...
Entropy, a statistical approach
... The system’s microstate is described by: o Positions of all particles o Momenta of all particles (p = mv) o Occupied energy levels for each particle This would be a lot of variables if each particle was considered independently. A system with a mass of ~1 mg will contain millions of millions of mill ...
... The system’s microstate is described by: o Positions of all particles o Momenta of all particles (p = mv) o Occupied energy levels for each particle This would be a lot of variables if each particle was considered independently. A system with a mass of ~1 mg will contain millions of millions of mill ...
Thermodynamic principles. - med.muni
... – Thermodynamic system: A region of space bounded by arbitrary surfaces which delineate the portion of the universe we are interested in – Isolated system: one which cannot exchange particles or energy with its environment. – Open system: one which can exchanges both particles and energy with its en ...
... – Thermodynamic system: A region of space bounded by arbitrary surfaces which delineate the portion of the universe we are interested in – Isolated system: one which cannot exchange particles or energy with its environment. – Open system: one which can exchanges both particles and energy with its en ...
Summary - Clarkson University
... It is also apparent that, as TL → TH , ε → 0. Thus, it is impossible for a system operating in a cycle and connected to a single heat reservoir to produce a positive amount of work in the surroundings. I. Entropy and irreversible processes. For real (i.e., irreversible) processes: ...
... It is also apparent that, as TL → TH , ε → 0. Thus, it is impossible for a system operating in a cycle and connected to a single heat reservoir to produce a positive amount of work in the surroundings. I. Entropy and irreversible processes. For real (i.e., irreversible) processes: ...
Chapter 17 notes ppt
... (randomness) = increasing in entropy • Third Law = entropy of a perfect crystal is zero at 0K = (absolute entropy can be determined for any temp higher than 0K) ...
... (randomness) = increasing in entropy • Third Law = entropy of a perfect crystal is zero at 0K = (absolute entropy can be determined for any temp higher than 0K) ...