Liver Functions Part II
... In the small intestines • Complete digestion occurs in the small intestines • End products (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol) diffuse into the blood vessels lining the small intestines. • This process is called Absorption. ...
... In the small intestines • Complete digestion occurs in the small intestines • End products (glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol) diffuse into the blood vessels lining the small intestines. • This process is called Absorption. ...
Document
... Some people never develop symptoms, others develop chronic symptoms that stay with them their whole life. ...
... Some people never develop symptoms, others develop chronic symptoms that stay with them their whole life. ...
Digestive Anatomy
... of peritoneum which attaches to small intestine • Omentum- attached to greater curvature of the stomach and is laced with fat deposits ...
... of peritoneum which attaches to small intestine • Omentum- attached to greater curvature of the stomach and is laced with fat deposits ...
biliary system
... bloodstream. The third type, cholestatic, or obstructive, jaundice, occurs when essentially normal liver cells are unable to transport bilirubin either through the hepatic-bile capillary membrane, because of damage in that area, or through the biliary tract, because of anatomical obstructions such a ...
... bloodstream. The third type, cholestatic, or obstructive, jaundice, occurs when essentially normal liver cells are unable to transport bilirubin either through the hepatic-bile capillary membrane, because of damage in that area, or through the biliary tract, because of anatomical obstructions such a ...
Liver Functions and Abnormalities
... • Elevated In extra and intrahepatic obstruction , the extent does not differentiate between either, does can not help identify etiology (CBD stone or stricture, Ca, PSC , Drug-induced hepatitis , PBC ) • Modest increases in AP ~ Three times the normal ~ 350 are nonspecific and may occur in any live ...
... • Elevated In extra and intrahepatic obstruction , the extent does not differentiate between either, does can not help identify etiology (CBD stone or stricture, Ca, PSC , Drug-induced hepatitis , PBC ) • Modest increases in AP ~ Three times the normal ~ 350 are nonspecific and may occur in any live ...
Slide 1
... Pattern of Blood Vessels Three major arteries • Coeliac • Superior mesenteric • Inferior mesenteric ...
... Pattern of Blood Vessels Three major arteries • Coeliac • Superior mesenteric • Inferior mesenteric ...
The digestive system
... Bile is a yellow, brown, or green, watery solution containing bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, phospholipids and a variety of electrolytes. pH of 7.6 – ...
... Bile is a yellow, brown, or green, watery solution containing bile salts, bile pigments, cholesterol, phospholipids and a variety of electrolytes. pH of 7.6 – ...
Summary for Chapter 3 – Digestion, Absorption, and
... The many folds and villi of the small intestine dramatically increase its surface area, facilitating nutrient absorption. Nutrients pass through the cells of the villi and enter either the blood (if they are water soluble or small fat fragments) or the lymph (if they are fat soluble). Nutrients leav ...
... The many folds and villi of the small intestine dramatically increase its surface area, facilitating nutrient absorption. Nutrients pass through the cells of the villi and enter either the blood (if they are water soluble or small fat fragments) or the lymph (if they are fat soluble). Nutrients leav ...
The Digestive System - Part 1
... The mouth, aided by salivary glands and teeth, break down the food and prepare it for digestion. The salivary glands (there are 3 pairs of them) produce saliva, which encourages parasympathetic action in your nervous system, is the key to stimulating digestive activity. The pharynx and esophagus mov ...
... The mouth, aided by salivary glands and teeth, break down the food and prepare it for digestion. The salivary glands (there are 3 pairs of them) produce saliva, which encourages parasympathetic action in your nervous system, is the key to stimulating digestive activity. The pharynx and esophagus mov ...
Section IX – Digestive System
... Section IX – Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source of energy through absorption of nutrients and to eliminate solid waste products. The GI tract ...
... Section IX – Digestive System The digestive system refers to the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. It consists of organs and glands that break down food products to be used by the body as a source of energy through absorption of nutrients and to eliminate solid waste products. The GI tract ...
Nutrition Issues in Liver Disease
... – High calorie/protein requirements – start slowly Limit protein (0.6 g/kg/day) in coma/severe PSE (? role of BCAA) Make adjustments based on patient’s condition ...
... – High calorie/protein requirements – start slowly Limit protein (0.6 g/kg/day) in coma/severe PSE (? role of BCAA) Make adjustments based on patient’s condition ...
Gut Tube and Digestion
... Directs blood that has already been through gut capillaries into liver capillaries (or sinusoids) Allows nutrients and toxins to be removed from blood ...
... Directs blood that has already been through gut capillaries into liver capillaries (or sinusoids) Allows nutrients and toxins to be removed from blood ...
Gut Tube and Digestion
... Directs blood that has already been through gut capillaries into liver capillaries (or sinusoids) Allows nutrients and toxins to be removed from blood ...
... Directs blood that has already been through gut capillaries into liver capillaries (or sinusoids) Allows nutrients and toxins to be removed from blood ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... The Liver • The Bile Duct System – Liver secretes bile fluid • Into a network of narrow channels (bile canaliculi) • Between opposing membranes of adjacent liver cells ...
... The Liver • The Bile Duct System – Liver secretes bile fluid • Into a network of narrow channels (bile canaliculi) • Between opposing membranes of adjacent liver cells ...
Frog
... 3. Find the conus anteriosus, a single, wide arterial vessel leaving the ventricle and passing ventrally over the right atrium. Follow the conus anteriosus forward to where it divides into three branches on each side. The middle artery on each side is the systemic artery, which fuses behind the hear ...
... 3. Find the conus anteriosus, a single, wide arterial vessel leaving the ventricle and passing ventrally over the right atrium. Follow the conus anteriosus forward to where it divides into three branches on each side. The middle artery on each side is the systemic artery, which fuses behind the hear ...
Amino Acids: From Ingestion To Excretion.
... pancreas to secrete bicarbonate into the small intestine to neutralize the pH to about pH 7. Zymogens trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and procarboxypeptidase are also secreted by the pancreas and activated by other enzymes, like enteropeptidase. These activated enzymes further hydrolyze the incoming ...
... pancreas to secrete bicarbonate into the small intestine to neutralize the pH to about pH 7. Zymogens trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and procarboxypeptidase are also secreted by the pancreas and activated by other enzymes, like enteropeptidase. These activated enzymes further hydrolyze the incoming ...
The Digestive System - Mrs Frank Science Wiki
... by the liver, intestines and stomach. Bile is squeezed from the gallbladder into the small intestine, where it breaks up large fat droplets into very small ones. This allows more fat molecules to be exposed to the enzymes. Storing Nutrients and Protecting the Body After all the nutrients are broken ...
... by the liver, intestines and stomach. Bile is squeezed from the gallbladder into the small intestine, where it breaks up large fat droplets into very small ones. This allows more fat molecules to be exposed to the enzymes. Storing Nutrients and Protecting the Body After all the nutrients are broken ...
diet and your liver - Dr. Imtiaz Alam, MD
... blood sugar. This enables us to keep an even level of energy throughout the day. Without this balance, we would need to eat constantly to keep up our energy. Proteins reach the liver in their simpler form called amino acids. Once in the liver, they are either released to the muscles as energy, store ...
... blood sugar. This enables us to keep an even level of energy throughout the day. Without this balance, we would need to eat constantly to keep up our energy. Proteins reach the liver in their simpler form called amino acids. Once in the liver, they are either released to the muscles as energy, store ...
19 Digestive flashcards short
... 48. What is an accurate test for colon cancer? 49. Varicose veins in the rectum. 50. This is the largest internal organ of the body, located on the right side, below the diaphragm, and extends below the costal margin (can palpate). It has many functions and is the most complex organ except the brain ...
... 48. What is an accurate test for colon cancer? 49. Varicose veins in the rectum. 50. This is the largest internal organ of the body, located on the right side, below the diaphragm, and extends below the costal margin (can palpate). It has many functions and is the most complex organ except the brain ...
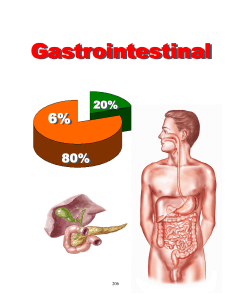
Gastrointestinal
... typically present for the first 12 weeks. It if followed by the anti-HBs antibody indicating recovery or immunity. HBeAg appears during infection and is present in the chronic carrier state. Anti-HBe denotes recovery. The Anti-HBc-IgM indicates acute infection and the AntiHBc indicates that the indi ...
... typically present for the first 12 weeks. It if followed by the anti-HBs antibody indicating recovery or immunity. HBeAg appears during infection and is present in the chronic carrier state. Anti-HBe denotes recovery. The Anti-HBc-IgM indicates acute infection and the AntiHBc indicates that the indi ...
Anden
... (belly button) to your left side about the 10th rib, and then it goes down to just inside your other hip bone ...
... (belly button) to your left side about the 10th rib, and then it goes down to just inside your other hip bone ...
Digestion and Alcohol - Alberta Health Services
... Alcohol and Medications Many prescribed and over-the-counter medications interact with alcohol, thereby altering the metabolism or effects of alcohol and/or the medication. ...
... Alcohol and Medications Many prescribed and over-the-counter medications interact with alcohol, thereby altering the metabolism or effects of alcohol and/or the medication. ...
File
... Diverticulitis: small, bulging sacs of the inner lining of the intestine that become inflammed Diverticulosis: abnormal presence of out pockets on the surface of the small intestine or colon Esophagitis: inflammation of the esophagus Fistula: abnormal opening between two internal organs Gastritis/ga ...
... Diverticulitis: small, bulging sacs of the inner lining of the intestine that become inflammed Diverticulosis: abnormal presence of out pockets on the surface of the small intestine or colon Esophagitis: inflammation of the esophagus Fistula: abnormal opening between two internal organs Gastritis/ga ...
Liver transplantation

Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with some or all of a healthy liver from another person (allograft). The most commonly used technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic location as the original liver. Liver transplantation is a viable treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure. Typically three surgeons and two anesthesiologists are involved, with up to four supporting nurses. The surgical procedure is very demanding and ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Numerous anastomoses and sutures, and many disconnections and reconnections of abdominal and hepatic tissue, must be made for the transplant to succeed, requiring an eligible recipient and a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match.