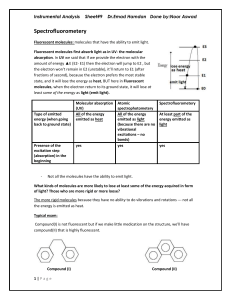
L09 Instru Spectrofluorometery
... *detector*(the photocell in UV designed to measure I° and It and take the ratio but here in spectrofluorometer it will measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light). Note the design of the spectrofluorometer: The angle between the incident light and the photocell is 90° (but in UV all th ...
... *detector*(the photocell in UV designed to measure I° and It and take the ratio but here in spectrofluorometer it will measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light). Note the design of the spectrofluorometer: The angle between the incident light and the photocell is 90° (but in UV all th ...
Problem Set 9: SOLUTIONS
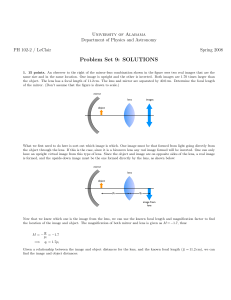
... 3. 15 points. As light from the Sun enters the atmosphere, it refracts due to the small difference between the speeds of light in air and in vacuum. The optical length of the day is defined as the time interval between the instant when the top of the Sun is just visibly observed above the horizon, t ...
... 3. 15 points. As light from the Sun enters the atmosphere, it refracts due to the small difference between the speeds of light in air and in vacuum. The optical length of the day is defined as the time interval between the instant when the top of the Sun is just visibly observed above the horizon, t ...
3. How to - TYC Physics Workshop Project
... It is possible to produce both upright and upside-down images in an everyday metal teaspoon. It is also possible for the upright image to be larger than or smaller than the object. Explain how to hold the spoon and where to put the object for each of type of image that may be produced by a metal spo ...
... It is possible to produce both upright and upside-down images in an everyday metal teaspoon. It is also possible for the upright image to be larger than or smaller than the object. Explain how to hold the spoon and where to put the object for each of type of image that may be produced by a metal spo ...
Lab 5: Polarization of Light 1 Introduction 2 Linear Polarization 3
... structure, with the following interesting property: light polarized parallel to the optic axis experiences a different index of refraction (and therefore has a different velocity) than light polarized perpendicular to the optic axis. Such crystals are called birefringent, and can be used to make a r ...
... structure, with the following interesting property: light polarized parallel to the optic axis experiences a different index of refraction (and therefore has a different velocity) than light polarized perpendicular to the optic axis. Such crystals are called birefringent, and can be used to make a r ...
Sensors - UCLA IEEE Micromouse
... One emitter/receiver pair can be used to detect walls in one direction Use infrared light to avoid visible ambient light interference ...
... One emitter/receiver pair can be used to detect walls in one direction Use infrared light to avoid visible ambient light interference ...
Measuring cellular structure at submicrometer scale with light
... diluting the stock suspension with de-ionized and distilled water to obtain the required optical density. Fig. 3 summarizes the experimental results obtained for polystyrene particles. To demonstrate the symmetry of the A/LSS scattering patterns, the parallel-polarized component of the backscattered ...
... diluting the stock suspension with de-ionized and distilled water to obtain the required optical density. Fig. 3 summarizes the experimental results obtained for polystyrene particles. To demonstrate the symmetry of the A/LSS scattering patterns, the parallel-polarized component of the backscattered ...
Select Safety Light Curtain Terms
... is allowed to ignore the presence of an object within their portion of the protection field. However, unlike fixed blanking (where the inactive beams are fixed), “floating blanking” allows the set number of adjacent beams to move within protected field … thus allowing the object to be ignored to mov ...
... is allowed to ignore the presence of an object within their portion of the protection field. However, unlike fixed blanking (where the inactive beams are fixed), “floating blanking” allows the set number of adjacent beams to move within protected field … thus allowing the object to be ignored to mov ...
Electricity and Magnetism Experiment
... polarized components with equal amplitudes. For a material that is birefringent, the indices of refraction are different for the left and right circularly polarized components of light passing through the material. Each polarization component traverses the sample with a different refractive index an ...
... polarized components with equal amplitudes. For a material that is birefringent, the indices of refraction are different for the left and right circularly polarized components of light passing through the material. Each polarization component traverses the sample with a different refractive index an ...
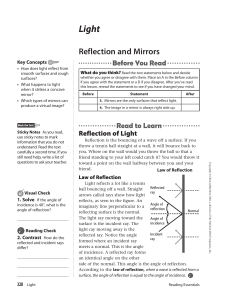
Reflection and Mirrors
... The word plane means “flat,” so a plane mirror has a flat reflecting surface. The image a plane mirror forms is the same size as the object. However, it is a virtual image because no object is located at the place where the image appears. A virtual image is an image of an object that your brain perc ...
... The word plane means “flat,” so a plane mirror has a flat reflecting surface. The image a plane mirror forms is the same size as the object. However, it is a virtual image because no object is located at the place where the image appears. A virtual image is an image of an object that your brain perc ...
The diffraction of light by sound waves of high
... index is minimum along CD. A simple consideration of the above shows that the difference between the optical lengths of A'B' and C'D' is less than that between those of AB and CD. As this difference gives twice the amplitude of the corrugation of the emerging wave-front, it follows, in the case show ...
... index is minimum along CD. A simple consideration of the above shows that the difference between the optical lengths of A'B' and C'D' is less than that between those of AB and CD. As this difference gives twice the amplitude of the corrugation of the emerging wave-front, it follows, in the case show ...
Nanophotonics: Shrinking light-based technology
... are nanophotonic elements designed to achieve this functionality, transducing free-space, far-field radiation to localized electromagnetic energy. The simplest nanoantenna is a single metal nanoparticle whose free electrons can support localized plasmon resonances at visible wavelengths, implying th ...
... are nanophotonic elements designed to achieve this functionality, transducing free-space, far-field radiation to localized electromagnetic energy. The simplest nanoantenna is a single metal nanoparticle whose free electrons can support localized plasmon resonances at visible wavelengths, implying th ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.