Properties of Radiation What`s this?
... • Model the scattering process (path radiance) to remove its effect • Dark target subtraction • Measure reflectance and calibrate satellite data http://nature.berkeley.edu/~penggong/textbook/chapter5/html/sect52.htm ...
... • Model the scattering process (path radiance) to remove its effect • Dark target subtraction • Measure reflectance and calibrate satellite data http://nature.berkeley.edu/~penggong/textbook/chapter5/html/sect52.htm ...
September 20, 2000 - University of South Florida
... Although simple in meaning, Lw can never be measured directly. Instead it can only be derived using measurements from either under- or above-water instruments (see Mueller and Austin, 1995 and references therein). An above-water sensor will not only detect Lw, but also the sky radiance reflected by ...
... Although simple in meaning, Lw can never be measured directly. Instead it can only be derived using measurements from either under- or above-water instruments (see Mueller and Austin, 1995 and references therein). An above-water sensor will not only detect Lw, but also the sky radiance reflected by ...
ppt document
... 1. Magnification: M = fo/fe depends on the focal lengths of the two lenses. 2. Light gathering ability: depends on area of objective lens, so depends on diameter of objective lens squared (D2). 3. Resolution ability: depends on diameter of objective lens: Max magnification = 60 power/in * D. ...
... 1. Magnification: M = fo/fe depends on the focal lengths of the two lenses. 2. Light gathering ability: depends on area of objective lens, so depends on diameter of objective lens squared (D2). 3. Resolution ability: depends on diameter of objective lens: Max magnification = 60 power/in * D. ...
DOWNLOAD Lesson 201 Handout
... 18. Compare and contrast the 3 types of spectra: continuous, absorption, and emission. 19. How do scientists determine the elements that make up a star? 20. Why do sailors at sea like to wear polarized sunglasses on sunny days? 21. How do rainbows form in Earth's atmosphere? 22. How can you be sure ...
... 18. Compare and contrast the 3 types of spectra: continuous, absorption, and emission. 19. How do scientists determine the elements that make up a star? 20. Why do sailors at sea like to wear polarized sunglasses on sunny days? 21. How do rainbows form in Earth's atmosphere? 22. How can you be sure ...
Two-dimensional control of light with light on metasurfaces
... We demonstrate all-optical wavefront control by projecting images onto opposite sides of the free-standing gold metasurface using coherent light. By modulating the relative phase of the two beams, we control the absorption of light, and hence the wavefront, with high spatial resolution. This is illu ...
... We demonstrate all-optical wavefront control by projecting images onto opposite sides of the free-standing gold metasurface using coherent light. By modulating the relative phase of the two beams, we control the absorption of light, and hence the wavefront, with high spatial resolution. This is illu ...
Multifilamentation transmission through fog
... with radius r ⬃ 100 m has a MFP of only ⬃0.5 mm, so that one individual filament hits about 2000 particles per meter of propagation. This may possibly induce substantial damage on the filamentary structure. However, the droplet radius 共1 m兲 is typically 100 times smaller than the filament size. Si ...
... with radius r ⬃ 100 m has a MFP of only ⬃0.5 mm, so that one individual filament hits about 2000 particles per meter of propagation. This may possibly induce substantial damage on the filamentary structure. However, the droplet radius 共1 m兲 is typically 100 times smaller than the filament size. Si ...
Optical Low-pass Filter
... optical low-pass filter, and this is proportional to the width of the low-pass filter. Pseudo-signal: Generated by solid-state image pickup devices, pseudo-signals causes horizontal lines to look jagged or the black-and-white lattice fringe to be colored. ...
... optical low-pass filter, and this is proportional to the width of the low-pass filter. Pseudo-signal: Generated by solid-state image pickup devices, pseudo-signals causes horizontal lines to look jagged or the black-and-white lattice fringe to be colored. ...
Chapter 25
... The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited due to the wave nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as non-coherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker ...
... The ability of an optical system to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited due to the wave nature of light If two sources of light are close together, they can be treated as non-coherent sources Because of diffraction, the images consist of bright central regions flanked by weaker ...
here - Gonit Sora
... •μ>0, Є>0, being most known materials, natural or otherwise. •μ>0, Є<0, being materials not well investigated. •μ<0, Є>0, also being materials not well investigated •μ<0, Є<0, where these materials do not exist naturally(Metamaterials) ...
... •μ>0, Є>0, being most known materials, natural or otherwise. •μ>0, Є<0, being materials not well investigated. •μ<0, Є>0, also being materials not well investigated •μ<0, Є<0, where these materials do not exist naturally(Metamaterials) ...
6,
... is presented. This system can be used to work in white light. The holographic optical elements (holographic lenses) are made as thick phase holograms on silver halide sensitized gelatin (SHSG) and they present a maximum diffraction efficiency of 75 %. Geometrical conditions at reconstruction with co ...
... is presented. This system can be used to work in white light. The holographic optical elements (holographic lenses) are made as thick phase holograms on silver halide sensitized gelatin (SHSG) and they present a maximum diffraction efficiency of 75 %. Geometrical conditions at reconstruction with co ...
Laser Distance and Speed Detection
... of triangulation. ? For this example there are 3 satellites that are used to pinpoint the location of the transmitting vehicle on earth ...
... of triangulation. ? For this example there are 3 satellites that are used to pinpoint the location of the transmitting vehicle on earth ...
Lecture 1/ Chapter 1/ Measurements
... In chapter 34, we considered the propagation of light along a straight path Ray Optics”. However we learned in chapter 33, that light is an electromagnetic wave. This means that it must undergo interference and diffraction just like a mechanical wave. In this chapter, we will discuss how light wav ...
... In chapter 34, we considered the propagation of light along a straight path Ray Optics”. However we learned in chapter 33, that light is an electromagnetic wave. This means that it must undergo interference and diffraction just like a mechanical wave. In this chapter, we will discuss how light wav ...
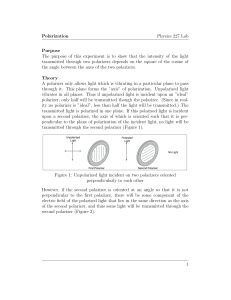
Polarization Physics 227 Lab Purpose The purpose of this
... polarizer, only half will be transmitted though the polarizer. (Since in reality no polarizer is ”ideal”, less than half the light will be transmitted.) The transmitted light is polarized in one plane. If this polarized light is incident upon a second polarizer, the axis of which is oriented such th ...
... polarizer, only half will be transmitted though the polarizer. (Since in reality no polarizer is ”ideal”, less than half the light will be transmitted.) The transmitted light is polarized in one plane. If this polarized light is incident upon a second polarizer, the axis of which is oriented such th ...
Lecture 10: Surface Plasmon Excitation
... Notes: Light intensity reflected from the back surface depends on the film thickness There exists a film thickness for perfect coupling (destructive interference between two refl. beams) When light coupled in perfectly, all the EM energy dissipated in the film) ...
... Notes: Light intensity reflected from the back surface depends on the film thickness There exists a film thickness for perfect coupling (destructive interference between two refl. beams) When light coupled in perfectly, all the EM energy dissipated in the film) ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.