The Equation of Number the Total Internal of Reflection Angles
... angles have different path length and therefore take different times to traverse the fiber.In graded – index fiber, the index of refraction in the core decreases continuously between the axis and the cladding. This causes light rays to bend smoothly as they approach the cladding, rather than reflect ...
... angles have different path length and therefore take different times to traverse the fiber.In graded – index fiber, the index of refraction in the core decreases continuously between the axis and the cladding. This causes light rays to bend smoothly as they approach the cladding, rather than reflect ...
Post-print of: J. Mater. Chem. , 2010, 20, 6408
... We must remark that using the described methodology and the chosen individual layer thickness no significant light scattering at short wavelengths was observed. The high quality of the reflection curves in Fig. 3 and 4 and the fact that multilayered films with different positions of their reflectivi ...
... We must remark that using the described methodology and the chosen individual layer thickness no significant light scattering at short wavelengths was observed. The high quality of the reflection curves in Fig. 3 and 4 and the fact that multilayered films with different positions of their reflectivi ...
Two-color cross-correlation in small-angle static light
... very small. In particular, d q can be considered negligible if it is less than the uncertainty associated to each q mode. In fact, there is a natural uncertainty in the measure of q—due to the finite size of the scattering volume—that is associated with the finite speckles size @18#. It is useful to ...
... very small. In particular, d q can be considered negligible if it is less than the uncertainty associated to each q mode. In fact, there is a natural uncertainty in the measure of q—due to the finite size of the scattering volume—that is associated with the finite speckles size @18#. It is useful to ...
geometrical optics
... direct or control rays of light. The refraction of light at the surface of a lens depends on its shape, its index of refraction, and the nature of the medium surrounding it (usually air), in accordance with Snell’s Law. Lenses that are thicker in the center than at their edges are called positive, o ...
... direct or control rays of light. The refraction of light at the surface of a lens depends on its shape, its index of refraction, and the nature of the medium surrounding it (usually air), in accordance with Snell’s Law. Lenses that are thicker in the center than at their edges are called positive, o ...
NSS-MIC 2009 Conference Record Template
... where is the scintilator decay time, N phe is the number of photoelectrons and ENF is the excess noise factor of the photodetector. Besides the photostatistics gain another factor, not apparent in the simplified formula (1), plays a determinant role in the timing resolution and is related to the s ...
... where is the scintilator decay time, N phe is the number of photoelectrons and ENF is the excess noise factor of the photodetector. Besides the photostatistics gain another factor, not apparent in the simplified formula (1), plays a determinant role in the timing resolution and is related to the s ...
New method for estimating the refractive index of optical materials in
... A further increase in the refractive index up to 5.0 leads to converse redistribution of energy peaks (Fig. 8). However, the relative magnitude of the peaks is less than of the average level of scattering intensity. The increase in the refractive index up to the values of 5.6…6.5 leads to redistribu ...
... A further increase in the refractive index up to 5.0 leads to converse redistribution of energy peaks (Fig. 8). However, the relative magnitude of the peaks is less than of the average level of scattering intensity. The increase in the refractive index up to the values of 5.6…6.5 leads to redistribu ...
Development of Organic Imaging Device
... incident light, its structure, including its lens, make drastic camera size reduction difficult. In the case of consumer model video cameras and digital cameras, their mainstream imaging system is a single plate color device consisting of three or four colored filters pasted over an image sensor lik ...
... incident light, its structure, including its lens, make drastic camera size reduction difficult. In the case of consumer model video cameras and digital cameras, their mainstream imaging system is a single plate color device consisting of three or four colored filters pasted over an image sensor lik ...
Enhanced visualization of choroidal vessels using ultrahigh
... local minimum at ~1060 nm (µ a ~0.013 mm-1 at λ = 1060 nm, as compared to µ a ~0.002 mm-1 at λ = 800 nm) and a second one at ~ 1300 nm (µ a ~0.1 mm-1 at λ = 1300 nm), meaning that power losses due to water absorption will be 48% at 1060 nm and 99.3% at ~1300 nm as compared to 10% at ~800 nm for a do ...
... local minimum at ~1060 nm (µ a ~0.013 mm-1 at λ = 1060 nm, as compared to µ a ~0.002 mm-1 at λ = 800 nm) and a second one at ~ 1300 nm (µ a ~0.1 mm-1 at λ = 1300 nm), meaning that power losses due to water absorption will be 48% at 1060 nm and 99.3% at ~1300 nm as compared to 10% at ~800 nm for a do ...
Suppression of optical damage at 532 nm in
... Measurements were carried out with the Y axis parallel to the propagation direction of the light because under this configuration all the samples had the same interacting thickness. From this point forward, the 0.0047, 0.047, 0.47 and 0.94 mol. % Ho:cLN crystals will be referred to as Samples 1, 2, ...
... Measurements were carried out with the Y axis parallel to the propagation direction of the light because under this configuration all the samples had the same interacting thickness. From this point forward, the 0.0047, 0.047, 0.47 and 0.94 mol. % Ho:cLN crystals will be referred to as Samples 1, 2, ...
1.9 W yellow, CW, high-brightness light from a high efficiency
... The setup for obtaining efficient frequency doubling of the NIR light is sketched in figure 1. The laser diode is described in18. It is mounted p-side up and has two contacts for controlling injection current: One for the ridge waveguide section and one for the tapered amplifier section. A distribut ...
... The setup for obtaining efficient frequency doubling of the NIR light is sketched in figure 1. The laser diode is described in18. It is mounted p-side up and has two contacts for controlling injection current: One for the ridge waveguide section and one for the tapered amplifier section. A distribut ...
Analysis and Compensation of Four Wave Mixing Products in
... It is often used for demultiplexing channels when time-division multiplexing is used in the optical domain [4]. It can also be used for wavelength conversion. Wavelength conversion is a significant function in the future broadband multichannel light wave system because it makes many other possible u ...
... It is often used for demultiplexing channels when time-division multiplexing is used in the optical domain [4]. It can also be used for wavelength conversion. Wavelength conversion is a significant function in the future broadband multichannel light wave system because it makes many other possible u ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... Figure 3 shows the CD and CB spectra for the two 2D enantiomorphous (mirror image) gammadia arrays. As anticipated, CD and CB are approximately the same for forward and backward propagation, since optical activity is a reciprocal phenomenon. This is always true, even if for backward propagation the ...
... Figure 3 shows the CD and CB spectra for the two 2D enantiomorphous (mirror image) gammadia arrays. As anticipated, CD and CB are approximately the same for forward and backward propagation, since optical activity is a reciprocal phenomenon. This is always true, even if for backward propagation the ...
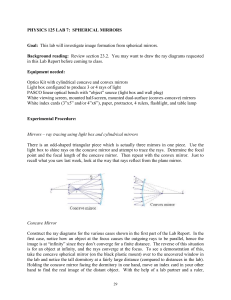
Spherical Mirrors
... Review the ray diagram for this case. Set up the situation on the optical bench, with the “object source” at one end of the bench. The wall transformer should be plugged into the outlets on the sides of the bench, after connecting the power cord to the “object source”. The concave mirror should be l ...
... Review the ray diagram for this case. Set up the situation on the optical bench, with the “object source” at one end of the bench. The wall transformer should be plugged into the outlets on the sides of the bench, after connecting the power cord to the “object source”. The concave mirror should be l ...
Mirrors - Purdue Physics
... light rays that are close to the optical axis § If the light rays are far from the optical axis, they will not be focused through the focal point of the mirror § Thus we will see a distorted image § In the drawing several light rays are incident on a spherical concave mirror § You can see that the r ...
... light rays that are close to the optical axis § If the light rays are far from the optical axis, they will not be focused through the focal point of the mirror § Thus we will see a distorted image § In the drawing several light rays are incident on a spherical concave mirror § You can see that the r ...
Experimental studies of far-field superlens for sub-diffractional optical imaging
... have to be separated and relocated to its original position. This can be done by taking multiple measurements with relative phase-shift between the object and the grating and followed by a data processing procedure [32]. As the object and the grating are in each other’s near-field, very complicated ...
... have to be separated and relocated to its original position. This can be done by taking multiple measurements with relative phase-shift between the object and the grating and followed by a data processing procedure [32]. As the object and the grating are in each other’s near-field, very complicated ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.