It`s Time For Earth Science Chapter 1
... This term most likely means straightening motion; movement to increase the angle between bones ...
... This term most likely means straightening motion; movement to increase the angle between bones ...
Practice Questions: Anatomy Lecture Exam II
... 10. A bipennate muscle can be described as:_______. A convergent muscle can be described as:_______. 1. converging to a central tendon from one side 2. diverging to a narrow point of attachment 3. tapered at ends with a ‘belly’ in the middle 4. converging to central tendon from both sides 5. long st ...
... 10. A bipennate muscle can be described as:_______. A convergent muscle can be described as:_______. 1. converging to a central tendon from one side 2. diverging to a narrow point of attachment 3. tapered at ends with a ‘belly’ in the middle 4. converging to central tendon from both sides 5. long st ...
Connective tissue
... Ligaments of the knee joint are often the most commonly known e.g. Anterior cruciate ...
... Ligaments of the knee joint are often the most commonly known e.g. Anterior cruciate ...
Study guide for final exam
... What are the three types of muscle tissue? How are they similar? Different? Where are the three types of muscle tissue located in the body? What are the names and characteristics of the three connective tissue sheaths associated with skeletal muscle? Muscle origin and insertion. What is the structur ...
... What are the three types of muscle tissue? How are they similar? Different? Where are the three types of muscle tissue located in the body? What are the names and characteristics of the three connective tissue sheaths associated with skeletal muscle? Muscle origin and insertion. What is the structur ...
Tissues task sheet
... rhythmically and do not get tired easily. They are known as involuntary muscles as we cannot control their contractions. It is called : ...
... rhythmically and do not get tired easily. They are known as involuntary muscles as we cannot control their contractions. It is called : ...
Review for Anatomy midterm
... What is the name of the tissue that can distend and is usually found in the bladder? ...
... What is the name of the tissue that can distend and is usually found in the bladder? ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
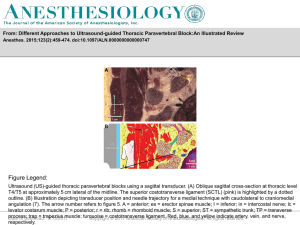
... Ultrasound (US)-guided thoracic paravertebral blocks using a sagittal transducer. (A) Oblique sagittal cross-section at thoracic level T4/T5 at approximately 5 cm lateral of the midline. The superior costotransverse ligament (SCTL) (pink) is highlighted by a dotted outline. (B) Illustration depictin ...
... Ultrasound (US)-guided thoracic paravertebral blocks using a sagittal transducer. (A) Oblique sagittal cross-section at thoracic level T4/T5 at approximately 5 cm lateral of the midline. The superior costotransverse ligament (SCTL) (pink) is highlighted by a dotted outline. (B) Illustration depictin ...
Intramuscular Injections
... • Small muscle with little subcu fat • Absorbed quickly • Smaller volume of medication (no more than 1 mL) • Anatomical risk: radial nerve and brachial artery ...
... • Small muscle with little subcu fat • Absorbed quickly • Smaller volume of medication (no more than 1 mL) • Anatomical risk: radial nerve and brachial artery ...
Slide 1
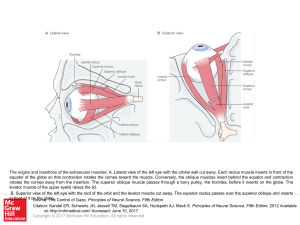
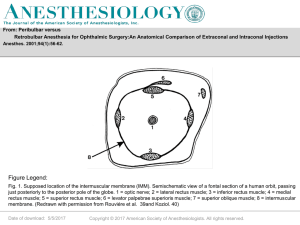
... The origins and insertions of the extraocular muscles. A. Lateral view of the left eye with the orbital wall cut away. Each rectus muscle inserts in front of the equator of the globe so that contraction rotates the cornea toward the muscle. Conversely, the oblique muscles insert behind the equator a ...
... The origins and insertions of the extraocular muscles. A. Lateral view of the left eye with the orbital wall cut away. Each rectus muscle inserts in front of the equator of the globe so that contraction rotates the cornea toward the muscle. Conversely, the oblique muscles insert behind the equator a ...
MMHS Anatomy and Physiology
... ATP can run out and must be regenerated. a. creatine phosphate is 4-6 times more abundant than ATP b. creatine phosphate converts ADP back to ATP. ...
... ATP can run out and must be regenerated. a. creatine phosphate is 4-6 times more abundant than ATP b. creatine phosphate converts ADP back to ATP. ...
The Muscle System
... In this activity you will explore both the structure (anatomy) and function (physiology) of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles work by pulling on bones. In order to pull on the bones the muscle length must shorten. This is a characteristic of muscle tissue known as contractility. The proposed mechani ...
... In this activity you will explore both the structure (anatomy) and function (physiology) of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscles work by pulling on bones. In order to pull on the bones the muscle length must shorten. This is a characteristic of muscle tissue known as contractility. The proposed mechani ...
2 Skeletal muscle contractions - delano
... What causes muscle proteins to slide? 1.) Cross bridges attach to myosin binding sites on the thin filaments 2.) Calcium Ions are released into the Sarcoplasm (from the SR) 3.) Sliding begins 4.) Cross bridges act like oars to attach and detach several times during the contraction ...
... What causes muscle proteins to slide? 1.) Cross bridges attach to myosin binding sites on the thin filaments 2.) Calcium Ions are released into the Sarcoplasm (from the SR) 3.) Sliding begins 4.) Cross bridges act like oars to attach and detach several times during the contraction ...
Identify the following muscles
... based on shape/movement? Is it relatively strong or weak? Tell me why? ...
... based on shape/movement? Is it relatively strong or weak? Tell me why? ...
Chap 12
... What does the term “Rigor Mortis” mean? Know the 10 steps of “Excitation-Contraction Coupling” (posted on my home page.) What is the mechanism that brings Ca ++ back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum? What do the terms “Twitch”, “Summation”, and “Tetanus” mean? What do “Isotonic” and “Isometric” contr ...
... What does the term “Rigor Mortis” mean? Know the 10 steps of “Excitation-Contraction Coupling” (posted on my home page.) What is the mechanism that brings Ca ++ back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum? What do the terms “Twitch”, “Summation”, and “Tetanus” mean? What do “Isotonic” and “Isometric” contr ...
Smooth muscle tissue

Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle. It is divided into two subgroups; the single-unit (unitary) and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit cells, the whole bundle or sheet contracts as a syncytium (i.e. a multinucleate mass of cytoplasm that is not separated into cells). Multiunit smooth muscle tissues innervate individual cells; as such, they allow for fine control and gradual responses, much like motor unit recruitment in skeletal muscle.Smooth muscle is found within the walls of blood vessels (such smooth muscle specifically being termed vascular smooth muscle) such as in the tunica media layer of large (aorta) and small arteries, arterioles and veins. Smooth muscle is also found in lymphatic vessels, the urinary bladder, uterus (termed uterine smooth muscle), male and female reproductive tracts, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, arrector pili of skin, the ciliary muscle, and iris of the eye. The structure and function is basically the same in smooth muscle cells in different organs, but the inducing stimuli differ substantially, in order to perform individual effects in the body at individual times. In addition, the glomeruli of the kidneys contain smooth muscle-like cells called mesangial cells.