A complex Tibetan upper mantle A fragmented Indian slab and no
... Three-dimensional resolution tests were performed to evaluate the data coverage and the ability of the inversion to recover the mantle structure (see Supplementary Figs. S6, S7, S8, S9, S10 and S11 in the Appendix). For this purpose, the synthetic travel times were computed by multiplying the G-matr ...
... Three-dimensional resolution tests were performed to evaluate the data coverage and the ability of the inversion to recover the mantle structure (see Supplementary Figs. S6, S7, S8, S9, S10 and S11 in the Appendix). For this purpose, the synthetic travel times were computed by multiplying the G-matr ...
Discrete visco-elastic lattice methods for seismic wave propagation
... across the fracture) and dynamic rupture (introducing a bond failure criteria). We have focused only on dynamic deformation. Static deformation can be modelled by applying external forces. Therefore, the method can be used in examining changes in the seismic wavefield as a consequence of static defo ...
... across the fracture) and dynamic rupture (introducing a bond failure criteria). We have focused only on dynamic deformation. Static deformation can be modelled by applying external forces. Therefore, the method can be used in examining changes in the seismic wavefield as a consequence of static defo ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... A mass damper is a computer-controlled weight that is placed in the roof of a building to counteract the building’s movement. Base isolators at the base of the building absorb seismic waves and prevent the waves from traveling through the building. Steel cross braces counteract pressure that pushes ...
... A mass damper is a computer-controlled weight that is placed in the roof of a building to counteract the building’s movement. Base isolators at the base of the building absorb seismic waves and prevent the waves from traveling through the building. Steel cross braces counteract pressure that pushes ...
A ubiquitous lowvelocity layer at the base of the mantle transition zone
... We slant-stacked receiver functions as a function of time and slowness (Figures 2c and 2d). The slant-stack technique [Schultz and Claerbout, 1978] can determine the slowness of the converted phases, thus separating the primary conversions from the multiples. The maxima in the positive slowness rang ...
... We slant-stacked receiver functions as a function of time and slowness (Figures 2c and 2d). The slant-stack technique [Schultz and Claerbout, 1978] can determine the slowness of the converted phases, thus separating the primary conversions from the multiples. The maxima in the positive slowness rang ...
Northern Houtman Sub-basin prospectivity
... structures are imaged on the seismic in the inboard part of the basin, and range from small basins with less than 1,000 m of sediments to very large half-graben with up to 6,000 m of synrift sediments. The orientation of these grabens is predominantly north–south to north-northwest–south-southeast, ...
... structures are imaged on the seismic in the inboard part of the basin, and range from small basins with less than 1,000 m of sediments to very large half-graben with up to 6,000 m of synrift sediments. The orientation of these grabens is predominantly north–south to north-northwest–south-southeast, ...
Investigating the lithospheric velocity structures beneath the Taiwan
... other prominent feature revealed in the horizontal slices is a NW-SE trending deflection of the slab around latitude 23.2°N at the depth of 60 km, which can be shown more clearly in the profile AA′ to CC′ with a retreat of Moho interface to the west (top of MP denoted by dotted line). To the south, th ...
... other prominent feature revealed in the horizontal slices is a NW-SE trending deflection of the slab around latitude 23.2°N at the depth of 60 km, which can be shown more clearly in the profile AA′ to CC′ with a retreat of Moho interface to the west (top of MP denoted by dotted line). To the south, th ...
Earthquakes: prediction, forecasting and mitigation
... occur globally. Many of these go undetected because their magnitude is small or they occur in areas which are not closely monitored. Most seismic events (earthquakes) are very minor, and do not cause any damage – they may not even be felt by the local population. Others cause devastation, much of it ...
... occur globally. Many of these go undetected because their magnitude is small or they occur in areas which are not closely monitored. Most seismic events (earthquakes) are very minor, and do not cause any damage – they may not even be felt by the local population. Others cause devastation, much of it ...
Earthquakes
... trees and houses to fall over or to sink into the ground • Earthquake waves can be amplified as they travel through a soil • Soft materials have little resistance to deformation, so seismic waves are amplified in such materials • Wave size and earthquake intensity are greatest in soft, unconsolidate ...
... trees and houses to fall over or to sink into the ground • Earthquake waves can be amplified as they travel through a soil • Soft materials have little resistance to deformation, so seismic waves are amplified in such materials • Wave size and earthquake intensity are greatest in soft, unconsolidate ...
glossary of seismic terminology
... which diagonal bracing is arranged eccentric to column/beam joints. Effective Peak Acceleration – A coefficient shown on NEHRP maps used to determine seismic forces. Elasticity – The ability of a material to return to its original form or condition after a displacing force is removed. Materials have ...
... which diagonal bracing is arranged eccentric to column/beam joints. Effective Peak Acceleration – A coefficient shown on NEHRP maps used to determine seismic forces. Elasticity – The ability of a material to return to its original form or condition after a displacing force is removed. Materials have ...
`4M? 5 Z
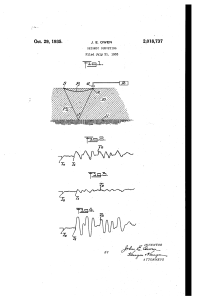
... turbances will be largely canceled out as such disturbances are at random and are not periodic or uniform. Furthermore, the amplitude of the 35 composite record will materially exceed the am plitude of the record which would be obtained from detonation of a single charge of explosive. ...
... turbances will be largely canceled out as such disturbances are at random and are not periodic or uniform. Furthermore, the amplitude of the 35 composite record will materially exceed the am plitude of the record which would be obtained from detonation of a single charge of explosive. ...
Introduction - Stanford Exploration Project
... (Appelbaum, 2002). The well penetrated stacked reservoir sands saturated with oil, ranging in overall column thickness from 400 to over 1,000ft. The quality of the oil from these zones is 35-45 degree API gravity, with very low sulphur content and preliminary data indicates the reservoirs contain se ...
... (Appelbaum, 2002). The well penetrated stacked reservoir sands saturated with oil, ranging in overall column thickness from 400 to over 1,000ft. The quality of the oil from these zones is 35-45 degree API gravity, with very low sulphur content and preliminary data indicates the reservoirs contain se ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE)
... of any specific seismic shaking demand and replaces the base shear capacity of conventional design procedures. If the building displaces laterally, its response must lie on this capacity curve. A point on the curve defines a specific damage state for the structure, since the deformation for all comp ...
... of any specific seismic shaking demand and replaces the base shear capacity of conventional design procedures. If the building displaces laterally, its response must lie on this capacity curve. A point on the curve defines a specific damage state for the structure, since the deformation for all comp ...