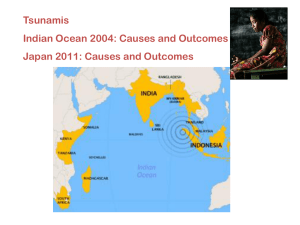
Tsunami ppt - Elder Grove
... .Tsunami can be generated when the see floor abruptly deforms and vertically displaces the overlying water. .Tectonic earthquakes are a particular kind of earthquake that are associated with the earth’s crustal deformation, when these earthquakes occur beneath the see, the water above the deformed ...
... .Tsunami can be generated when the see floor abruptly deforms and vertically displaces the overlying water. .Tectonic earthquakes are a particular kind of earthquake that are associated with the earth’s crustal deformation, when these earthquakes occur beneath the see, the water above the deformed ...
Tsunami Warning System (28 December 2004)
... (28 December 2004) that the chance of a big tsunami affecting Hong Kong was very small because of its geographical location. He added that Hong Kong was part of the Pacific Tsunami Warning System, an international cooperation among countries around the Pacific, and the Hong Kong Observatory would ...
... (28 December 2004) that the chance of a big tsunami affecting Hong Kong was very small because of its geographical location. He added that Hong Kong was part of the Pacific Tsunami Warning System, an international cooperation among countries around the Pacific, and the Hong Kong Observatory would ...
TSUNAMI GLOSSARY
... earthquake occurred. It is one of the indicators, along with magnitude and type of fault motion, of whether a tsunami will be propagated as a result of an earthquake. Area that should be evacuated prior to the arrival of a tsunami. The number of times a wave is produced within a certain time period. ...
... earthquake occurred. It is one of the indicators, along with magnitude and type of fault motion, of whether a tsunami will be propagated as a result of an earthquake. Area that should be evacuated prior to the arrival of a tsunami. The number of times a wave is produced within a certain time period. ...
The Study of Earthquakes
... • An earthquake can cause a huge tidal wave called a ___________? • What actually causes an earthquake? ...
... • An earthquake can cause a huge tidal wave called a ___________? • What actually causes an earthquake? ...
Tsunami Lecture
... UN categorizes disasters as follows: Hydro-meteorological disasters: including floods and wave surges, storms, droughts and related disasters (extreme temperatures and forest/scrub fires), and landslides & ...
... UN categorizes disasters as follows: Hydro-meteorological disasters: including floods and wave surges, storms, droughts and related disasters (extreme temperatures and forest/scrub fires), and landslides & ...
low-pressure system - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... What is an Earthquake? Ground movement caused by the sudden release of seismic energy due to tectonic forces. The focus of an earthquake is the actual location of the energy released inside the Earth’s crust. The epicentre is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus. ...
... What is an Earthquake? Ground movement caused by the sudden release of seismic energy due to tectonic forces. The focus of an earthquake is the actual location of the energy released inside the Earth’s crust. The epicentre is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above the focus. ...
Lesson 4 Earthquakes Notes
... Out at sea the energy is spread through deep water and the wave is not very tall. ...
... Out at sea the energy is spread through deep water and the wave is not very tall. ...
tsunami - Pacific Disaster Net
... A tsunami (a Japanese word meaning "harbour wave") is a series of waves, traveling at speeds of over 800 km/h in the deep ocean and often going unnoticed. They travel harmlessly until they reach the shallow water of a coastline where they slow down and steepen, cresting to heights of more than 10m a ...
... A tsunami (a Japanese word meaning "harbour wave") is a series of waves, traveling at speeds of over 800 km/h in the deep ocean and often going unnoticed. They travel harmlessly until they reach the shallow water of a coastline where they slow down and steepen, cresting to heights of more than 10m a ...
What is an earthquake - GDTL CDU E
... pencil horizontally. If you were to apply a force to both ends of the pencil by pushing down on them, you would see the pencil bend. After enough force was applied, the pencil would break in the middle, releasing the stress you have put on it. The Earth's crust acts in the same way. As the plates mo ...
... pencil horizontally. If you were to apply a force to both ends of the pencil by pushing down on them, you would see the pencil bend. After enough force was applied, the pencil would break in the middle, releasing the stress you have put on it. The Earth's crust acts in the same way. As the plates mo ...
Two Tsunamis on the BC Coast
... • Complex Wave train with wave groups of 5-6, 9-13 min (as in Samoan) waves superposed on much longer 120-140 min waves ...
... • Complex Wave train with wave groups of 5-6, 9-13 min (as in Samoan) waves superposed on much longer 120-140 min waves ...
GEOLOGIC HAZARDS PART 1
... diagram below shows how as waves approach shallow water, the wavelength shortens and the wave height increases. The wave period (the time necessary for successive waves to pass a given point) and the ...
... diagram below shows how as waves approach shallow water, the wavelength shortens and the wave height increases. The wave period (the time necessary for successive waves to pass a given point) and the ...
Great Tsunamis:
... Island Alaska - 5 deaths • 160 deaths in Hawaii • Led to Tsunami Warning System • A “tsunami” earthquake - larger waves than expected for a 7.4 EQ ...
... Island Alaska - 5 deaths • 160 deaths in Hawaii • Led to Tsunami Warning System • A “tsunami” earthquake - larger waves than expected for a 7.4 EQ ...
Tsunami Troy Barone 5/15/15 Science Project
... times a year, strong earthquakes of at least 7 (out of 10) on the Richter scale result in tsunamis. ...
... times a year, strong earthquakes of at least 7 (out of 10) on the Richter scale result in tsunamis. ...
Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... • Result of vibrations deep in the earth that release energy – Usually at transform boundaries where plates grind past each other and friction builds up when they get stuck in one spot until the point where they slip past each other releasing all the energy from the friction being released ...
... • Result of vibrations deep in the earth that release energy – Usually at transform boundaries where plates grind past each other and friction builds up when they get stuck in one spot until the point where they slip past each other releasing all the energy from the friction being released ...
23-11-2005 10:30 am have laid the foundations for
... ”The early warning system would be enhanced if the seismicity monitoring stations throughout the region are better connected.” El-Baz stressed. Arab Gulf countries.. On 29 November, the University of Sharjah at United Arab Emirates (UAE) has signed an agreement with the Geophysics Institute of the ...
... ”The early warning system would be enhanced if the seismicity monitoring stations throughout the region are better connected.” El-Baz stressed. Arab Gulf countries.. On 29 November, the University of Sharjah at United Arab Emirates (UAE) has signed an agreement with the Geophysics Institute of the ...
Tsunami
... Tsunami run-up Run-up = measurement of height of water onshore observed above a reference sea level Generally don’t get big gigantic wave Water comes as a fast moving rise in tide that ...
... Tsunami run-up Run-up = measurement of height of water onshore observed above a reference sea level Generally don’t get big gigantic wave Water comes as a fast moving rise in tide that ...
New Earthquake Review
... 15. How many major plates are there on Earth? 16. How do convection currents play a role in earthquakes? ...
... 15. How many major plates are there on Earth? 16. How do convection currents play a role in earthquakes? ...
A 13-Page Resource of Earth and Space Science Worksheets
... Pacific Ocean- about 90% of the world's earthquakes occur there. This is the number that characterises the relative size of an earthquake. This is a sea wave of local or distant origin that results from large-scale seafloor displacements associated with large earthquakes, major submarine slides, or ...
... Pacific Ocean- about 90% of the world's earthquakes occur there. This is the number that characterises the relative size of an earthquake. This is a sea wave of local or distant origin that results from large-scale seafloor displacements associated with large earthquakes, major submarine slides, or ...
Brent Bass
... Engineering Simulation (NEES) to facilitate these international research efforts. The team prefaced their journey by spending four weeks in the University’s Advanced Hazards Mitigation Laboratory learning structural dynamics and control, and gaining familiarity with the NEES cyber-infrastructure. A ...
... Engineering Simulation (NEES) to facilitate these international research efforts. The team prefaced their journey by spending four weeks in the University’s Advanced Hazards Mitigation Laboratory learning structural dynamics and control, and gaining familiarity with the NEES cyber-infrastructure. A ...
Tsunami review reinforces need for public preparedness
... The review shows the maximum possible size of some local and regional tsunami is bigger than previously understood, though tsunami are no more likely. (A tsunami from a local earthquake would arrive in less than one hour, and that from a regional earthquake would arrive in one to three hours.) This ...
... The review shows the maximum possible size of some local and regional tsunami is bigger than previously understood, though tsunami are no more likely. (A tsunami from a local earthquake would arrive in less than one hour, and that from a regional earthquake would arrive in one to three hours.) This ...
Chapter 8
... • Seismology is the study of earthquakes • Most quakes occur at the edge of tectonic plates • Tectonic plates are pieces of the lithosphere that move on top of the asthenosphere ...
... • Seismology is the study of earthquakes • Most quakes occur at the edge of tectonic plates • Tectonic plates are pieces of the lithosphere that move on top of the asthenosphere ...
Name Oceanography Video Worksheet Waves and Erosion 1. Most
... 9. T / F The building of inland dams can effect beaches at the coast? 10. One way to protect houses along ocean property is to build what structure? ...
... 9. T / F The building of inland dams can effect beaches at the coast? 10. One way to protect houses along ocean property is to build what structure? ...
The wave that shook the world
... 3. How many quakes have occurred along the Cascadian fault in 3500 years? ____________ 4. It has been __________ years since the last quake. AUGUST 27, 1883 1. The small island of ____________ erupted and collapsed in 1883 killing ________ people. 2. How long had it been dormant? ___________________ ...
... 3. How many quakes have occurred along the Cascadian fault in 3500 years? ____________ 4. It has been __________ years since the last quake. AUGUST 27, 1883 1. The small island of ____________ erupted and collapsed in 1883 killing ________ people. 2. How long had it been dormant? ___________________ ...
Tsunami

A tsunami (plural: tsunamis or tsunami; from Japanese: 津波, lit. ""harbor wave"";English pronunciation: /tsuːˈnɑːmi/), also known as a seismic sea wave, is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater explosions (including detonations of underwater nuclear devices), landslides, glacier calvings, meteorite impacts and other disturbances above or below water all have the potential to generate a tsunami. In being generated by the displacement of water, a tsunami contrasts both with a normal ocean wave generated by wind and with tides, which are generated by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on bodies of water.Tsunami waves do not resemble normal sea waves, because their wavelength is far longer. Rather than appearing as a breaking wave, a tsunami may instead initially resemble a rapidly rising tide, and for this reason they are often referred to as tidal waves, although this usage is not favored by the scientific community because tsunamis are not tidal in nature. Tsunamis generally consist of a series of waves with periods ranging from minutes to hours, arriving in a so-called ""wave train"". Wave heights of tens of meters can be generated by large events. Although the impact of tsunamis is limited to coastal areas, their destructive power can be enormous and they can affect entire ocean basins; the 2004 Indian Ocean tsunami was among the deadliest natural disasters in human history with at least 230,000 people killed or missing in 14 countries bordering the Indian Ocean.The Greek historian Thucydides suggested in his late-5th century BC History of the Peloponnesian War, that tsunamis were related to submarine earthquakes, but the understanding of a tsunami's nature remained slim until the 20th century and much remains unknown. Major areas of current research include trying to determine why some large earthquakes do not generate tsunamis while other smaller ones do; trying to accurately forecast the passage of tsunamis across the oceans; and also to forecast how tsunami waves would interact with specific shorelines.