MATH 1190 - Lili Shen
... A lemma is a helping theorem or a result which is needed to prove a theorem. A corollary is a result which follows directly from a theorem. Less important theorems are sometimes called propositions. ...
... A lemma is a helping theorem or a result which is needed to prove a theorem. A corollary is a result which follows directly from a theorem. Less important theorems are sometimes called propositions. ...
KnotandTonk 1 Preliminaries
... least, to tell us which kinds of semantic constraints succeed in ‘suitably’ assigning meanings. The situation here reverses the dialectic concerning Tonk perfectly: since Tonk has well-defined inference rules, inferentialists need, at least, to tell us which kinds of inference rules succeed in ‘suit ...
... least, to tell us which kinds of semantic constraints succeed in ‘suitably’ assigning meanings. The situation here reverses the dialectic concerning Tonk perfectly: since Tonk has well-defined inference rules, inferentialists need, at least, to tell us which kinds of inference rules succeed in ‘suit ...
Nonmonotonic Logic II: Nonmonotonic Modal Theories
... (a) Proof of AS1. For every formulap, eitherp is in X o r it is not. If it is, then by the statement calculus (SC), Lp D p is in X. If p is not in X, M~p is in X. So ~ M - p D p is in X, but this is just Lp D p. Either way, this instance of AS1 is in X, so every instance is in every fixed point. (b) ...
... (a) Proof of AS1. For every formulap, eitherp is in X o r it is not. If it is, then by the statement calculus (SC), Lp D p is in X. If p is not in X, M~p is in X. So ~ M - p D p is in X, but this is just Lp D p. Either way, this instance of AS1 is in X, so every instance is in every fixed point. (b) ...
Introduction to formal logic - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Why should we care about this? • Because in formal logic we determine whether arguments are valid or not by reference to their form. • And that assumes we can identify the form of sentences, i.e. that we can identify main connectives. • In doing formal derivations in particular, we have be able to ...
... Why should we care about this? • Because in formal logic we determine whether arguments are valid or not by reference to their form. • And that assumes we can identify the form of sentences, i.e. that we can identify main connectives. • In doing formal derivations in particular, we have be able to ...
SEQUENT SYSTEMS FOR MODAL LOGICS
... normal modal logics will not be considered in the present chapter. In relational proof systems the logical object language is associated with a language of relational terms. These terms may contain subterms representing the accessibility relation in possible-worlds models, so that semantic informati ...
... normal modal logics will not be considered in the present chapter. In relational proof systems the logical object language is associated with a language of relational terms. These terms may contain subterms representing the accessibility relation in possible-worlds models, so that semantic informati ...
Predicate Calculus - National Taiwan University
... Example 2: S={P(x)∨Q(x),R(z),T(y)∨∼W(y)} There is no constant in S, so we let H0={a} There is no function symbol in S, hence H=H0=H1=…={a} Example 3: S={P(f(x),a,g(y),b)} H0={a,b} H1={a,b,f(a),f(b),g(a),g(b)} H2={a,b,f(a),f(b),g(a),g(b),f(f(a)),f(f(b)),f(g(a)),f(g (b)),g(f(a)),g(f(b)),g(g( ...
... Example 2: S={P(x)∨Q(x),R(z),T(y)∨∼W(y)} There is no constant in S, so we let H0={a} There is no function symbol in S, hence H=H0=H1=…={a} Example 3: S={P(f(x),a,g(y),b)} H0={a,b} H1={a,b,f(a),f(b),g(a),g(b)} H2={a,b,f(a),f(b),g(a),g(b),f(f(a)),f(f(b)),f(g(a)),f(g (b)),g(f(a)),g(f(b)),g(g( ...
19_pl
... Say you write a program that, according to you, proves whether a sentence is entailed by The thing your program does is called deductive inference We don’t trust your inference program (yet), so we write things your program finds as ...
... Say you write a program that, according to you, proves whether a sentence is entailed by The thing your program does is called deductive inference We don’t trust your inference program (yet), so we write things your program finds as ...
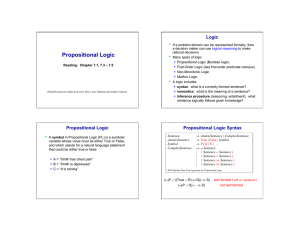
Propositional Logic
... § level 0 clauses: KB clauses and ¬ query § level k clauses: resolvents computed from 2 clauses: • one of which must be from level k-1 • other from any earlier level § compute all possible level 1 clauses, then all possible level 2 clauses, etc. § complete but very inefficient ...
... § level 0 clauses: KB clauses and ¬ query § level k clauses: resolvents computed from 2 clauses: • one of which must be from level k-1 • other from any earlier level § compute all possible level 1 clauses, then all possible level 2 clauses, etc. § complete but very inefficient ...
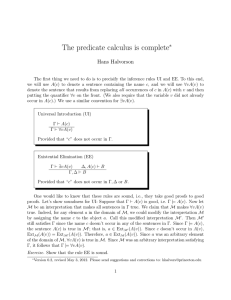
Completeness of the predicate calculus
... In the second case, for each k ≥ j, all truth valuations v in Sk assign T to P0 . In either case, then, for all j, there is a v ∈ Sj such that v(P0 ) = ε0 . Inductive step (i = n + 1) Suppose that ε0 , . . . , εn have been defined such that: (?) for each i = 1, . . . , n and for each j ∈ N, there i ...
... In the second case, for each k ≥ j, all truth valuations v in Sk assign T to P0 . In either case, then, for all j, there is a v ∈ Sj such that v(P0 ) = ε0 . Inductive step (i = n + 1) Suppose that ε0 , . . . , εn have been defined such that: (?) for each i = 1, . . . , n and for each j ∈ N, there i ...
Available on-line - Gert
... Of course no one supposes that this is a logical guarantee, or even an empirical one; it is as easy to make logical mistakes in practice as it is to be run over by a bus. But the formal logic of the present logical situation is still, I claim, clear to all of us. We all know perfectly well that the ...
... Of course no one supposes that this is a logical guarantee, or even an empirical one; it is as easy to make logical mistakes in practice as it is to be run over by a bus. But the formal logic of the present logical situation is still, I claim, clear to all of us. We all know perfectly well that the ...
A Resolution Method for Modal Logic S5
... from hybrid logics to define a simple and elegant system for S5. Hybrid logics were mainly introduced to explicitly express the relativity of truth in modal logics [5, 3]. This relativity is obtained by adding a new kind of propositional symbols, called nominals, which are used to refer to specific ...
... from hybrid logics to define a simple and elegant system for S5. Hybrid logics were mainly introduced to explicitly express the relativity of truth in modal logics [5, 3]. This relativity is obtained by adding a new kind of propositional symbols, called nominals, which are used to refer to specific ...
Notes on Propositional and Predicate Logic
... formulas, or simply on evaluating a given set of logic formulas repeatedly in particular ways. Yet another type of logic-based computation is theoremproving, where the program searches for a proof with a desired conclusion, or a conclusion that belongs to a given class of desired conclusions. The le ...
... formulas, or simply on evaluating a given set of logic formulas repeatedly in particular ways. Yet another type of logic-based computation is theoremproving, where the program searches for a proof with a desired conclusion, or a conclusion that belongs to a given class of desired conclusions. The le ...
Easyprove: a tool for teaching precise reasoning
... recent proof step in a proof branch. A user interface for restructuring a proof would aid active experimentation, and therefore improve the learning experience. More use of natural language. Easyprove currently presents formulas in symbolic form. Adding an option to present them in natural language ...
... recent proof step in a proof branch. A user interface for restructuring a proof would aid active experimentation, and therefore improve the learning experience. More use of natural language. Easyprove currently presents formulas in symbolic form. Adding an option to present them in natural language ...