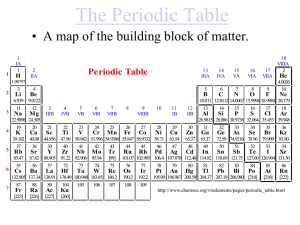
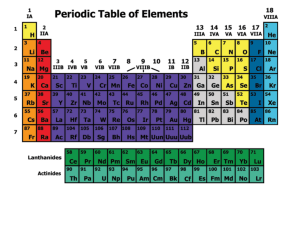
Title?
... mixture is a good conductor of electric current. Silicon can be cut into wafers, and used to make computer chips. ...
... mixture is a good conductor of electric current. Silicon can be cut into wafers, and used to make computer chips. ...
Scientific Method and Atomic Structure: A Brief Review
... Chemistry 1c. Students know how to use the periodic table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. The periodic table is full of patterns. In addition to predicting the number of ...
... Chemistry 1c. Students know how to use the periodic table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals, trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and the relative sizes of ions and atoms. The periodic table is full of patterns. In addition to predicting the number of ...
Periodic_Tendancies
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
File
... o These elements have a ___________________________________________ and are extremely reactive. Never found in nature ______________________________ (example table salt) o Not all the elements in a group are equally reactive Na is more reactive than lithium, potassium is more reactive than lithi ...
... o These elements have a ___________________________________________ and are extremely reactive. Never found in nature ______________________________ (example table salt) o Not all the elements in a group are equally reactive Na is more reactive than lithium, potassium is more reactive than lithi ...
File
... So he left the gaps in the table and hypothesized that elements that had not yet been discovered would fit right in AND HE WAS RIGHT! The new elements fit his pattern They later realized that it was more useful to group the elements based on atomic number instead of mass and this led to what we now ...
... So he left the gaps in the table and hypothesized that elements that had not yet been discovered would fit right in AND HE WAS RIGHT! The new elements fit his pattern They later realized that it was more useful to group the elements based on atomic number instead of mass and this led to what we now ...
Chapter 5 Chem classnotes
... from a neutral atom of an element. As atomic number increases going down a group, more electrons lie between the nucleus and the electrons in the outer orbits. This shields the outer electrons from the nuclear forces of attraction. IE increases left to right (across a period) and decrease top to bot ...
... from a neutral atom of an element. As atomic number increases going down a group, more electrons lie between the nucleus and the electrons in the outer orbits. This shields the outer electrons from the nuclear forces of attraction. IE increases left to right (across a period) and decrease top to bot ...
Test 1. 2nd prep. ques
... 2- The measuring unit of atomic radius which is used to measure the atomic size.(--picometer-) 3- Elements present in group zero.( noble gases ) 4- It is the series in which metals are arranged in a descending order according to their chemical activity . (--chemical activity series ) 5- Oxides of me ...
... 2- The measuring unit of atomic radius which is used to measure the atomic size.(--picometer-) 3- Elements present in group zero.( noble gases ) 4- It is the series in which metals are arranged in a descending order according to their chemical activity . (--chemical activity series ) 5- Oxides of me ...
The Atom Hypothesis
... 2.Elements which are similar as regards their chemical properties have atomic weights which are either of nearly the same value (eg. Pt, Ir, Os) or which increase regularly (eg. K, Ru, Cs). 3.The arrangement of the elements, or of groups of elements in the order of their atomic weights, corresponds ...
... 2.Elements which are similar as regards their chemical properties have atomic weights which are either of nearly the same value (eg. Pt, Ir, Os) or which increase regularly (eg. K, Ru, Cs). 3.The arrangement of the elements, or of groups of elements in the order of their atomic weights, corresponds ...
Atomic radii generally decrease along each period (row) of the
... Register for FREE to stop seeing ads ...
... Register for FREE to stop seeing ads ...
Study Guide
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
... the number of electrons each energy level can hold. The first energy level holds 2 electrons, the second holds 8, the third holds 18, the fourth holds 32, and the fifth holds 50. The number of electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom is referred to as the atoms valence electrons. The numbe ...
Year 9 study the new AQA GCSE specification for first examination
... The elements in Group 0 of the periodic table are called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. ...
... The elements in Group 0 of the periodic table are called the noble gases. They are unreactive and do not easily form molecules because their atoms have stable arrangements of electrons. The noble gases have eight electrons in their outer energy level, except for helium, which has only two electrons. ...
Ionization energy
... 1) All the elements known at that time could not be arranged in triads. 2) The law did not work for very low or very high massed elements such as F, Cl, and Br. 3) As techniques improved for measuring atomic masses accurately, the law became obsolete. Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at grou ...
... 1) All the elements known at that time could not be arranged in triads. 2) The law did not work for very low or very high massed elements such as F, Cl, and Br. 3) As techniques improved for measuring atomic masses accurately, the law became obsolete. Dobereiner’s research made chemists look at grou ...
Chapter 5 Organizing The Elements
... • In 1789 Antoine Lavoisier grouped elements according to categories called______, non-metals, ______and earths • In 1860 Mendeleev (Russian) needed to describe the now known 63 elements to his students • On cards, he listed the name, mass and properties of the 63 elements • He arranged them in orde ...
... • In 1789 Antoine Lavoisier grouped elements according to categories called______, non-metals, ______and earths • In 1860 Mendeleev (Russian) needed to describe the now known 63 elements to his students • On cards, he listed the name, mass and properties of the 63 elements • He arranged them in orde ...
Periodic Table
... Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families ...
... Elements in the same group have similar physical and chemical properties Sometimes groups are called families ...
A scientist named Henry Mosley developed the modern period table
... the structure and properties of elements. Today we will investigate these patterns and discover that the periodic table is a useful tool when studying chemistry. Materials: Periodic table, colored pencils, Science textbook Part one… Origins of the periodic table Use your science notes and chapter 6 ...
... the structure and properties of elements. Today we will investigate these patterns and discover that the periodic table is a useful tool when studying chemistry. Materials: Periodic table, colored pencils, Science textbook Part one… Origins of the periodic table Use your science notes and chapter 6 ...
Name
... He said properties repeated every _________________ element. This worked for ________________ elements but did not work well for _______________ elements. ...
... He said properties repeated every _________________ element. This worked for ________________ elements but did not work well for _______________ elements. ...
Study Guide Chapter 6
... Stability chart in the notebook). The Zones of Stability (see Zones of Stability chart in the notebook) shows that some electron configurations are more stable than others. The most stable electron configuration is a full outer level of electrons which is an octet for all levels except the first lev ...
... Stability chart in the notebook). The Zones of Stability (see Zones of Stability chart in the notebook) shows that some electron configurations are more stable than others. The most stable electron configuration is a full outer level of electrons which is an octet for all levels except the first lev ...
Periodic Table
... Each element is arranged in a box on the Periodic Table. The box contains the element’s chemical properties The atomic number stands for the number of protons in the nucleus. ...
... Each element is arranged in a box on the Periodic Table. The box contains the element’s chemical properties The atomic number stands for the number of protons in the nucleus. ...
The Periodic Table
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element in atomic mass units ("amu"). The first 20 elements have an atomic mass about two times the atomic number. ...
... The atomic mass is the average mass of an element in atomic mass units ("amu"). The first 20 elements have an atomic mass about two times the atomic number. ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... The periodic table has not always looked as it does today. The first periodic table was arranged by Dmitri Mendelev according to atomic mass. He noticed that physical and chemical appeared to be in a repeating or PERIODIC pattern. He continued to arrange his table in groups according to similar prop ...
... The periodic table has not always looked as it does today. The first periodic table was arranged by Dmitri Mendelev according to atomic mass. He noticed that physical and chemical appeared to be in a repeating or PERIODIC pattern. He continued to arrange his table in groups according to similar prop ...
Name Period
... 8. What can you predict about an element from its position in the periodic table? (other than atomic mass and atomic number) Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence. atomic mass unit (amu) electron family group neutron nucleus period proton periodic table 9. ...
... 8. What can you predict about an element from its position in the periodic table? (other than atomic mass and atomic number) Vocabulary From the list below, choose the term that best completes each sentence. atomic mass unit (amu) electron family group neutron nucleus period proton periodic table 9. ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.