Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... o The period number refers to the number of electron shells or energy levels an atom of each element has. Ex: Period 3 elements—Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, and Ar—have three primary electron energy levels. o Atomic mass (i.e. an approximation of the number of protons + number of neutrons) increases as ...
... o The period number refers to the number of electron shells or energy levels an atom of each element has. Ex: Period 3 elements—Na, Mg, Al, Si, P, S, Cl, and Ar—have three primary electron energy levels. o Atomic mass (i.e. an approximation of the number of protons + number of neutrons) increases as ...
Name Date ______ Period ______ Chapter 5: Periodic Table
... 1. Organized elements on the periodic table by increasing ___________________ ________________________. 2. Fixed problems in Mendeleev’s arrangement. C. Periodic Law 1. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when ___________________ _________________________ are used to arrange elements ...
... 1. Organized elements on the periodic table by increasing ___________________ ________________________. 2. Fixed problems in Mendeleev’s arrangement. C. Periodic Law 1. Properties of elements repeat in a predictable way when ___________________ _________________________ are used to arrange elements ...
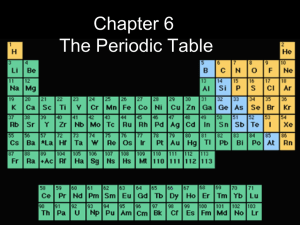
Periodicity of Elements and Periodic Table CHAPTER – 4
... 1. They are mono atomic. 2. They exist in gaseous state. 3. Outer most shell of these elements is either complete or contains eight electrons. 4. These elements are mostly chemically non-reactive. 5. These elements have no tendency to form compounds (only a few of these compounds are known). Atomic ...
... 1. They are mono atomic. 2. They exist in gaseous state. 3. Outer most shell of these elements is either complete or contains eight electrons. 4. These elements are mostly chemically non-reactive. 5. These elements have no tendency to form compounds (only a few of these compounds are known). Atomic ...
Periodicity Jeopardy
... Ge hadn’t yet been discovered, so he left a place for it Some elements (potassium, for example) did not “fit” according to their atomic mass ...
... Ge hadn’t yet been discovered, so he left a place for it Some elements (potassium, for example) did not “fit” according to their atomic mass ...
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE p
... Each Group of The p-Block The elements comprising s-block and p-block are called main groups or representative elements. Since the atomic radii decrease across a period, the p-block atoms are smaller than their nearest s or d block atoms; thus F atom has the smallest radius. Associated with small at ...
... Each Group of The p-Block The elements comprising s-block and p-block are called main groups or representative elements. Since the atomic radii decrease across a period, the p-block atoms are smaller than their nearest s or d block atoms; thus F atom has the smallest radius. Associated with small at ...
Patterns in The Periodic Table
... Patterns in The Periodic Table – Reactivity Evidence suggests that when an alkali metal reacts with water, the alkali metal atoms lose one electron. The most likely electron to be lost is the single electron in the outermost orbit. This electron is farthest from the nucleus, so it has the weakest at ...
... Patterns in The Periodic Table – Reactivity Evidence suggests that when an alkali metal reacts with water, the alkali metal atoms lose one electron. The most likely electron to be lost is the single electron in the outermost orbit. This electron is farthest from the nucleus, so it has the weakest at ...
Elements and Their Properties
... The noble gases exist as isolated atoms. They are stable because their outermost energy levels are full. No naturally occurring noble gas compounds are known. ...
... The noble gases exist as isolated atoms. They are stable because their outermost energy levels are full. No naturally occurring noble gas compounds are known. ...
The Periodic Table
... USING THE PERIODIC TABLE Rows are called periods. Columns are called groups. ...
... USING THE PERIODIC TABLE Rows are called periods. Columns are called groups. ...
Section 1 How Are Elements Organized
... called the d-block elements because of their position in the periodic table. • A transition metal is one of the metals that can use the inner shell before using the outer shell to bond. • A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it rea ...
... called the d-block elements because of their position in the periodic table. • A transition metal is one of the metals that can use the inner shell before using the outer shell to bond. • A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it rea ...
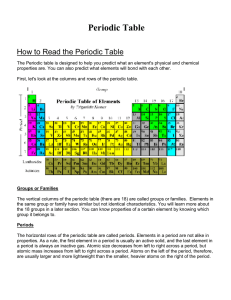
How to Read the Periodic Table
... The vertical columns of the periodic table (there are 18) are called groups or families. Elements in the same group or family have similar but not identical characteristics. You will learn more about the 18 groups in a later section. You can know properties of a certain element by knowing which grou ...
... The vertical columns of the periodic table (there are 18) are called groups or families. Elements in the same group or family have similar but not identical characteristics. You will learn more about the 18 groups in a later section. You can know properties of a certain element by knowing which grou ...
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
... organization are shown by the boxes of the Gizmo. Each box represents an orbital. The subshells are labeled with letters (s, p, d, and f) and the shells are labeled with numbers. Question: How are electrons arranged in elements with atomic numbers 1 through 10? 1. Infer: Based on its atomic number, ...
... organization are shown by the boxes of the Gizmo. Each box represents an orbital. The subshells are labeled with letters (s, p, d, and f) and the shells are labeled with numbers. Question: How are electrons arranged in elements with atomic numbers 1 through 10? 1. Infer: Based on its atomic number, ...
The Periodic Table
... Patterns, atomic number and electrons The periodic table shows that patterns in the properties of elements are linked to atomic number. atomic number = number of protons number of protons = number of electrons atomic number = number of electrons Therefore, as atomic number increases by one, the num ...
... Patterns, atomic number and electrons The periodic table shows that patterns in the properties of elements are linked to atomic number. atomic number = number of protons number of protons = number of electrons atomic number = number of electrons Therefore, as atomic number increases by one, the num ...
Chemistry: Matter and Change
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
... • Metals are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. • Alkali metals are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. • Alkaline earth metals are in group 2, and are also highly reactive. ...
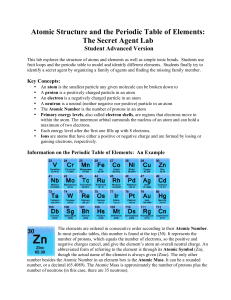
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... Today, the elements of the Periodic Table are arranged by atomic number, which also indicates the number of protons in an atom (see Periodic Table Tutorial above). Neutrons are uncharged particles in the atom’s nucleus that only affect the overall weight of the atom, not the charge. The Periodic Tab ...
... Today, the elements of the Periodic Table are arranged by atomic number, which also indicates the number of protons in an atom (see Periodic Table Tutorial above). Neutrons are uncharged particles in the atom’s nucleus that only affect the overall weight of the atom, not the charge. The Periodic Tab ...
Periodic Table Funsheet
... 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? _________________________________________________ 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? __________________________________________________ 11. Elements of Group 1 are called _____________________________________________________________. 12. ...
... 9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? _________________________________________________ 10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? __________________________________________________ 11. Elements of Group 1 are called _____________________________________________________________. 12. ...
File
... elements had been determined. John Newlands: – hypothesized that the chemistry of the elements might be related to their masses; – arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic masses; – discovered that every 7th element had similar properties (noble gases were still unknown during this ...
... elements had been determined. John Newlands: – hypothesized that the chemistry of the elements might be related to their masses; – arranged the known elements in order of increasing atomic masses; – discovered that every 7th element had similar properties (noble gases were still unknown during this ...
Chemistry 1 Chapter 4, The Periodic Table
... valence electrons and are very reactive • they are never found in nature as pure elements because they are so reactive they are always combined with other elements as compounds •group 2 – alkaline-earth metals, they have 2 valence electrons, they must lose 2 electrons to have a stable configuration, ...
... valence electrons and are very reactive • they are never found in nature as pure elements because they are so reactive they are always combined with other elements as compounds •group 2 – alkaline-earth metals, they have 2 valence electrons, they must lose 2 electrons to have a stable configuration, ...
2+ - West Ada
... macromolecular covalent structure (network) with very strong bonds resulting in a very high melting point. ...
... macromolecular covalent structure (network) with very strong bonds resulting in a very high melting point. ...
Instructional Objectives 3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... • Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. • Describe the basic properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number 3.2 Describe and define atomic and mass numbers • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and el ...
... • Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. • Describe the basic properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number 3.2 Describe and define atomic and mass numbers • Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and el ...
Instructional-Objectives
... Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. Describe the basic properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number 3.2 Describe and define atomic and mass numbers Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and elec ...
... Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. Describe the basic properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number 3.2 Describe and define atomic and mass numbers Calculate the number of protons, neutrons, and elec ...
Periodic Table
... considered to be periodic. Today, this arrangement is called a periodic table of elements. ...
... considered to be periodic. Today, this arrangement is called a periodic table of elements. ...
IT`S ATOMIC
... considered to be nonmetals. Metals and nonmetals have very different properties. As a result, metals and nonmetals will combine to form Group Figure 1 new substances. In addition to the zigzag line, the periodic table contains vertical columns of elements as well as horizontal rows of elements. The ...
... considered to be nonmetals. Metals and nonmetals have very different properties. As a result, metals and nonmetals will combine to form Group Figure 1 new substances. In addition to the zigzag line, the periodic table contains vertical columns of elements as well as horizontal rows of elements. The ...
Periodic classificatiion of elements
... the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases across a period, the tendency to lose electrons will decrease. 38. Why tendency to lose electrons increases on moving down in a group? A. Down the group the effective nuclear charge experience by valence electrons is decrea ...
... the effective nuclear charge acting on the valence shell electrons increases across a period, the tendency to lose electrons will decrease. 38. Why tendency to lose electrons increases on moving down in a group? A. Down the group the effective nuclear charge experience by valence electrons is decrea ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE
... • Describe the historical development of the periodic table. • Describe the organization of the modern periodic table according to the periodic law. A. Patterns in Element Properties 1. The elements vary widely in their properties, but in an orderly way. 2. English chemist, John Newlands was the fir ...
... • Describe the historical development of the periodic table. • Describe the organization of the modern periodic table according to the periodic law. A. Patterns in Element Properties 1. The elements vary widely in their properties, but in an orderly way. 2. English chemist, John Newlands was the fir ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.