Chapter 9 - HCC Learning Web
... 62. In the Lewis structure of the iodate ion, IO3-, that satisfies the octet rule, the formal charge on the central iodine atom is A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 62. In the Lewis structure of the iodate ion, IO3-, that satisfies the octet rule, the formal charge on the central iodine atom is A. B. C. D. E. ...
Topological Analysis of Electron Density
... very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au. ...
... very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au. ...
Basic Agricultural Chemistry - Macmillan Education South Africa
... group share similar chemical properties. The Roman numerals listed above each group are the usual number of valence electrons. For example: l Group IA is the alkali metals where the element has one electron in the orbital, for example sodium, potassium and rubidium. Alkali metals form salts and man ...
... group share similar chemical properties. The Roman numerals listed above each group are the usual number of valence electrons. For example: l Group IA is the alkali metals where the element has one electron in the orbital, for example sodium, potassium and rubidium. Alkali metals form salts and man ...
sec chemistry may 2011 marking scheme
... A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Carbon can catenate / form chains of C atoms • An atom of carbon can form stable (or strong) covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Gases (or fuel gas) (Do not accept LPG) Petrol (or gasoline) / naphtha Any two from: • different sized molec ...
... A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. • Carbon can catenate / form chains of C atoms • An atom of carbon can form stable (or strong) covalent bonds with other carbon atoms. Gases (or fuel gas) (Do not accept LPG) Petrol (or gasoline) / naphtha Any two from: • different sized molec ...
jyvaskla2 - School of Chemistry
... very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au. ...
... very much like the balls and spheres of molecular models !!! The simple binary hydrides of the second period elements show that the relative volumes of space associated with each element is determined by their relative electronegativities. Surfaces are truncated at 0.001 au. ...
Answers to Selected Exercises
... its kinetic energy) drops to zero. Most of the kinetic energy is transferred to the sand, which deforms when the ball lands. Some energy is released as heat through friction between the ball and the sand. 4.11 The energy source of a 100-watt light bulb is electrical current from household wiring. En ...
... its kinetic energy) drops to zero. Most of the kinetic energy is transferred to the sand, which deforms when the ball lands. Some energy is released as heat through friction between the ball and the sand. 4.11 The energy source of a 100-watt light bulb is electrical current from household wiring. En ...
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Geometry
... a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: ...
... a neutral atom loses one or more electrons from its valence shell, and an anion (a negative ion) forms when a neutral atom gains one or more electrons in its valence shell. Compounds composed of ions are called ionic compounds (or salts), and their constituent ions are held together by ionic bonds: ...
Hadronic Chemistry and Binding Energies
... molecules by different methods and techniques are being extensively explored since last more than 50 years. The quantum mechanical calculations of binding energies of neutral molecules by different methods have always fascinated chemists and physicists across the globe. The most commonly used are th ...
... molecules by different methods and techniques are being extensively explored since last more than 50 years. The quantum mechanical calculations of binding energies of neutral molecules by different methods have always fascinated chemists and physicists across the globe. The most commonly used are th ...
CHEM 101 Fall 09 Final Exam (a)
... 12. What is the frequency (s-1) of a photon that has an energy of 4.38 × 10-18 J? a. 436 b. 6.61 × 1015 c. 1.45 × 10-16 d. 2.30 × 107 e. 1.31 × 10-9 13. Which answer shows all possible values of the second quantum number when n = 3? a. l = 0 b. l = 0, 1 c. l = 0, 1, 2 d. l = 0, 1, 2, 3 e. l = 0, 1, ...
... 12. What is the frequency (s-1) of a photon that has an energy of 4.38 × 10-18 J? a. 436 b. 6.61 × 1015 c. 1.45 × 10-16 d. 2.30 × 107 e. 1.31 × 10-9 13. Which answer shows all possible values of the second quantum number when n = 3? a. l = 0 b. l = 0, 1 c. l = 0, 1, 2 d. l = 0, 1, 2, 3 e. l = 0, 1, ...
CHAPTER 21 NONMETALLIC ELEMENTS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS
... The density of a gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the molar mass of the substance. When two gases are at the same pressure and temperature, the ratio of their densities should be the same as the ratio of their molar masses. The molar mass of ammonium chloride is 53.5 g/mol, and the ratio of ...
... The density of a gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the molar mass of the substance. When two gases are at the same pressure and temperature, the ratio of their densities should be the same as the ratio of their molar masses. The molar mass of ammonium chloride is 53.5 g/mol, and the ratio of ...
chap-4-atomic-weights
... things to vaporize probably meant that atoms repelled each other - so no more would stick together than were needed. This made him assume (incorrectly) that the correct formula for something would be the simplest one - e.g., water was HO. Following the reasoning above, he proposed that if 1 H atom = ...
... things to vaporize probably meant that atoms repelled each other - so no more would stick together than were needed. This made him assume (incorrectly) that the correct formula for something would be the simplest one - e.g., water was HO. Following the reasoning above, he proposed that if 1 H atom = ...
covalent - Typepad
... 53. To draw a Lewis structure, it is NOT necessary to know a. bond energies. b. the types of atoms in the molecule. c. the number of valence electrons for each atom. d. the number of atoms in the molecule. 54. In drawing a Lewis structure, each nonmetal atom except hydrogen should be surrounded by a ...
... 53. To draw a Lewis structure, it is NOT necessary to know a. bond energies. b. the types of atoms in the molecule. c. the number of valence electrons for each atom. d. the number of atoms in the molecule. 54. In drawing a Lewis structure, each nonmetal atom except hydrogen should be surrounded by a ...
AL Chemistry Past paper essay questions
... Write an essay on amino acids, polypeptides and proteins. Your essay should include the properties of amino acids in aqueous solutions and a method of separation for a mixture of amino acids, as well as the constitution of polypeptides and proteins and their hydrolysis. ...
... Write an essay on amino acids, polypeptides and proteins. Your essay should include the properties of amino acids in aqueous solutions and a method of separation for a mixture of amino acids, as well as the constitution of polypeptides and proteins and their hydrolysis. ...
Chapter 17: An Introduction to Organic Chemistry, Biochemistry, and
... sends it back. The smell of the amine called trimethylamine let him know that it was spoiled. The number of natural and synthetic organic, or carbon-based, compounds runs into the millions. Fortunately, the task of studying them is not so daunting as their number would suggest, because organic compo ...
... sends it back. The smell of the amine called trimethylamine let him know that it was spoiled. The number of natural and synthetic organic, or carbon-based, compounds runs into the millions. Fortunately, the task of studying them is not so daunting as their number would suggest, because organic compo ...
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
... of Chemical Bonding expand their valence shell to 10 to 12 electrons. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... of Chemical Bonding expand their valence shell to 10 to 12 electrons. © 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... In CO2 there are 2 CO σ-bonds, 2 CO π-bonds and 4 lone pairs, 2 on each oxygen. At each oxygen the σ-pair structure is formed by a triangle made up from the CO σ-bond and the 2 lone pairs. For these 3 electron pairs on each oxygen three hybrid orbitals are needed and thus an sp2 hybrid on each oxyge ...
... In CO2 there are 2 CO σ-bonds, 2 CO π-bonds and 4 lone pairs, 2 on each oxygen. At each oxygen the σ-pair structure is formed by a triangle made up from the CO σ-bond and the 2 lone pairs. For these 3 electron pairs on each oxygen three hybrid orbitals are needed and thus an sp2 hybrid on each oxyge ...
POGIL - Basic Skills Supplement - The Mole-1
... 3. There are an equal number of nitrogen atoms in one mole of NH3 and one mole of N2. 4. The number of Cu atoms in 100 grams of pure copper metal is the same as the number of atoms in 100 grams of cupric oxide. 5. The number of Ni atoms in 100 moles of pure nickel metal is the same as the number of ...
... 3. There are an equal number of nitrogen atoms in one mole of NH3 and one mole of N2. 4. The number of Cu atoms in 100 grams of pure copper metal is the same as the number of atoms in 100 grams of cupric oxide. 5. The number of Ni atoms in 100 moles of pure nickel metal is the same as the number of ...
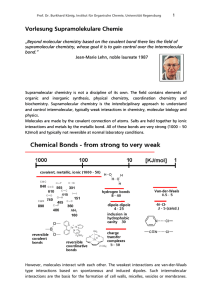
Vorlesung Supramolekulare Chemie
... but they add up. If we now look at the enthalpies of covalent bonds, it is obvious that entropy does not play a significant role in the formation of bonds. Example: Reaction of two molecules forming one new C-C bond: ΔG = - 415 KJ/mol + 23 KJ/mol. The entropic effect accounts for less than 5% of the ...
... but they add up. If we now look at the enthalpies of covalent bonds, it is obvious that entropy does not play a significant role in the formation of bonds. Example: Reaction of two molecules forming one new C-C bond: ΔG = - 415 KJ/mol + 23 KJ/mol. The entropic effect accounts for less than 5% of the ...
Chapter 8 - Cengage Learning
... Would you say ammonia (NH3) is mostly nitrogen or mostly hydrogen? Your answer depends on if you are looking at the number of atoms or the mass of the atoms. In terms of numbers of atoms, ammonia is ¾ hydrogen (there are four atoms making up an ammonia molecule, and three of them are hydrogen). But ...
... Would you say ammonia (NH3) is mostly nitrogen or mostly hydrogen? Your answer depends on if you are looking at the number of atoms or the mass of the atoms. In terms of numbers of atoms, ammonia is ¾ hydrogen (there are four atoms making up an ammonia molecule, and three of them are hydrogen). But ...
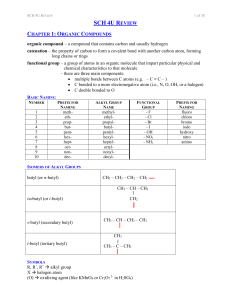
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made up of two monomers ADDITION POLYMERS addition p ...
... monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made up of two monomers ADDITION POLYMERS addition p ...
12 U Chem Review
... monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made up of two monomers ADDITION POLYMERS addition p ...
... monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made up of two monomers ADDITION POLYMERS addition p ...
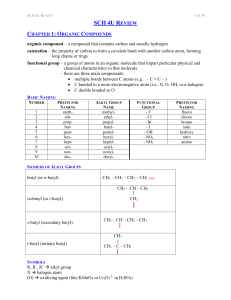
sch4ureview
... monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made up of two monomers ADDITION POLYMERS addition p ...
... monomer – a molecule or compound usually containing carbon and of relatively low molecular weight and simple structure which is capable of conversion to polymers by combination with itself or other similar molecules or compounds dimer – a molecule made up of two monomers ADDITION POLYMERS addition p ...
A review of oxygen-17 solid-state NMR of organic materials
... are anisotropic NMR interactions that can be used as probes for characterizing the local environment of the nucleus. The advantage of exploiting such anisotropic interactions (2nd rank tensors) is that they are able to provide three-dimensional information about the local electronic structure. Indee ...
... are anisotropic NMR interactions that can be used as probes for characterizing the local environment of the nucleus. The advantage of exploiting such anisotropic interactions (2nd rank tensors) is that they are able to provide three-dimensional information about the local electronic structure. Indee ...
Chem-CH8-Review Guide
... ) is mostly nitrogen or mostly hydrogen? Your answer depends on if you ...
... ) is mostly nitrogen or mostly hydrogen? Your answer depends on if you ...
pH and pOH (cont.)
... − When dissolved in water, the salt dissociates into ammonium ions and chloride ions. ...
... − When dissolved in water, the salt dissociates into ammonium ions and chloride ions. ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.