4 - Practice Calculations - Empirical formulas and % by mass
... d. A hydrocarbon containing 17.4% hydrogen by mass, with a molar mass of 58.1g. 2. Use the following information to determine the empirical and molecular formula for each of the following: a. 5.00g of a sample is found to contain 3.10g carbon, 0.695g hydrogen and 1.205g nitrogen. Its molar mass is 1 ...
... d. A hydrocarbon containing 17.4% hydrogen by mass, with a molar mass of 58.1g. 2. Use the following information to determine the empirical and molecular formula for each of the following: a. 5.00g of a sample is found to contain 3.10g carbon, 0.695g hydrogen and 1.205g nitrogen. Its molar mass is 1 ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 2 Notes, Part 1 – The Basics of
... 15. The attractions between nearby water molecules are called hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonding occurs whenever a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule is attracted to a slightly negative nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine on another molecule (think H-NOF). These bonds are usually depicted with a do ...
... 15. The attractions between nearby water molecules are called hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonding occurs whenever a slightly positive hydrogen on one molecule is attracted to a slightly negative nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine on another molecule (think H-NOF). These bonds are usually depicted with a do ...
Bonding in Atoms
... • States that an atom will lose or gain electrons in order to fill the outer sublevels (s and p) • Modeled by the Lewis Dot Diagram • Gain of electrons = anion • Loss of electrons = cations ...
... • States that an atom will lose or gain electrons in order to fill the outer sublevels (s and p) • Modeled by the Lewis Dot Diagram • Gain of electrons = anion • Loss of electrons = cations ...
Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... 6. Apply the octet rule to describe molecular structures. 7. List exceptions to the octet rule. 8. Define bond energies and explain how they can be used to compare bond strengths of different chemical bonds. 9. Describe polarity in bonds and how that can create hydrogen bonding. 10. Explain how a mo ...
... 6. Apply the octet rule to describe molecular structures. 7. List exceptions to the octet rule. 8. Define bond energies and explain how they can be used to compare bond strengths of different chemical bonds. 9. Describe polarity in bonds and how that can create hydrogen bonding. 10. Explain how a mo ...
Chapt9
... the H-Cl bond is described as "polar" and is said to have a "dipole" the entire HCl molecule is also polar as a result more complex molecules can be polar or nonpolar, depending on their 3-D shape (Later) ...
... the H-Cl bond is described as "polar" and is said to have a "dipole" the entire HCl molecule is also polar as a result more complex molecules can be polar or nonpolar, depending on their 3-D shape (Later) ...
Biochemistry I (CHE 418 / 5418)
... Covalent Bonds (Cont) • Some elements form double or triple covalent bonds by sharing two pairs or three pairs of electrons. – Draw Lewis dot structure and line structure for molecular oxygen (O2), which forms double bonds. – Draw Lewis dot structure and line structure for acetylene (C2H2), which c ...
... Covalent Bonds (Cont) • Some elements form double or triple covalent bonds by sharing two pairs or three pairs of electrons. – Draw Lewis dot structure and line structure for molecular oxygen (O2), which forms double bonds. – Draw Lewis dot structure and line structure for acetylene (C2H2), which c ...
urbano, mariajose
... carbon will form. • Usually has an atomic number of 6; therefore, it has 4 valence electrons. • Usually completes its outer energy shell by sharing valence electrons in four covalent bonds. (Not likely to form ionic bonds.) Emergent properties, such as the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form, ...
... carbon will form. • Usually has an atomic number of 6; therefore, it has 4 valence electrons. • Usually completes its outer energy shell by sharing valence electrons in four covalent bonds. (Not likely to form ionic bonds.) Emergent properties, such as the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form, ...
Summer Assignment Ch. 2-5
... Here is an idea that will recur throughout your study of the function of molecules: Change the structure, change the function. You see this in enantiomers, you will see it in proteins and enzymes, and now we are going to look at testosterone and estradiol. Notice how similar these two molecules are, ...
... Here is an idea that will recur throughout your study of the function of molecules: Change the structure, change the function. You see this in enantiomers, you will see it in proteins and enzymes, and now we are going to look at testosterone and estradiol. Notice how similar these two molecules are, ...
sample paper chemistry clas xi set 3
... (c) A mixture if a dil. NaOH and aluminuim piece is used to open holes. (d) Carbon shows catenation but silicon does not. (e) Tin (II) is a reducing agent but Pb(II) is not. ...
... (c) A mixture if a dil. NaOH and aluminuim piece is used to open holes. (d) Carbon shows catenation but silicon does not. (e) Tin (II) is a reducing agent but Pb(II) is not. ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... • VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs aro ...
... • VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of atoms about a central atom in a covalent compound, or charged ion, is determined solely by the repulsions between electron pairs present in the valence shell of the central atom. • The number of electron pairs aro ...
Paper
... (b) From July 2008 changes will apply to the way in which taxes are levied on new cars bought in Ireland. Vehicles that, in controlled tests, have higher levels of carbon dioxide emission per kilometre travelled will be subject to higher levels of taxation. The measures are designed to encourage the ...
... (b) From July 2008 changes will apply to the way in which taxes are levied on new cars bought in Ireland. Vehicles that, in controlled tests, have higher levels of carbon dioxide emission per kilometre travelled will be subject to higher levels of taxation. The measures are designed to encourage the ...
Final Exam Review – Free Response Section Name: 1. A sample of
... 7. 2.00 L of a gas at 25 oC and 1.05 atm is heated to 30 oC and the pressure is reduced to 0.550 atm. Calculate the new volume. ...
... 7. 2.00 L of a gas at 25 oC and 1.05 atm is heated to 30 oC and the pressure is reduced to 0.550 atm. Calculate the new volume. ...
2. Essential Chemistry
... o But the electrons of the covalent bonds are not shared equally between oxygen and hydrogen o This unequal sharing makes water a polar molecule ...
... o But the electrons of the covalent bonds are not shared equally between oxygen and hydrogen o This unequal sharing makes water a polar molecule ...
Take notes on this document while you are watching the recorded
... Organic molecules always contain carbon bonded to hydrogen. ...
... Organic molecules always contain carbon bonded to hydrogen. ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... Hybrid Orbitals Orbital hybridization describes how orbitals from different energy levels combine to make equivalent hybrid orbitals. Information about the kind and shape of the bonds is explained by hybridization. Hybrid orbitals can form with single, double, or triple covalent bonds. After reading ...
... Hybrid Orbitals Orbital hybridization describes how orbitals from different energy levels combine to make equivalent hybrid orbitals. Information about the kind and shape of the bonds is explained by hybridization. Hybrid orbitals can form with single, double, or triple covalent bonds. After reading ...
Bio 102 Lecture - chapter 2 The Chemical Basis of Life
... The Octet Rule for Distribution of Electrons 8-electron configuration is stable because this atom is having 8 valence electrons. ...
... The Octet Rule for Distribution of Electrons 8-electron configuration is stable because this atom is having 8 valence electrons. ...
PSI AP Chemistry Name Unit 4: Chemical Bonding MC Review Part
... (C) Bond length and bond strength are not related. (D) The relationship between bond length and bond strength depends on other factors. 13. Of the bonds C–C, C=C, and C≡C, the C–C bond is __________. (A) strongest/shortest (B) strongest/longest (C) weakest/longest (D) weakest/shortest (E) intermedia ...
... (C) Bond length and bond strength are not related. (D) The relationship between bond length and bond strength depends on other factors. 13. Of the bonds C–C, C=C, and C≡C, the C–C bond is __________. (A) strongest/shortest (B) strongest/longest (C) weakest/longest (D) weakest/shortest (E) intermedia ...
i principi di base - Structural Biology
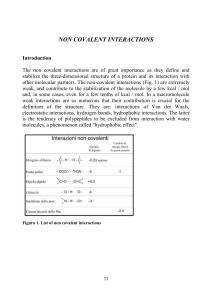
... stabilize the three-dimensional structure of a protein and its interaction with other molecular partners. The non-covalent interactions (Fig. 1) are extremely weak, and contribute to the stabilization of the molecule by a few kcal / mol and, in some cases, even for a few tenths of kcal / mol. In a m ...
... stabilize the three-dimensional structure of a protein and its interaction with other molecular partners. The non-covalent interactions (Fig. 1) are extremely weak, and contribute to the stabilization of the molecule by a few kcal / mol and, in some cases, even for a few tenths of kcal / mol. In a m ...
Intermolecular and Weak Interactions
... “Hydrogen bonding occurs when an electron deficient hydrogen that is bonded to an atom, has an attractive interaction with another electron rich region either within the same or another molecular entity” ...
... “Hydrogen bonding occurs when an electron deficient hydrogen that is bonded to an atom, has an attractive interaction with another electron rich region either within the same or another molecular entity” ...
video slide
... Happens between molecules a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
... Happens between molecules a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is also attracted to another electronegative atom in a different molecule In living cells, the electronegative partners are usually oxygen or nitrogen atoms ...
Practice Exam 2 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... A) atoms are held together by sharing electrons. B) oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrical attractions. C) atoms of different metals form bonds. D) atoms of noble gases are held together by attractions between oppositely charged ions. E) atoms of metals form bonds to atoms of ...
... A) atoms are held together by sharing electrons. B) oppositely charged ions are held together by strong electrical attractions. C) atoms of different metals form bonds. D) atoms of noble gases are held together by attractions between oppositely charged ions. E) atoms of metals form bonds to atoms of ...
Chem 150 - Fall 2015 Exam I
... e. If the pKa for lactic acid is 3.90, what is the pH of a solution made by mixing equal amounts of lactic acid and sodium lactate? ...
... e. If the pKa for lactic acid is 3.90, what is the pH of a solution made by mixing equal amounts of lactic acid and sodium lactate? ...
H 2 O
... • Most of the strongest bonds in organisms are covalent bonds that form a cell’s molecules • Weak chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, are also important • Weak chemical bonds reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each ...
... • Most of the strongest bonds in organisms are covalent bonds that form a cell’s molecules • Weak chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, are also important • Weak chemical bonds reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.